Items tagged “physics”
132 results found
Case
Inverse square law

Published
26 Apr 2015
32% complete
Diagram
Case
Incomplete projection artifact

Published
18 May 2015
77% complete
CT
Article
Helical CT image acquisition
Helical (a.k.a. spiral) CT image acquisition was a major advance on the earlier stepwise ("stop and shoot") method.
With helical CT, the patient is moved through a rotating x-ray beam and detector set. From the perspective of the patient, the x-ray beam from the CT traces a helical path. The he...
Case
Radiation dose for coronary CTA 256 vs 64 detectors

Published
20 Dec 2015
63% complete
Photo
Case
Zipper artifact (MRI) from RF noise
Published
02 Jun 2016
33% complete
MRI
Case
Diagram depicting scatter from an ultrasound wave interacting with a small structure

Published
07 Jul 2016
22% complete
Diagram
Case
Diagrams of an ultrasound wave interacting with a specular reflector and a diffuse reflector

Published
07 Jul 2016
22% complete
Ultrasound
Article
Scattering (ultrasound)
Scattering occurs when a sound wave strikes a structure with a different acoustic impedance to the surrounding tissue and which is smaller than the wavelength of the incident sound wave. Such structures are known as “diffuse reflectors,” with examples being red blood cells and non-smooth surface...
Case
Lead zirconate titanate (PZT) diagrams

Published
24 Jul 2016
38% complete
Diagram
Article
Distance measurement
Ultrasound machines perform distance measurement to synthesize images from returning echoes. To generate images for an ultrasound scan, machines need to determine the distance of reflective interfaces from the transducer. Simply, the formula used is:
distance = (speed x time)/2
Where:
distanc...
Case
X-ray beam divergence (diagram)

Published
04 Aug 2016
38% complete
Article
Side lobe artifact
Side lobe artifacts occur where side lobes reflect sound from a strong reflector that is outside of the central beam, and where the echoes are displayed as if they originated from within the central beam.
Ultrasound transducer crystals expand and contract to produce primary ultrasound beams in ...
Case
Ring down artifact

Published
23 Sep 2016
47% complete
Annotated image
Case
Iodinated contrast (diagram)
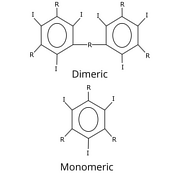
Published
15 Oct 2016
32% complete
Diagram
Article
Physics curriculum
The physics curriculum is one of our curriculum articles and aims to be a collection of articles that represent core physics and imaging technology knowledge:
physics and imaging technology: x-ray
physics and imaging technology: ultrasound
physics and imaging technology: CT
physics and imagi...
Article
High voltage generator
X-ray units require a high voltage generator to achieve the necessary power required of an x-ray tube. AC power will supply x-ray units with sinusoidal currents, resulting in 'peaks and troughs', limiting an x-ray tube to produce x-rays only half of the 1/60th of s second cycle.
A single-phase...
Article
Image intensifier
Image intensifiers are used to convert low-energy x-rays into visible light images. Image intensifiers are several thousand times more sensitive compared to standard 400-speed screen-film combinations, and in practice can produce images using several thousand times less radiation 3,4.
The bigge...
Article
Photon
A photon is, in simple terms, an elementary force-carrying particle i.e. a boson 2 (obeys the statistical law of Bose-Einstein). It has a zero mass (rest mass) and travels at, c, the speed of light in vacuo. It is defined as stable with no electric charge and exhibits both wave-like and particle...
Article
Biomolecular radiation damage
Biomolecular radiation damage may result from exposure of biological tissues to ionizing radiation from direct exposure, or via Compton scattering.
Mechanism of tissue radiation damage
Direct effect
occurs when energy is directly deposited to the biological macromolecule (e.g. DNA, RNA, prote...
Article
Energy difference between spin up and spin down states
The energy difference between spin up and spin down states of hydrogen are important in understanding net magnetization vector of tissue for magnetic resonance imaging.
Each hydrogen atom is formed by one proton and one orbiting electron. Because the atomic number is 1, it has a spin quantum nu...