Presentation
Visual impairment.
Patient Data


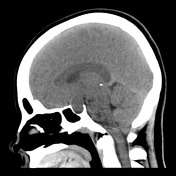

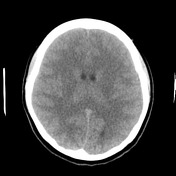

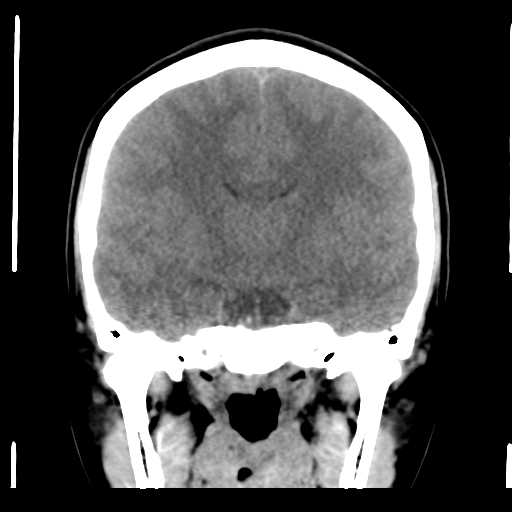
The pituitary fossa is enlarged by a lesion of intermediate density, similar to white matter. No calcification is present.


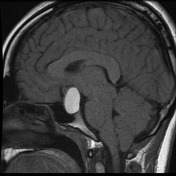

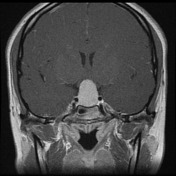

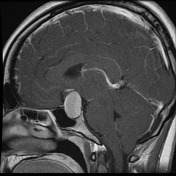

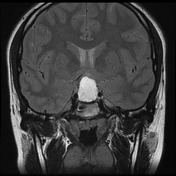

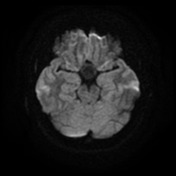

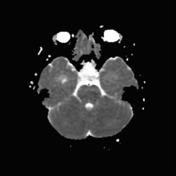

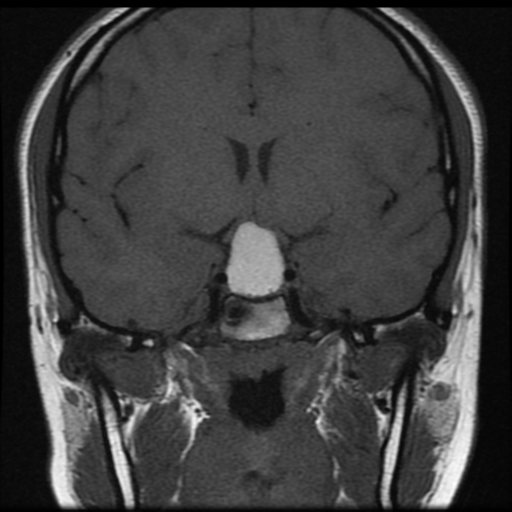
The pituitary fossa is expanded by a markedly intrinsically high T1 and high T2 signal lesion. The normal pituitary gland can be seen as a thin rim of enhancement stretched over the anterosuperior surface of this lesion, best appreciated on dynamic contrast-enhanced sequences (not seen). There is no appreciable solid component and posteriorly a number of small focal low T1 low T2 foci are noted which almost certainly represent debris within the cyst. The optic chiasm is stretched above this lesion.
There is no extension into the cavernous sinuses, although the lesion abuts both cavernous carotids.
Conclusion: The features are those of a large Rathke's cleft cyst with distortion of the optic chiasm.
Case Discussion
The patient went on to have surgery.
Histology
The cyst is covered by partly squamous and partly ciliated columnar epithelium. The underlying tissue shows trabeculae and cords of cells in a vascular stroma. The cells show round to oval nuclei many with basophilic cytoplasm and others with clear, vacuolated cytoplasm. There is no evidence of malignancy.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS: Rathke cleft cyst.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.