73 results found
Article
Synovial joints
Synovial joints are a type of joint with an articular capsule, consisting of an outer fibrous layer and an inner synovial membrane, which surrounds a fluid-filled synovial cavity. The articulating surfaces are covered by hyaline cartilage, designed to slide with little friction and to absorb com...
Case
Synovial joint
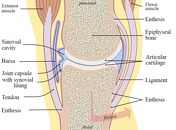
Published
30 Jun 2019
35% complete
Diagram
Case
Types of synovial joints (illustrations)

Published
03 Feb 2016
38% complete
Diagram
Article
Distal radioulnar joint
The distal radioulnar joint is a pivot-type synovial joint between the distal radius and ulna.
Summary
articulation: pivot-type synovial joint between the ulnar notch of the distal radius and the ulna head
movement: rotation of the distal radius
ligaments: triangular ligament, and anterior a...
Article
Typical ribs
Typical ribs are those numbered 2 to 10 with ribs 1, 11 and 12 considered atypical. Some authors however include ribs 2 and 10 also atypical.
Gross anatomy
A typical rib is long and flat. They contain a:
head
neck
tubercle
shaft
angle
Ribs have a rounded, smooth superior border. The infe...
Article
Atlanto-axial articulation
The atlanto-axial articulation is a complex of three synovial joints, which join the atlas (C1) to the axis (C2).
Gross anatomy
Articulations
paired lateral atlanto-axial joints: classified as planar-type synovial joint between the lateral masses of C1 and C2, though somewhat more complex in ...
Article
Carpometacarpal joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are synovial joints formed by articulations of the distal carpal row and the metacarpal bones.
Gross anatomy
Articulations
The carpometacarpal joints are made up of a number of bony articulations 1.
first carpometacarpal: distinct synovial curved saddle joint...
Article
Atlas (C1)
The atlas (plural: atlases) is the first cervical vertebra, commonly called C1. It is an atypical cervical vertebra with unique features. It articulates with the dens of the axis and the occiput, respectively allowing rotation of the head, and flexion, extension and lateral flexion of the head. ...
Article
Cartilaginous joints
Cartilaginous joints are a type of joint where the bones are entirely joined by cartilage, either hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage. These joints generally allow more movement than fibrous joints but less movement than synovial joints.
Primary cartilaginous joint
These cartilaginous joints...
Article
Ball and socket joint
Ball and socket joints are a type of synovial joint where the spheroid articular surface of one bone sits within a cup-like depression of another bone.
Movements
The ball and socket configuration allows for movement with 3 degrees of freedom, which is more than any other type of synovial joint...
Article
Sacroiliac joint
The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is a synovial joint between ilium and the sacrum. It has little movement and its main function is to transfer weight between the axial and lower appendicular skeletons. The sacroiliac joint is a symmetrical joint (i.e. is paired) with an oblique coronal orientation and...
Article
Proximal tibiofibular joint
The proximal (or superior) tibiofibular joint is a synovial joint between the superior aspects of the tibia and fibula and is one of the multiple sites of cartilaginous and fibrous articulation carrying the name of the tibiofibular joint.
Gross anatomy
Articulation
fibula: flat facet of the f...
Article
Acute gouty arthritis
Acute gouty arthritis, also known as a gout flare, is the acute symptomatic phase of gout due to the deposition of monosodium urate crystals in a synovial joint.
Clinical presentation
Acute gouty arthritis presents as a tender, erythematous, swollen joint. Involvement is typically monoarticula...
Article
Temporomandibular joint
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is an atypical synovial joint located between the condylar process of the mandible and the mandibular fossa and articular eminence of the temporal bone. It is divided into a superior discotemporal space and inferior discomandibular space by the TMJ disc (or meni...
Article
Acromioclavicular joint
The acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) is a planar diarthrodial synovial joint of the pectoral girdle.
Gross anatomy
The acromioclavicular joint is between the small facet of the convex distal clavicle and flat anteromedial acromion. The articular surfaces are lined with fibrocartilage (like the st...
Article
Costovertebral joint
The costovertebral joint is the articulations between the ribs and the vertebral column.
Gross Anatomy
The ribs articulate with the thoracic vertebrae via two distinctly different joints:
costovertebral joint - articulation between the head of the rib and the vertebral body
costotransverse j...
Article
Tibiofemoral joint
The tibiofemoral joint is a modified hinge synovial joint between the distal femur and the proximal tibia.
Summary
articulation: modified hinge joint between the medial and lateral condyles of the femur and the tibial condyles
joint: knee
ligaments: transverse ligament of the knee, medial an...
Article
Empyema
Empyemas are purulent inflammatory collections within a body cavity. Contrast this with abscesses, which arise within parenchymal tissue, rather than occupying a pre-existing anatomical space.
Terminology
Colloquially, the standalone term empyema is used to refer to thoracic empyemas but there...
Article
Ankle radiograph (an approach)
Ankle radiographs are frequently performed in emergency departments, usually, after trauma, the radiographic series is comprised of three views: an anteroposterior, mortise, and a lateral. They may be performed to assess degenerative or inflammatory arthritis as well as to look for the sequela o...
Article
Sternoclavicular joint
The sternoclavicular joint is a synovial joint between the medial clavicle, manubrium and the first costal cartilage that joins the upper limb with the axial skeleton.
Gross anatomy
There are two non-congruent articular surfaces forming a saddle joint 3:
medial clavicle: larger of the two
c...









 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.