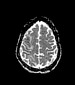
MRI
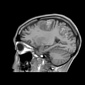
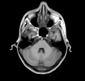
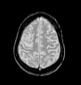
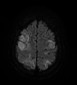
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reveals focal cortical/subcortical areas of mild T1 hypointensity and high T2/FLAIR signal intensity scattered through both cerebral hemispheres, keeping with ischemic injuries, where some cortical laminar necrosis are also present and characterized by intrinsic high T1 signal. The largest region of the infarct is in the right frontoparietal lobe. The crescentic high signal on T1 and T2 around the right ICA correspond to subacute intramural hematomas in the false lumen, separated from the true lumen by a curvilinear intimal flap. Note left ICA loss of signal void on T2, representing occlusion due to luminal thrombus.
Impression: These findings are consistent with bilateral dissection of both ICAs.