Presentation
Cough, chills, myalgia, shortness of breath, and pleuritic chest pain. Recent COVID-19. Previous pneumothorax.
Patient Data
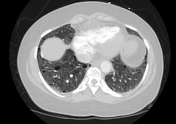

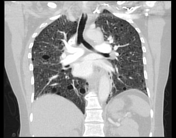

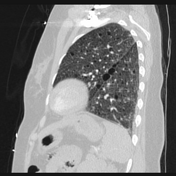


Numerous randomly distributed small pulmonary nodules, the majority of which are new compared with prior exams for which considerations include multinodular pneumocyte hyperplasia, or less likely infection, inflammation, or metastasis/malignancy.
Peripheral ill-defined airspace opacities in the right upper lobe and right lower lobe which could represent atelectasis or scarring.
Numerous thin-walled parenchymal cysts.
Numerous sclerotic lesions throughout the vertebral bodies and posterior elements are similar to the prior exam.


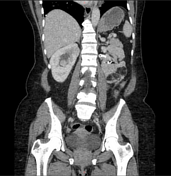

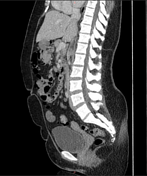

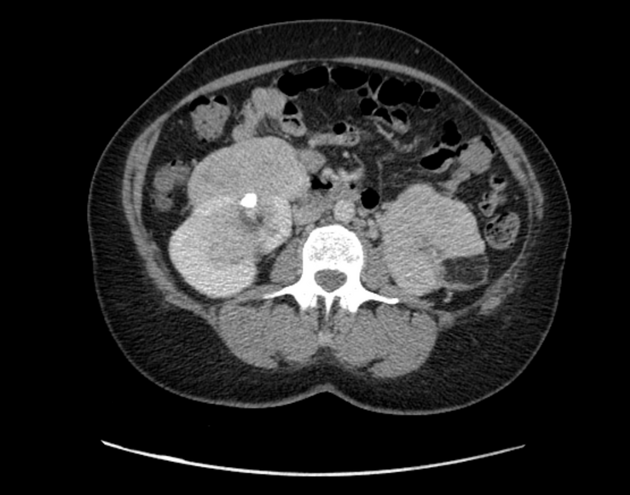
The left kidney is entirely replaced with enhancing mass with associated macroscopic fat likely representing complete replacement with angiomyolipomas. Embolic material is seen within the distal left renal artery unchanged. Multiple enhancing right renal masses some of which contain macroscopic fat grossly unchanged consistent with angiomyolipomas. Enhancing posterior right mid to lower pole exophytic lesion measuring 1.7 cm. The ureters are unremarkable.
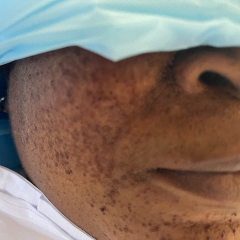
Facial angiofibromas commonly associated with tuberous sclerosis.
Case Discussion
The patient had previously received a diagnosis of lymphangioleiomyomatosis after presenting with a pneumothorax. Cystic lung disease lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) and renal angiomyolipomas (AMLs) are features of both LAM and TSC. Three or more cutaneous angiofibromas would satisfy the diagnostic criteria for TSC 1. No histology or follow up is available in this case.
In the setting of likely TSC, the lung nodules are most likely due to multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia and the sclerotic bone lesions are most likely due to multiple bone islands.
Case co-authors:
Zoha Huda, MD
Ahmad Munir, DO
Said Shukri, MD
Nazir Ahmad Lone, MD




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.