Items tagged “anatomy”
380 results found
Article
Sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is a large, complex, unpaired bone forming the central parts of the anterior and central skull base.
Gross anatomy
Parts of the sphenoid bone include:
body
jugum sphenoideum
contains the sphenoid sinus
greater wing
lesser wing
pterygoid process and plates
Articulations...
Article
Body of sphenoid
The body of the sphenoid bone is the midline cubical portion of the sphenoid bone, hollowed by the sphenoid air sinuses.
Gross anatomy
The body has superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, and lateral surfaces.
The superior surface features:
ethmoidal spine: prominent spine that articulates...
Article
Dorsal scapular nerve
The dorsal scapular nerve is a branch from the C5 root of the brachial plexus and supplies the rhomboid muscles.
Gross anatomy
Origin
Posterior aspect of the C5 root of the brachial plexus.
Course
It courses through scalenus medius then accompanies the dorsal scapular vessels inferiorly, de...
Article
Medial pectoral nerve
The medial pectoral nerve, also known as the medial anterior thoracic nerve arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus and supplies both the pectoralis minor and major muscles.
Gross anatomy
Origin
The medial pectoral nerve arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus with fibe...
Case
Intercostal space (diagram)

Published
19 Jun 2015
25% complete
Diagram
Article
Innermost intercostal muscles
The innermost intercostal muscles are muscles of respiration. They are the deepest intercostal muscles located in the intercostal spaces, and contract along with the internal intercostal muscles to reduce the transverse dimension of the thoracic cavity during expiration.
Gross anatomy
The inne...
Case
Brain ventricle anatomy diagram
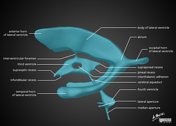
Published
23 Jun 2015
29% complete
Diagram
Article
Intercostal spaces
The intercostal spaces, also known as interspaces, are the space between the ribs. There are 11 spaces on each side and they are numbered according to the rib which is the superior border of the space.
Gross anatomy
The intercostal spaces contain three layers of muscle: the external, internal...
Article
Supraclavicular nerves
The supraclavicular nerves are three cutaneous nerves that emerge as a common trunk from the cervical plexus before branching to innervate the skin over the upper chest and shoulders.
Gross anatomy
Origin
The supraclavicular nerves arise from the ventral rami of C3 and C4 spinal nerves, alth...
Article
Punctum nervosum
Punctum nervosum, also known as Erb’s point or the nerve point of the neck, is a point half way along the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle from which all cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus converge and become superficial.
Gross anatomy
The punctum nervosum is located o...
Article
Lumbar plexus
The lumbar plexus is a complex neural network formed by the lower thoracic and lumbar ventral nerve roots (T12 to L5) which supplies motor and sensory innervation to the lower limb and pelvic girdle.
Summary
origin: ventral rami of T12 to L5
course: formed within the substance of the ps...
Article
Hyoid bone
The hyoid bone is a midline "U or horseshoe-shaped" bone that serves as a structural anchor in the mid-neck. It is the only bone in the human body that does not directly articulate with another bone (other than sesamoids). It is a place of convergence of multiple small neck muscles that permit t...
Article
Linea alba
The linea alba (Latin for white line) is a single midline fibrous line in the anterior abdominal wall formed by the median fusion of the layers of the rectus sheath medial to the bilateral rectus abdominis muscles. It attaches to the xiphoid process of the sternum and the pubic symphysis. The um...
Article
Angular gyrus
The angular gyrus is a portion of the parietal lobe of the brain. It is one of the two parts of the inferior parietal lobule, the other part being the supramarginal gyrus. It plays a part in language and number processing, memory and reasoning 1.
Gross anatomy
Relations
It lies as a horseshoe...
Article
Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
Extensor carpis radialis brevis (ECRB) muscle is a muscle of the superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm. It passes through the 2nd extensor compartment of the wrist. Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle is one of the three muscles forming the mobile wad of Henry. It is on...
Case
Labyrinthine artery: basilar artery origin

Published
01 Oct 2015
39% complete
MRI
Article
Hepatocystic triangle
The hepatocystic triangle (or Calot triangle) is a small triangular space at the porta hepatis of surgical importance as it is dissected during cholecystectomy. Its contents, the cystic artery and cystic duct, must be identified before ligation and division to avoid intraoperative injury.
Gros...
Case
Ipsilateral Spigelian hernia with cryptorchidism

Published
22 Nov 2015
95% complete
Ultrasound
CT
Case
Persistent sciatic artery

Published
23 Oct 2015
89% complete
CT
Case
Aberrant right subclavian artery

Published
13 Aug 2016
98% complete
CT
X-ray







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.