Presentation
Rapidly developing dyspnea and confusion. Anteroseptal ST elevation on EKG. Extremely high troponin, moderately elevated CRP.
Patient Data

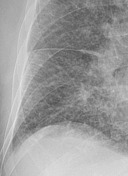

Bilateral perihilar haze, prominent upper pulmonary veins, diffuse alveolar (ill-defined opacities) and interstitial edema (Kerley B lines in the basal lung zones - see key image). Prominent horizontal fissure suggesting a small pleural effusion on the right.
Case Discussion
The patient demonstrated classic features of pulmonary edema including the bat's wing appearance of the hila, alveolar and insterstitial edema, upper lobe venous diversion, and a small amount of pleural effusion.
Consequent urgent echocardiography demonstrated an akinetic ventricular septum, decreased left ventricular function, and moderate mitral valve insufficiency. Considering all this the pulmonary edema was caused by the ongoing acute myocardial infarction whilst considering the elevated CRP an overlapping inflammatory component cannot be ruled out.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.