Presentation
This patient reports trauma to the elbow due to a fall while riding a bike two days ago.
Patient Data
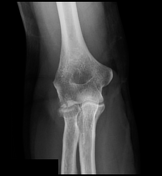
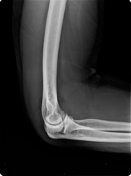
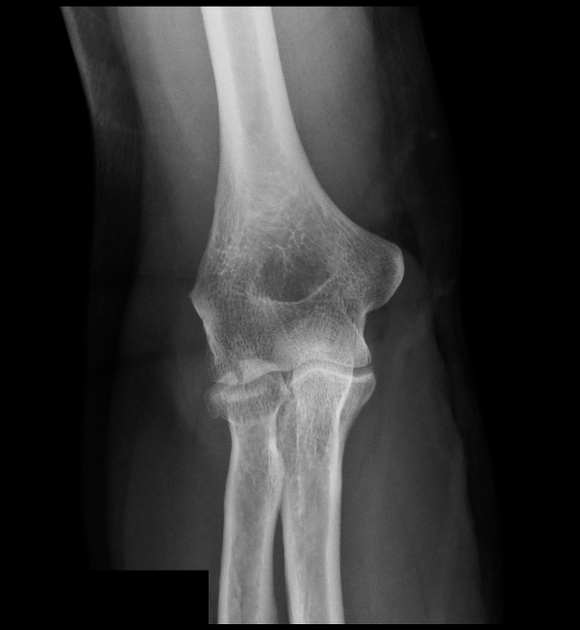
The elbow's AP and lateral radiographs reveal a slightly displaced radial head fracture, with posterior and more marked anterior fat pad elevation (the sail sign) indicative of elbow joint effusion.
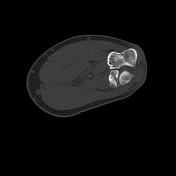

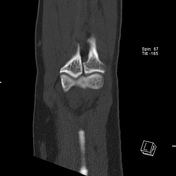



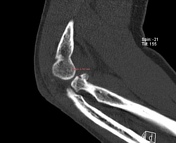
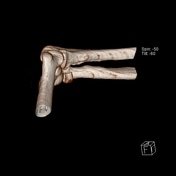

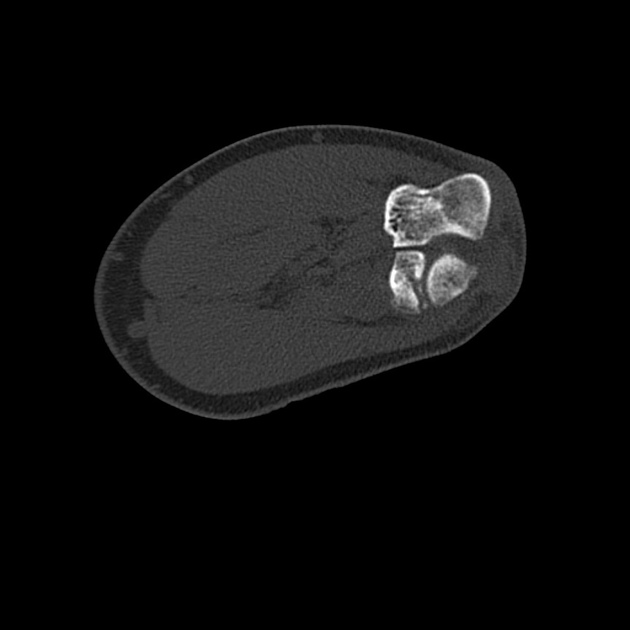
CT of the elbow reveals a displaced intra-articular fracture of the radial head, with more than 2 mm articular step off. There are two fracture lines, a vertical fracture line extending through the radial head's articular surface and an associated horizontal fracture line, representing comminution and favoring Mason type 3 fracture.
No supracondylar humeral fracture. It preserved unotrochlear articulation.
Impression: The findings are consistent with a Mason type 3 fracture.
Case Discussion
A common type of elbow injury in adults is radial head fracture 1-4. The Mason classification distinguishes radial head fracture into four groups: (type 1 = undisplaced; type 2 displaced; type 3 comminuted; type 4 associated with the elbow joint's dislocation 1-4. Early detection and appropriate radial head fracture classification are critical for ensuring their appropriate treatment 1-4.
This case illustrates radial head fracture, type 3, Mason classification, which usually requires surgical treatment.