Presentation
One month of right upper quadrant abdominal pain.
Patient Data
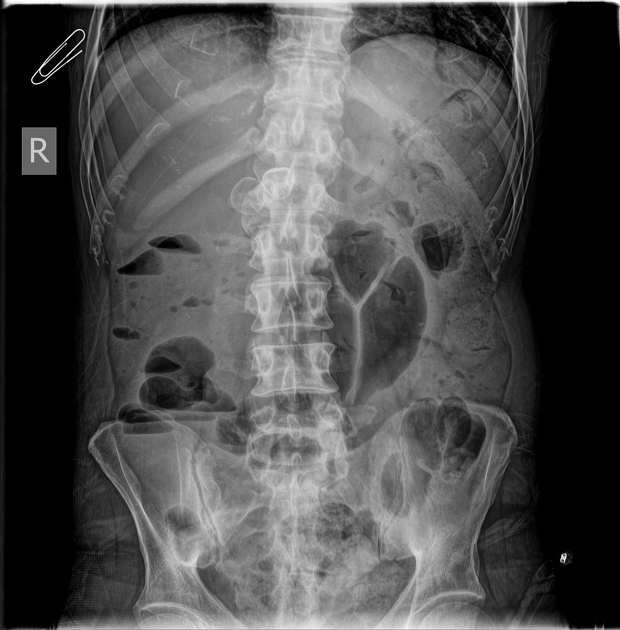
Erect abdominal x-ray shows two large peripheral calcified structures projected onto the L1 vertebra, that probably represent gallstones.
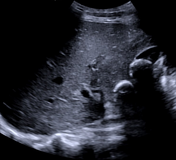
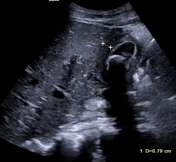
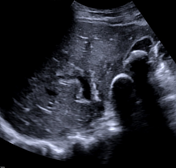
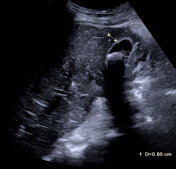
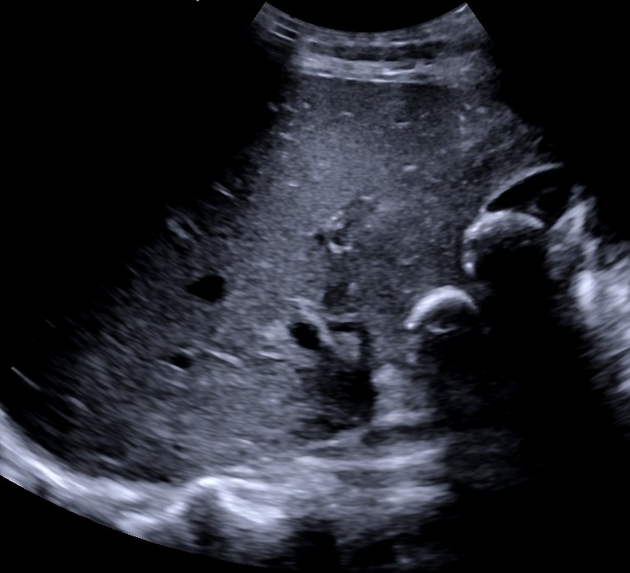
The gallbladder is non-distended, contains at least two large gallstones, and shows severe wall thickening. Impression of blurred boundaries of the gallbladder.
No dilation of the intrahepatic or common bile duct.
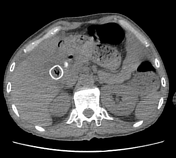

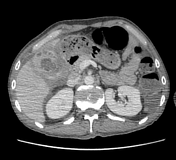

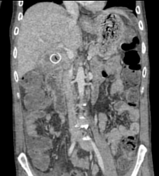

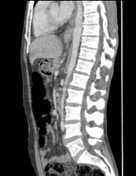

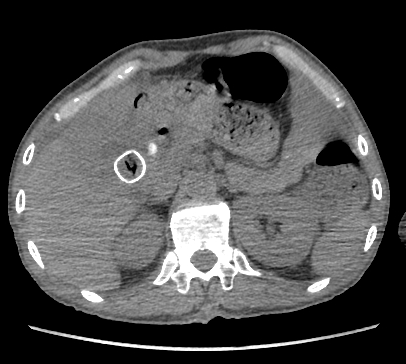
Thickening of the wall of the gallbladder and multiple large gallstones within it.
Intramural hypo-attenuating regions of varying sizes communicate with the gallbladder lumen.
Pericholecystic fluid collection.
Case Discussion
Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis is a rare inflammatory disease that makes it difficult to distinguish between benign and malignant conditions
A focal, diffuse chronic inflammatory process is caused by the dilation of hypo-enhancing spaces in the wall of the gallbladder due to the rise of the intraluminal pressure caused by an impacted stone in the neck, leading to rupture of the Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses into the wall.
The patient went on to open surgical cholecystectomy, where macroscopically characteristic xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis emerged.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.