Presentation
Seizures.
Patient Data
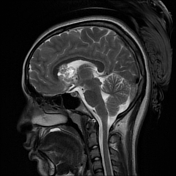

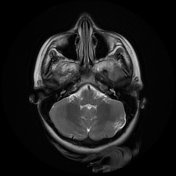

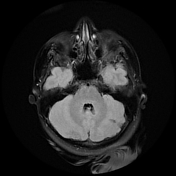

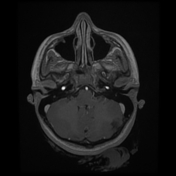

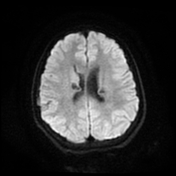


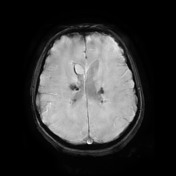

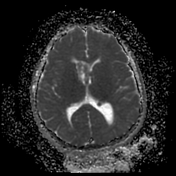

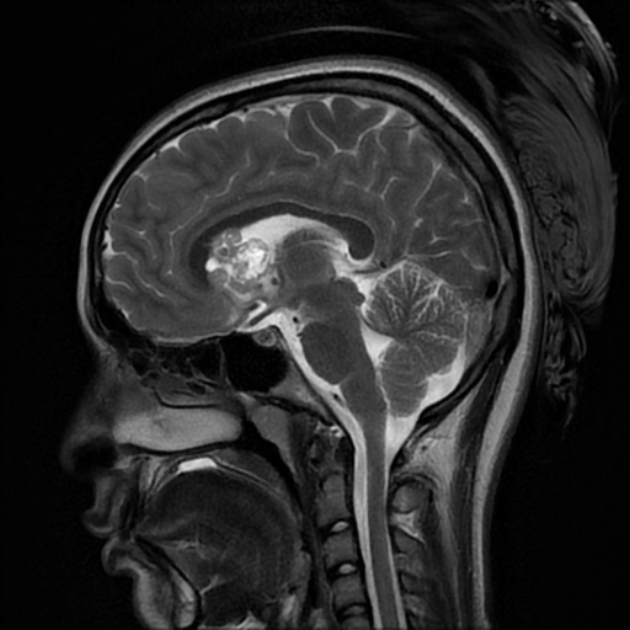
Bilateral multiple subependymal nodules, some of them appear calcific showing blooming on SWI images and some show mild post contrast enhancement.
Bilateral subcortical tubers which elicit high signal on FLAIR and T2 WI.
Right frontal large mass lesion at the foramen of Monro which elicits low signal on T1, heterogeneous signal on T2 with heterogeneous post contrast enhancement and encroaches upon the right frontal horn, in keeping with subependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
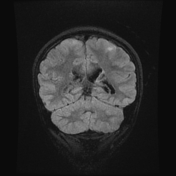
Bilateral cerebellar (larger on the left side) wedge shape areas of abnormal signal eliciting high signal on T2 and FLAIR with blooming on SWI and no significant post contrast enhancement. It shows retraction with Its apex is directed towards the 4th ventricle, in keeping with cerebellar tubers. A flow void vascular anomaly is seen adjacent to the right cerebellar tuber.
Case Discussion
The case shows typical radiological features of tuberous sclerosis including subependymal nodules with some appear calcific and others show mild enhancement, cortical tubers and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma. The case also shows an uncommon feature of the disease which is the presence of cerebellar tubers which appear as wedge shaped lesions with retraction and abnormal signal showing blooming on SWI with no post contrast enhancement.
Cerebellar tubers are less common than supratentorial tubers 1.
Cerebellar tubers are primarily seen in pediatric patients over 11.5 years of age and are rare in patients under the age of 8 2.
Tuberous sclerosis patients with cerebellar tubers are known to have a high association with TSC2 gene mutations 3
Cerebellar tubers are usually found in posterior cerebellar lobules 1. They are also associated with cerebellar atrophy that is not otherwise observed in supratentorial tubers. Also, patients with cerebellar tubers have a higher incidence of supratentorial cortical tubers, giant cell astrocytomas and associated vascular anomalies 4.
Imaging characteristics of cerebellar tubers1
wedge shaped lesions with their apex directed towards the 4th ventricle and elicit low T1 signal, high T2/FLAIR signal and variable contrast enhancement (similar to supratentorial tubers)
. Two unique features of cerebellar tubers are retraction, which was seen in 84% of patients and variable “zebra striped” enhancement seen in 51% of patients 3
Cerebellar tubers show dynamic changes over time, they might increase or decrease in size. They also might undergo calcifications or internal cystic degeneration. 4




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.