Pathology - Histopathology & Immu...
Histopathology & Immunohistochemistry
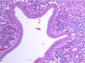
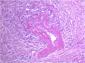
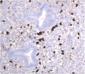
Microscopic sections revealed a fibro-inflammatory process with a prominent plasma cell component that extended into peri-pancreatic soft tissue. The inflammatory infiltrate had a prominent peri-ductal pattern and also involved small veins (venulitis). The involvement of the pancreatic head was patchy with intervening normal lobules of exocrine acini noted between fibrotic atrophic foci. IgG4 immunohistochemical staining revealed a high percentage of positivity within the plasma cells present (>30 per HPF).
The above features are consistent with the lobulocentric or lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis subtype of AIP, the significance of which includes an association with Sjogren's syndrome and a predilection for developing recurrent bile duct stenosis.