Presentation
Routine follow-up from clinic.
Patient Data

Large right hydropneumothorax and apical bulla.

Intercostal drain (attached to underwater seal).
Large hydropneumothorax and relaxation atelectasis.

Minimal residual pneumothorax.
The mediastinum has shifted to the right.
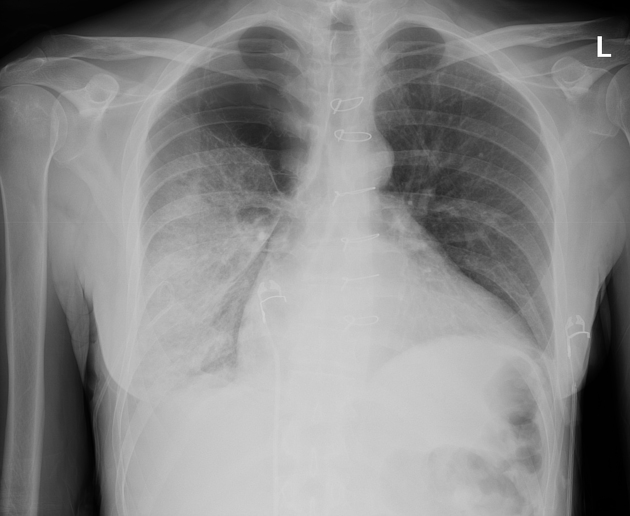
Rapid response call for chest discomfort and dyspnoea.
Dense right lung consolidation and large apical bullae.
Chest drain in situ.
Case Discussion
Patient recovered and was discharged 3 days later.
Re-expansion pulmonary oedema can be bilateral and fatal with a high mortality rate. Risk factors include chronic collapse of the lung. The duration was unknown in this case.
The rate of re-expansion should be limited to 1-1.5 L/hour, however the volume cannot be measured if an underwater seal is used.
Intermittent measured aspiration may prevent re-expansion pulmonary oedema.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.