Items tagged “variant”
426 results found
Article
Persistent primitive trigeminal artery
Persistent primitive trigeminal artery (PPTA) is the most common type of the four persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar anastomoses. It is present in 0.1-0.6% of cerebral angiograms and is usually unilateral.
In utero, the trigeminal artery supplies the basilar artery before the development of the...
Article
Pneumatized dorsum sella
Pneumatization of the dorsum sella is not uncommon, but needs to be remembered as an unusual site of sinus disease, which otherwise may be mistaken for intracranial of pituitary disease.
Article
Superior vena caval duplication
Superior vena caval (SVC) duplication is the most common form of a left-sided SVC, where the normal right-sided SVC remains. The right SVC, however, can be smaller in approximately two-thirds of such cases 3.
Epidemiology
Double SVC occurs in 0.3% of the general population. In those with conge...
Article
Hypertrophied column of Bertin
Columns of Bertin represent the extension of renal cortical tissue which separates the pyramids, and as such are normal structures. They become of radiographic importance when they are unusually enlarged and may be mistaken for a renal mass (renal pseudotumor).
Nomenclature of such enlarged col...
Article
Sublabral foramen
A sublabral foramen is simply a focal detachment of the anterosuperior labrum from the underlying glenoid and constitutes a normal labral variant of no clinical significance 1-4.
On imaging, it might be confused with a SLAP lesion or an anterior labral tear 1.
Gross anatomy
Sublabral foramina...
Article
Thyroidea ima artery
The thyroidea ima artery is an uncommon variant of the blood supply to the inferior aspect of the thyroid gland. It is reported in ~7.5% (range 1.5-12.2%) of individuals and can arise from:
brachiocephalic trunk (most common: 1.9-6.0%)
right common carotid artery
aortic arch
internal thoraci...
Article
Unfused spinous process
Unfused spinous process, which is really failure of fusion of the neural arch, is a relatively common anatomical variant and is part of the spectrum of spina bifida occulta.
This should be differentiated from accessory ossicles of the spinous process, which appear after non-fusion of the secon...
Article
Ureterocele
Ureteroceles represent abnormal congenital dilatation of the distal-most portion of the ureter. The dilated portion of the ureter may herniate into the bladder secondary to the abnormal structure of vesicoureteric junction (VUJ).
Epidemiology
A ureterocele occurs in about 1 in 5000 to 1 in 120...
Article
Vertebral anomalies
The vertebral column is affected by a range of anatomical variants of the body and/or neural arch as well as accessory ossicles. Knowledge of basic vertebral anatomy and ossification is essential for describing and understanding the range of anomalies.
Variant anatomy
Vertebral body
hemiverte...
Case
Diastematomyelia and tethered cord

Published
19 May 2008
71% complete
MRI
Article
Mega cisterna magna
Mega cisterna magna refers to a normal variant characterized by a truly focal enlargement of the CSF-filled subarachnoid space in the inferior and posterior portions of the posterior cranial fossa. It is an incidental finding on neuroimaging, and no imaging follow up is necessary.
Epidemiology...
Case
Pyramidal thyroid lobe
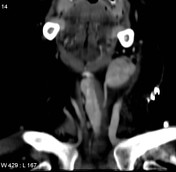
Published
18 Sep 2008
65% complete
CT
Article
Fetal posterior cerebral artery
A fetal (origin of the) posterior cerebral artery is a common variant in the posterior cerebral circulation, estimated to occur in 20-30% of individuals 2.
A fetal posterior communicating artery (PCom) describes a situation whereby the PCom is larger than the P1 segment of the posterior cerebra...
Article
Persistent proatlantal intersegmental artery
The proatlantal intersegmental artery is also known as the type I proatlantal artery, and is one of the persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar anastomoses. It arises from the internal carotid artery (similar to the persistent hypoglossal artery) but instead of heading for the hypoglossal canal, it j...
Article
Proatlantal artery
The proatlantal artery is one of the persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar anastomoses, and can be subdivided into two types depending on its origin:
type I: (~55%)
corresponds to the first segmental artery
arises from the internal carotid artery
also known as the proatlantal intersegmental art...
Article
Arc of Riolan
The arc of Riolan, refers to an anastomosis between the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA). However, there is no consensus on which anatomical structure this term precisely refers to. It is also known as the mesenteric meandering artery (of Moskowitz) or ce...
Article
Wormian bone
Wormian bones (also known as intrasutural bones) is the name given to the additional small bones sometimes found between the cranial sutures of the bones of the skull vault, most commonly in relation to the lambdoid suture. Some reserve the term Wormian bones to just the intrasutural bones proxi...
Article
Variant hepatic arterial anatomy
Variation in hepatic arterial anatomy is seen in 40-45% of people. Classic branching of the common hepatic artery from the celiac artery, and the proper hepatic artery into right and left hepatic arteries to supply the entire liver, is seen in 55-60% of the population.
Terminology
An accessor...
Case
Azygos continuation of the inferior vena cava

Published
06 Feb 2009
65% complete
CT
Article
Persistent stapedial artery
The persistent stapedial artery (PSA) is an abnormal small vessel arising from the petrous portion of the internal carotid artery and crossing through the middle ear. It results from the failure of regression of the embryonic stapedial artery.
Epidemiology
The prevalence is thought to range f...