Presentation
Abdominal pain, bloating, vomiting, inability to pass gas, inability to have a bowel movement.
Patient Data
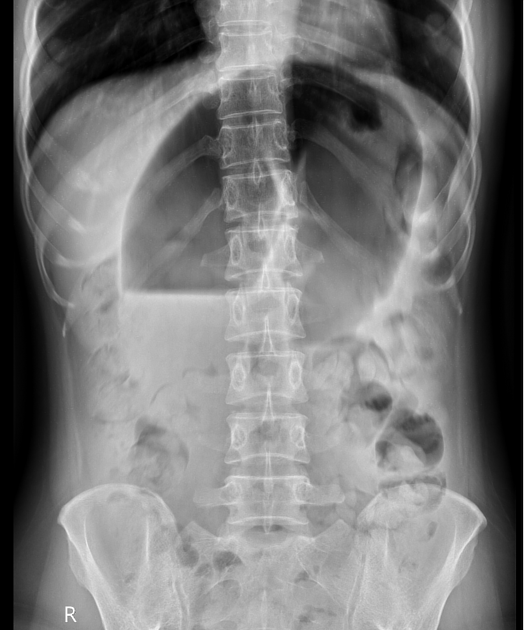
Anteroposterior radiograph of the abdomen shows significant dilation of the colonic loops, creating a 'coffee bean sign' indicative of sigmoid colon volvulus, along with a fluid-gas level inside. The 'coffee bean sign' is formed by the dilated bowel loops with a central radiolucent cleft between them. This radiolucent cleft indicates the double-wall thickness of the opposing bowel loops pressed together, with the outer bowel wall being thinner due to having only a single layer.
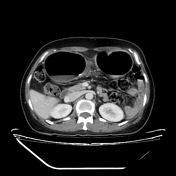

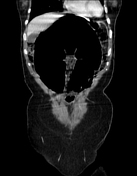

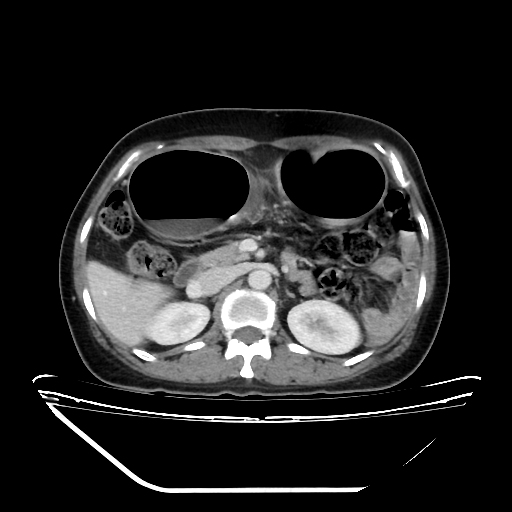
CT of the abdomen with contrast shows significant dilation of the sigmoid colon with a fluid-gas level in the lumen near the transition point, resembling a bird beak at the junction of the sigmoid colon and descending colon.
It is noted that the sigmoid colon is twisted 360 degrees around a fixed point of obstruction, leading to the mesentery and corresponding blood vessels being twisted along the axis of rotation (whirlpool sign).
Surgical report:
the sigmoid colon is twisted 360 degrees and dilated to 12-15 cm, occupying the entire abdominal cavity. The base of the twisted segment is necrotic, the intestinal wall is thinned and nearly ruptured, and there are multiple areas of serosal tearing. The non-twisted segment of the intestine is normal
the procedure involves resection of the twisted intestinal segment, release of the mesentery and lateral peritoneum, and exteriorization of the sigmoid colon to create a double-lumen colostomy
the specimen is sent for histopathological examination
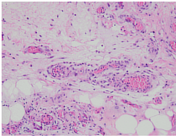
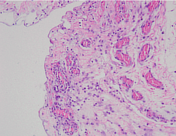
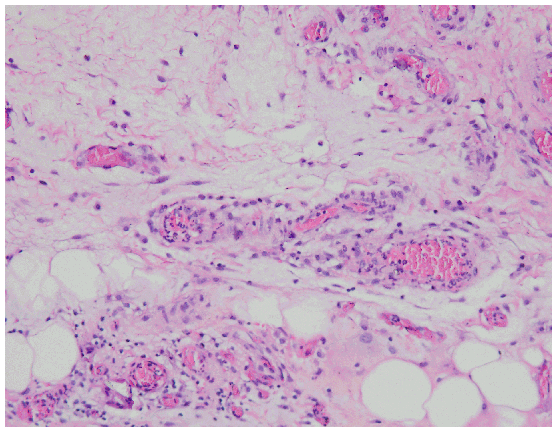
Histopathology report:
specimen site: sigmoid colon
staining method: Haematoxylin and eosin
macroscopic: a 20 cm segment of intestine with a smooth and glossy lumen, no lesions observed.
microscopic: the mucosa shows oedema, congestion, and scattered infiltration of nonspecific inflammatory cells. The structure of the glandular epithelium is normal
conclusion: mucosal haemorrhagic colitis
Case Discussion
Clinical, imaging, and surgery findings are consistent with sigmoid colon volvulus. It is important to note that the most serious complication is bowel ischaemia.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.