Acromial types
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mohammad Taghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mohammad Taghi Niknejad's current disclosures- Acromion types
- Types of the acromion
- Bigliani classification of acromion types
- Bigliani classification of acromion morphology
- Bigliani classification
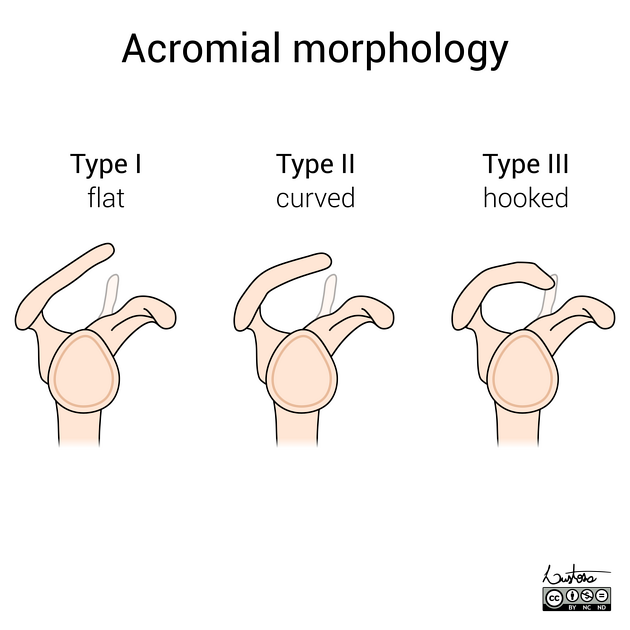
Acromial types were initially divided into three types (known as the Bigliani classification) 3, to which a fourth has been added 2. These classifications are used as a standardised way of describing the acromion and predicting to a degree the incidence of impingement.
Classification
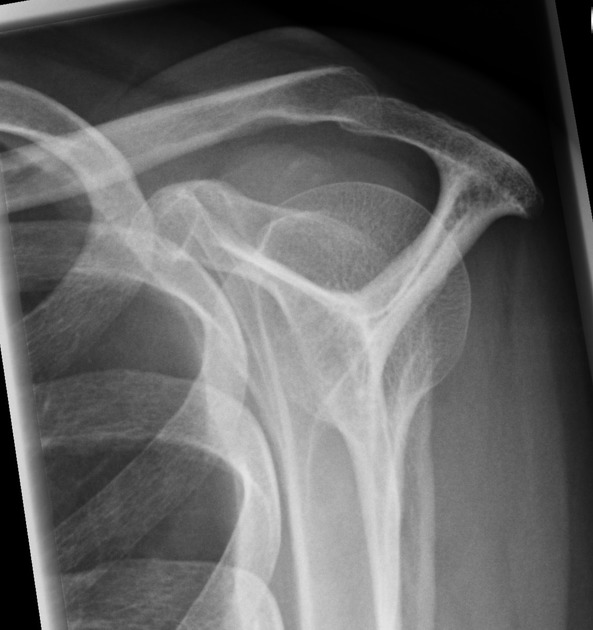
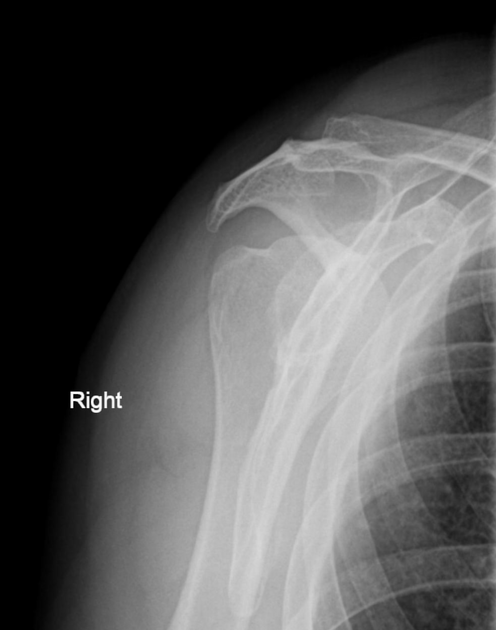
This classification was initially proposed by Bigliani et al. in 1986 on outlet view radiographs and later modified by Kitay et al. 7 and Vanarthos et al. in 1995, which remains the most widely accepted classification at the time of writing (2022).
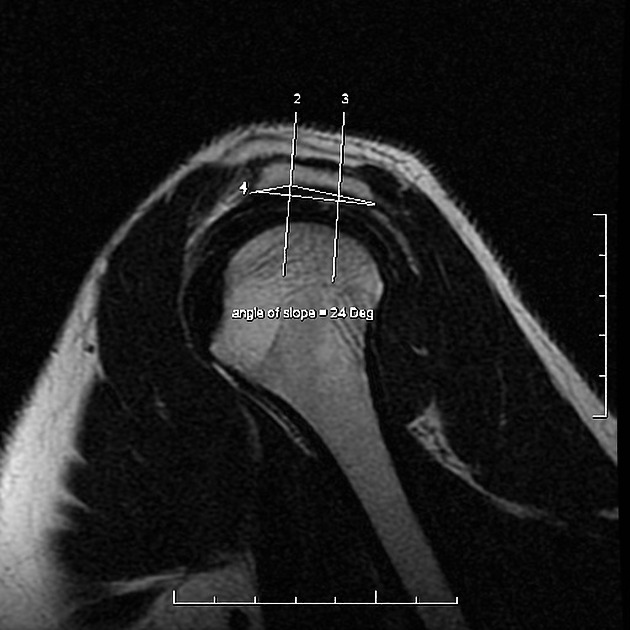
Acromial morphology is variable on sagittal oblique MRI, depending on the slice position. A slice position just lateral to the acromioclavicular joint (no joint capsule or acromioclavicular ligament visible) is considered the single best slice 8.
Acromion morphology (types) are based on sagittal oblique MRI:
flat inferiorly (12%) 6
-
curved (56%)
parallel to the humeral head with a concave undersurface
down-sloping in the middle-third of the acromion 8
considered the most common type 3
-
hooked (29%)
most anterior portion of the acromion has a hooked shape
down-sloping in the anterior-third of the acromion 8
associated with increased incidence of shoulder impingement
-
convex (upturned) (3%)
most recent classification of acromion process shape
the undersurface of the acromion is convex near the distal end 4
no convincing correlation between a type 4 acromion and impingement syndrome exists 4,5
See also
References
- 1. Phoebe Kaplan. Musculoskeletal MRI. (2001) ISBN: 0721690270 - Google Books
- 2. Vanarthos W & Monu J. Type 4 Acromion: A New Classification. Contemp Orthop. 1995;30(3):227-9. - Pubmed
- 3. Getz J, Recht M, Piraino D et al. Acromial Morphology: Relation to Sex, Age, Symmetry, and Subacromial Enthesophytes. Radiology. 1996;199(3):737-42. doi:10.1148/radiology.199.3.8637998
- 4. Chang E, Moses D, Babb J, Schweitzer M. Shoulder Impingement: Objective 3D Shape Analysis of Acromial Morphologic Features. Radiology. 2006;239(2):497-505. doi:10.1148/radiol.2392050324 - Pubmed
- 5. Haaga, John R. 1945-. CT and MR Imaging of the Whole Body. (2009) ISBN: 9780323053754 - Google Books
- 6. Mulyadi E, Harish S, O'Neill J, Rebello R. MRI of Impingement Syndromes of the Shoulder. Clin Radiol. 2009;64(3):307-18. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2008.08.013
- 7. Kitay G, Iannotti J, Williams G, Haygood T, Kneeland B, Berlin J. Roentgenographic Assessment of Acromial Morphologic Condition in Rotator Cuff Impingement Syndrome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1995;4(6):441-8. doi:10.1016/s1058-2746(05)80036-9
- 8. Mayerhoefer M, Breitenseher M, Roposch A, Treitl C, Wurnig C. Comparison of MRI and Conventional Radiography for Assessment of Acromial Shape. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184(2):671-5. doi:10.2214/ajr.184.2.01840671 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Bifid biceps tendon
- Os acromiale
- Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder
- Bigliani type 2 acromion
- Bifid biceps tendon
- Acromial fracture
- Bifid biceps tendon
- Acromial fracture
- Hill-Sachs and osseous Bankart lesions
- Bifid biceps tendon
- Supraspinatus tendinosis
- Subacromial Impingement
- Reverse Bankart lesion
- Bigliani type 3 acromion
- Bigliani type 2 acromion
- Bigliani type 1 acromion
- Acromial types
- Acromial keel spur
- Acromial spur
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centres
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centres
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centres
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.