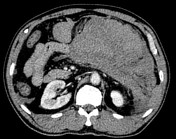
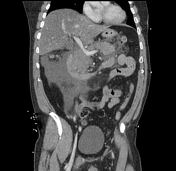
Acute Pancreatitis and Associated Pancreatic Collections
Diagnosis of acute pancreatitis:
At least two of
- abdominal pain consistent with the disease
- 3x serum amylase or lipase levels
- imaging findings consistent with acute pancreatitis.
Therefore acute pancreatitis is mainly a clinical diagnosis.
Imaging indicated in:
- ambiguous cases
- evaluate suspected complications (patient fails to improve within 48–72 hours after admission)
- determining the underlying cause.
Early imaging (<72 hr) can underestimate severity. Necrosis may not have developed yet, and early necrosis can be confused for oedema.
Revised Atlanta classification for pancreatic collections
Two types of acute pancreatitis:
- Non-necrotic = Interstitial oedematous pancreatitis
- Necrotic = Necrotizing pancreatitis
Four types of collections:
- Non-necrotic = Acute peripancreatic fluid collection vs Pseudocyst
- Necrotic = Acute necrotic collection vs Walled-off necrosis
based on:
- time from onset of symptoms
- under/over 4 weeks
- presence of necrosis (heterogeneity)
- if necrotic, can be peripancreatic/parenchymal/combined
All 4 types of collections can become infected. Infection is difficult to diagnose on CT.
Also assess for:
- Gas in collection
- Infection vs Fistula vs Drain
- Pseudoaneurysm/Haemorrhage
- Thrombosis
Other special types of pancreatitis:
- Paraduodenal/Groove pancreatitis (acute)
- Autoimmune pancreatitis (IgG4, chronic)