Paraurethral duct cyst
Updates to Article Attributes
Paraurethral duct cysts are retention cysts that form secondary to inflammatory obstruction of the paraurethral (Skene) ducts in females.
Pathology
The cysts are lined by stratified squamous epithelium due to their origin from the urogenital sinus.
Clinical presentation
Usually asymptomatic.
Radiographic features
Typically appear as round or oval masses that are located just laterally to the external urethral meatus and inferior to the pubic symphysis.
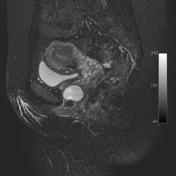
MRI
Skene duct cysts manifest as round or oval hyperintense lesions just lateral to the external urethral meatus.
Signal characteristics
-
T2
hyperintense signal if uncomplicated
may show fluid-fluid levels if there is a complicating haemorrhage
11
Treatment and prognosis
Large, symptomatic cysts may warrant surgical excision or marsupialisation, usually usually with excellent outcome. Large cysts may also require drainage or excision in the presence of superimposed infection.
Differential diagnosis
General considerations include:
urethral diverticulum(urethrocele): tend to be midurethral in location versus paraurethral gland cysts, which are located near the external urethral meatus
See also
-<li><p>may show fluid-fluid levels if there is a complicating haemorrhage<sup> 1</sup></p></li>- +<li><p>may show fluid-fluid levels if there is a complicating haemorrhage<sup> 1</sup></p></li>
-</li></ul><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>Large, symptomatic cysts may warrant surgical excision or marsupialisation, usually with excellent outcome. Large cysts may also require drainage or excision in the presence of superimposed infection.</p><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><p>General considerations include:</p><ul>- +</li></ul><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>Large, symptomatic cysts may warrant surgical excision or marsupialisation, usually with excellent outcome. Large cysts may also require drainage or excision in the presence of superimposed infection.</p><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><p>General considerations include:</p><ul>
-<li><p><a href="/articles/urethral-diverticulum">urethral diverticulum</a> (urethrocele): tend to be midurethral in location versus paraurethral gland cysts, which are located near the external urethral meatus</p></li>- +<li><p><a href="/articles/urethral-diverticulum">urethral diverticulum</a> (urethrocele): tend to be midurethral in location versus paraurethral gland cysts, which are located near the external urethral meatus</p></li>
Image 4 MRI (T2 fat sat) ( update )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.