Presentation
Known cerebral palsy. Presents for a follow-up assessment of the ankles.
Patient Data

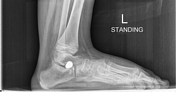
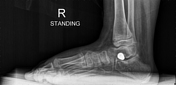

Weight-bearing views confirm severe hindfoot valgus, and the presence of bilateral, conical, threaded, subtalar implants inserted within the sinus tarsi.
Case Discussion
Lower limb spasticity in cerebral palsy is responsible for a variety of foot deformities1.
These include1:
equinus (plantar flexion)
hallux valgus (fixed abduction of the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the great toe)
equinocavovarus (plantar flexion, high-arched foot, adduction and inversion)
equinoplanovalgus (plantar flexion, flat foot, abduction and eversion)
Subtalar arthroereisis is a non-fusion surgical technique for the management of "collapsing" or flexible pes planus (flat feet) in a cerebral palsy child2.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.