Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP), also known as Hamman-Rich syndrome, is a rapidly progressive non-infectious interstitial lung disease of unknown etiology. It is considered the only acute process among the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias.
On this page:
Terminology
Acute interstitial pneumonia has a similar clinical presentation and histological features to those seen in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), showing extensive diffuse alveolar damage (DAD). Both conditions likely represent the same pathology, with acute interstitial pneumonia probably accounting for some of the idiopathic cases of ARDS.
Epidemiology
Truly idiopathic acute interstitial pneumonia tends to occur in those without pre-existing lung disease and typically affects middle-aged adults (mean ~50 years 5). However, in certain conditions such as leflunomide-induced acute interstitial pneumonia, patients have pre-existing lung disease.
Clinical presentation
Clinical features are varied. Patients often have a history of an antecedent illness such as a viral upper respiratory infection. Common initial symptoms include myalgia, arthralgia, pyrexia, chills, and malaise. Severe exertional dyspnea develops over a matter of days to weeks 13.
Pathology
Acute interstitial pneumonia is characterized histologically by diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) 2 and is indistinguishable from acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The alveolar damage comprises three phases:
an acute exudative phase
a subsequent organizing phase
a final fibrotic phase
Radiographic features
The clinical context is vital for correct image interpretation.
Plain radiograph
Non-specific and often shows bilateral patchy airspace opacification.
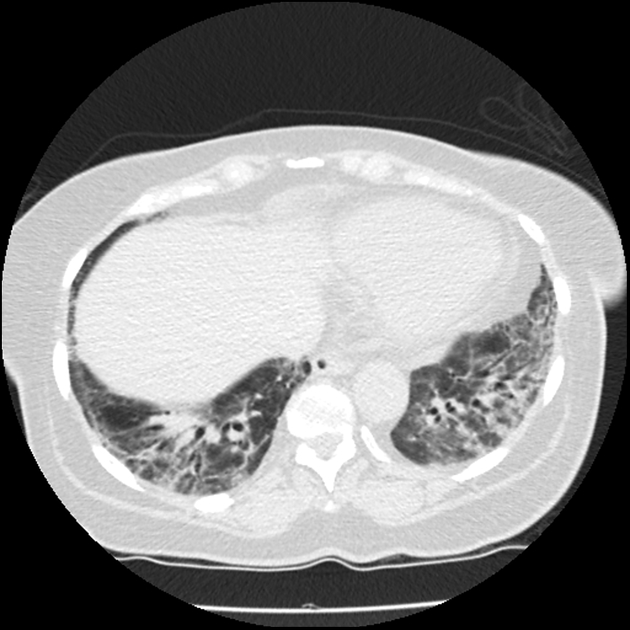
CT
During the initial stages, acute interstitial pneumonia can have features similar to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which include:
areas with ground-glass attenuation: generally tend to be bilateral and symmetrical 10
traction bronchiectasis: can be seen in ~80% of cases during the course of the disease 4 and correlates with disease duration 2
air space consolidation: may have a slight predilection towards the dependent portions 5
Treatment and prognosis
The condition usually progresses to respiratory failure that requires mechanical ventilation and corticosteroid therapy. Even despite mechanical ventilation, it often carries a grave prognosis with >70% mortality at ~3 months 1.
History and etymology
The clinical features of acute interstitial pneumonia were first described by L Hamman and A Rich in 1935 8, and the pathological processes were first described by A L Katzenstein et al. in 1986 3.
Differential diagnosis
Considerations in the early stages include:
acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): can involve other organs 9
-
infectious multifocal pneumonia
Other considerations include:
an acute interstitial pneumonitic process triggered by certain medications, e.g. leflunomide-induced acute interstitial pneumonia
For a more general differential, consider: