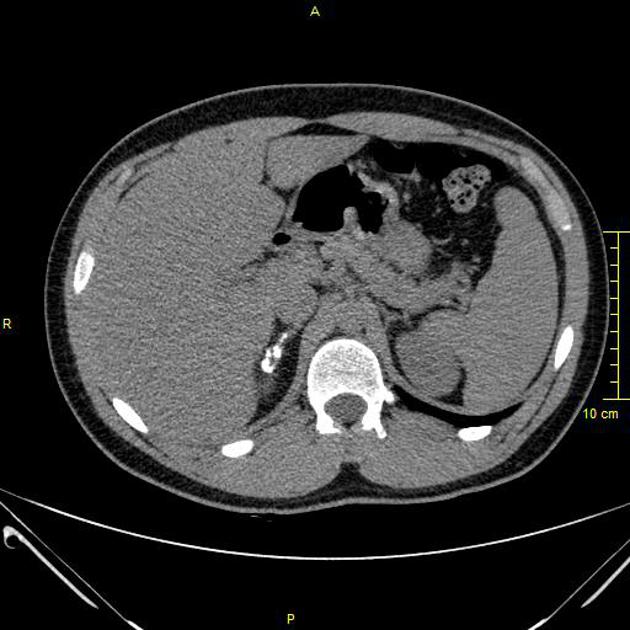
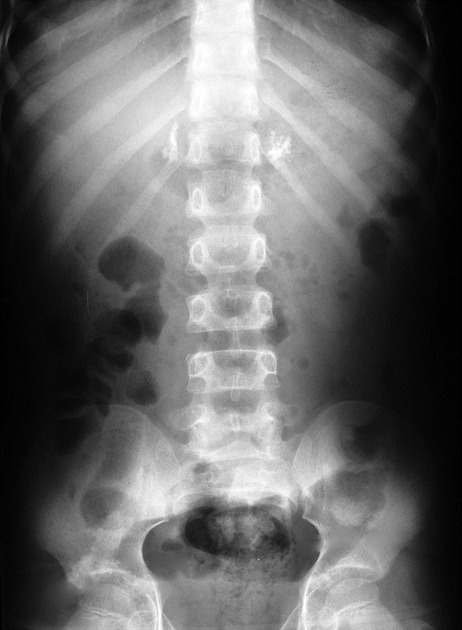
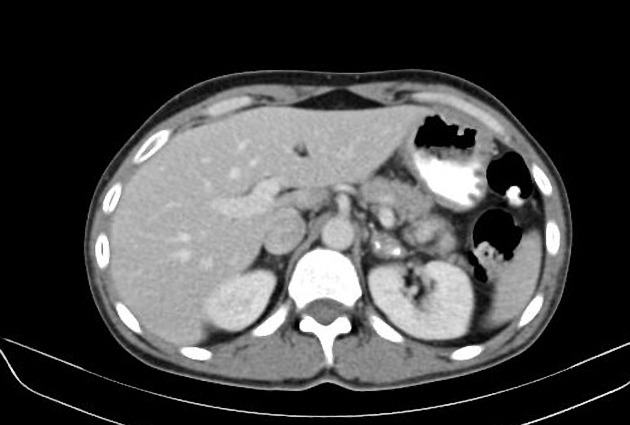
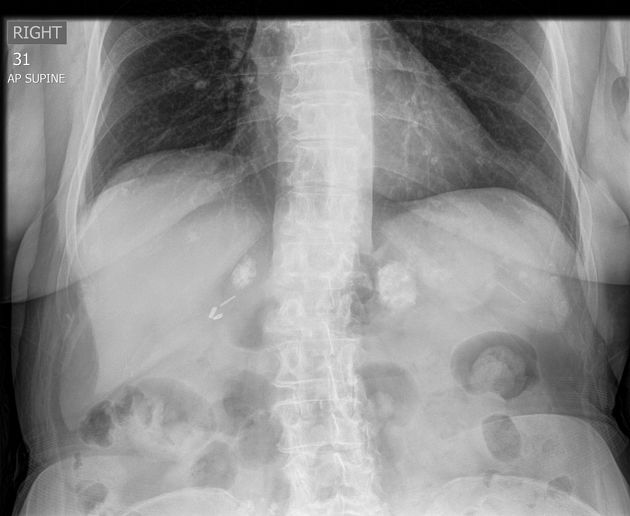
Adrenal calcification is not a rare finding in healthy asymptomatic people and is usually the result of previous haemorrhage or tuberculosis. Addison disease patients only occasionally develop calcification.
On this page:
Images:
Pathology
Aetiology
Haemorrhage
- sepsis: Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome
- blunt abdominal trauma
- adrenal pseudocyst
- neonatal asphyxia
- coagulopathy
- infants: calcification seen soon after haemorrhage (as early as 1-2 weeks)
Infection
Adrenal tumours
- adrenal metastases, especially melanoma
- neuroblastoma
- adrenal myelolipoma
- adrenal adenoma
- adrenocortical carcinoma
- phaeochromocytoma
- adrenal dermoid cyst 4
Others
-
Addison disease
- uncommon in primary Addison disease; calcification suggests an underlying cause (e.g. infection)
- Wolman disease
Radiographic features
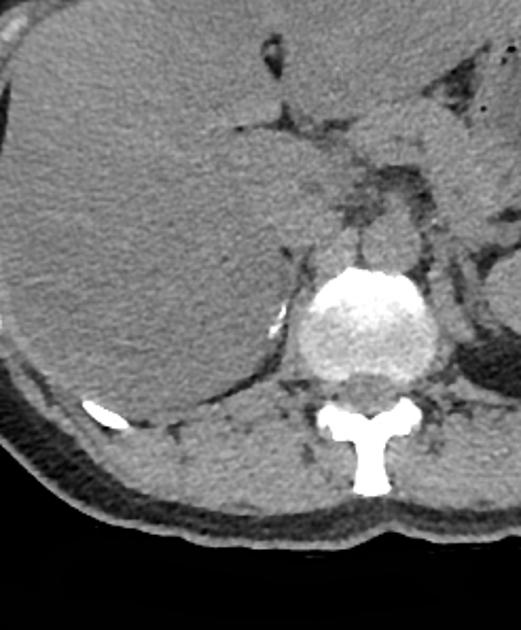
Adrenal calcification is best assessed on CT where it can be differentiated from a calcified adrenal mass or lesion. CT also allows simultaneous characterisation of any underlying lesions with size, density, enhancement, and washout.
In children, neuroblastoma has been reported as the commonest calcifying adrenal mass 4. In adults, simple calcified cysts have been reported as common adrenal masses, characteristically showing peripheral curvilinear calcification.
Post-haemorrhage calcification is usually seen after the initial adrenal haematoma has resolved and, hence, is not usually seen with an adrenal lesion. However, adrenal metastases such as from bronchogenic tumours can present with haemorrhage, making the diagnosis challenging.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.