Presentation
Massive haemoptysis. Hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state due to type 2 diabetes mellitus. History of chronic kidney disease.
Patient Data
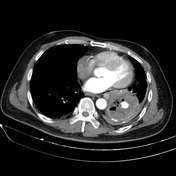

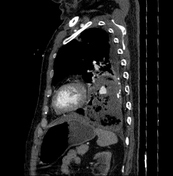

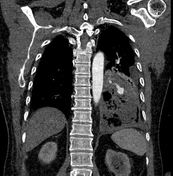

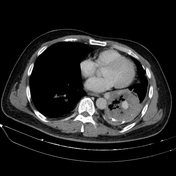

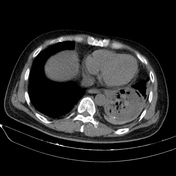

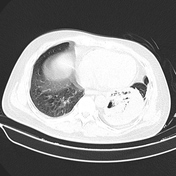

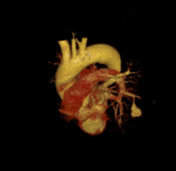

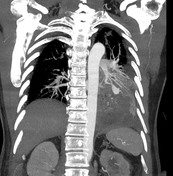

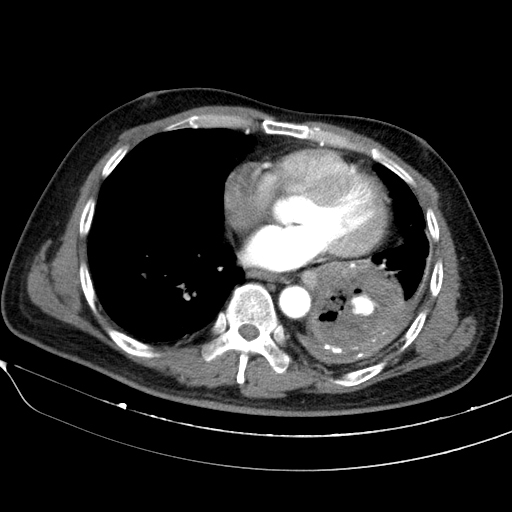
Cavitary mass lesion is seen in the left lower lobe, measuring approximately 80 x 63 x 100 mm (transverse x anteroposterior x height, along the lesion axis), with heterogeneous structure. Internally, it displays a honeycomb-like pattern with irregular walls and cavities, and heterogeneous density (fluid-air-blood). The walls are irregularly thickened (maximum thickness ~5 mm) with peripheral calcification. Poor contrast enhancement in a rim-like pattern is observed, with an intralesional pseudoaneurysm measuring approximately 14 x 13 x 19 mm, originating from a branch of the lower lobe artery, without evidence of active bleeding.
Consolidative lesions with ground-glass opacity and scattered nodular interstitial thickening are noted in the apices of both lungs. A cavitary lesion is also observed in the S4 segment of the left lung, measuring approximately 11 x 25 mm, with uniformly thick walls containing air, smooth inner margins, and surrounding interstitial nodules.
Partial collapse of the lung parenchyma in the left lower lobe, adjacent to a cavitary lesion.
Paraseptal emphysema at the apices of both lungs are seen.
There are small amount of fluid in the left pleural cavity and pleural calcification on the left side.
Endotracheal tube and central venous catheter remain in place.
Right kidney with stones and a simple cyst are observed. Left kidney is small with grade I hydronephrosis.
Laboratory test results:
direct AFB staining using Ziehl-Neelsen (performed twice): negative
Mycobacterium tuberculosis PCR using an automated system: negative
Case Discussion
Imaging and clinical findings are consistent with rupture of a pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm within the cavitary lesion.
Bilateral lung parenchymal lesions are suggestive of tuberculosis. Differential diagnosis: other aetiologies such as mycotic infections, syphilis, or even a tumour.
The patient was then discussed in a multidisciplinary consultation, and two treatment options were proposed: lung lobectomy or endovascular intervention to embolise the pseudoaneurysm. Since the patient was a high-risk surgical candidate, the decision was made to proceed with direct embolisation of the pseudoaneurysm using coils.
After the intervention, the patient was cared for in the ICU. Clinical symptoms and blood test results improved.
Case co-author: Consultant specialist Tran Quyet Thang, Military Hospital 175, Vietnam.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.