Amyloidosis (plural: amyloidoses) is a heterogeneous disease, or even considered a constellation of diseases, resulting in the deposition of relatively similar proteins. It has many causes and can affect any organ system.
On this page:
Epidemiology
The disease may have a male predilection. It typically affects middle-aged individuals around 60 years 5.
Associations
multiple myeloma: with primary amyloidosis ref
Clinical presentation
Given the wide variety of clinical forms of amyloidosis, the potential spectrum of symptoms and signs is extremely broad and can present in almost any way ref. Carpal tunnel syndrome may be the first presentation of amyloidosis 10.
Pathology
Amyloid comprises a group of proteins characterised by certain physical properties. At least 15 amyloid proteins are derived from diverse precursors. Some demonstrate the structural morphology of immunoglobulins ref.
Subtypes
primary amyloidosis: associated with monoclonal plasma cell dyscrasias
-
secondary amyloidosis: usually occurs secondary to a tissue-destructive and inflammatory process
hereditary amyloidosis: can be seen with familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)
senile amyloidosis
localised amyloidosis: sometimes classified as a separate entity with the above four accounting for the systemic forms
dialysis-related amyloidosis 7: can occur with either haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis
In certain scenarios, the amyloid proteins are produced and deposited locally, whereas in others, the protein is distributed systemically.
Systemic amyloidosis
The majority occur in the systemic form ref:
-
synthesised by plasma cells, and seen in conditions with monoclonal proliferation of these cells
-
AA (amyloid associated)
derived from SAA (serum amyloid A) protein which is synthesised by the liver and forms part of the HDL3 lipoproteins
typically seen in chronic inflammatory disease or familial Mediterranean fever
-
Aß2M (amyloid ß2-microglobulin)
derived from ß2-microglobulin
seen in patients on haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis
hereditary (AApoA1) (apolipoprotein)
hereditary (AFib) (mutant fibrinogen)
hereditary (ALys) (lysozyme)
-
seen in senile systemic amyloidosis/neuropathic cerebral angiopathy
is the most common form of familial amyloidosis 5
Localised amyloidosis
Accounts for ≈15% of amyloidosis ref:
A4ß2 (beta-amyloid protein): seen in Alzheimer disease
AANF (atrial natriuretic factor): isolated atrial amyloidosis
AIAPP (islet amyloid peptide): deposited in the pancreas in patients with type II diabetes mellitus
ACal: seen in medullary islet cell tumour
Finnish-type (AGel) (Gelsolin); lattice dystrophy of the cornea, corneal neuropathy
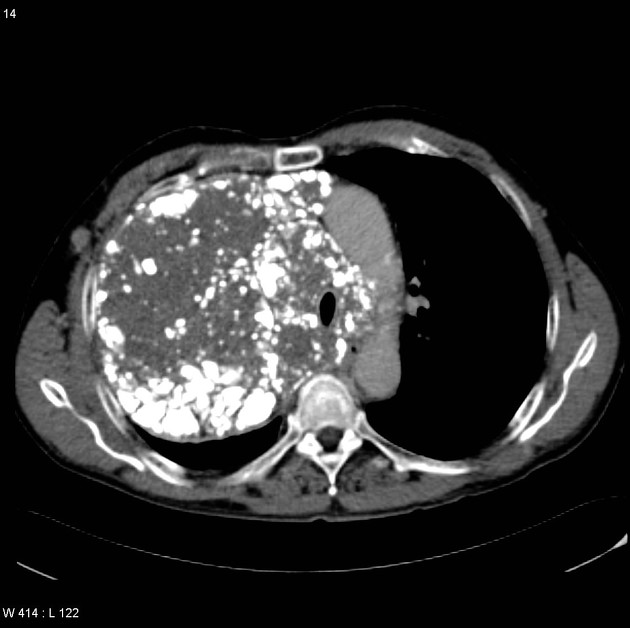
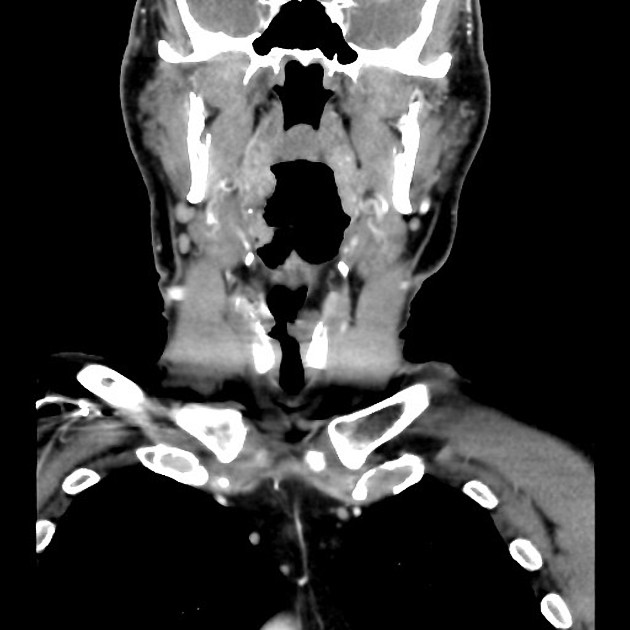
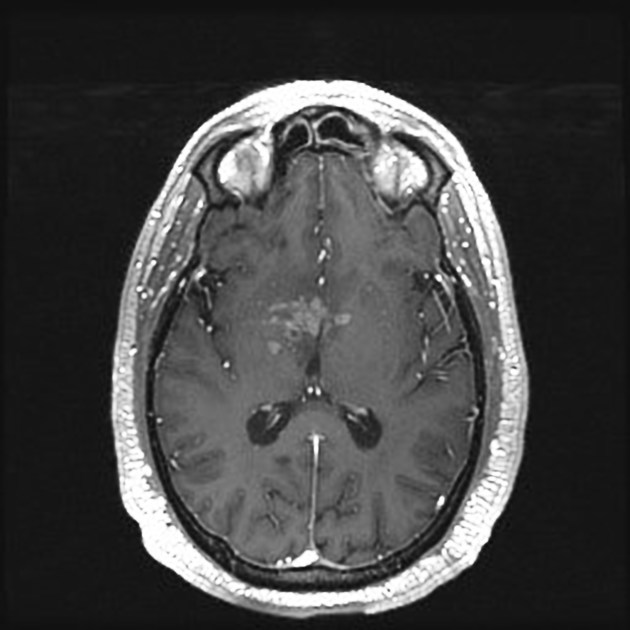
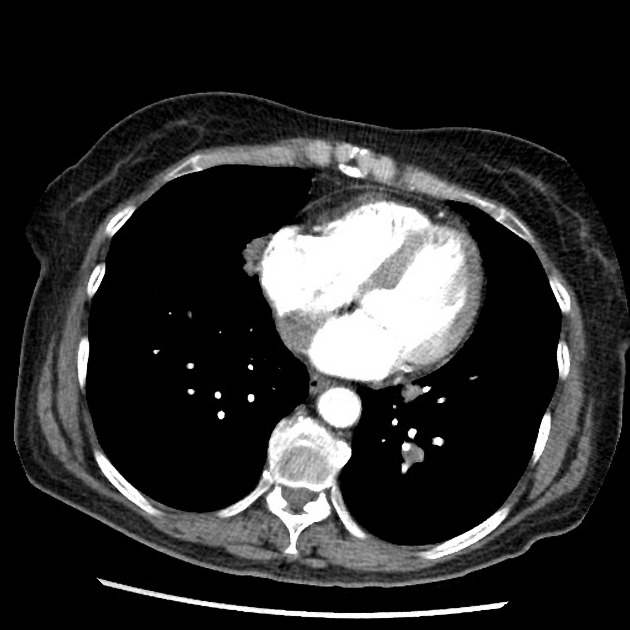
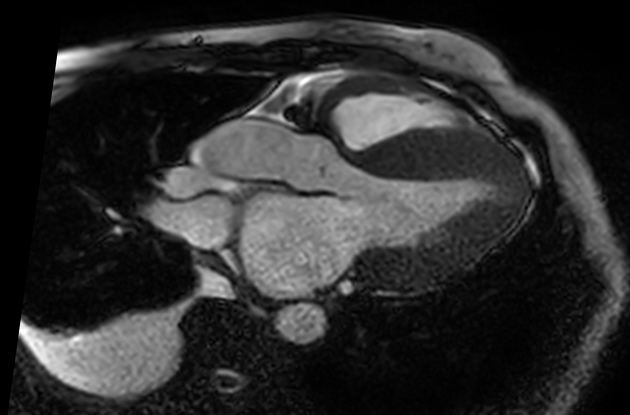
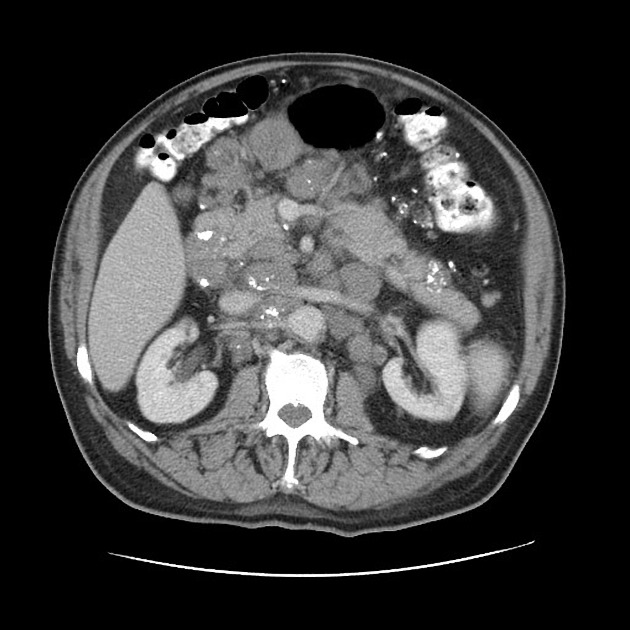
Organ-specific amyloidosis
Amyloid deposition can occur in any part of the body, although some are more common and have specific imaging findings. These conditions are best discussed separately:
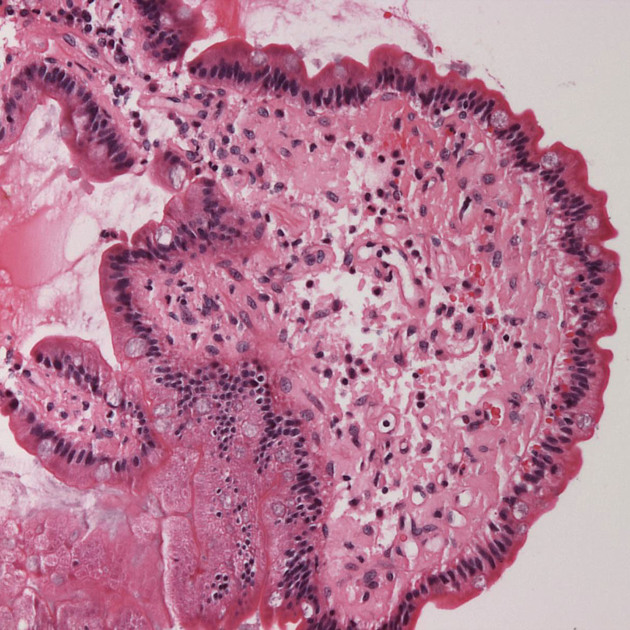
Microscopic appearance
Amyloid is an insoluble extracellular proteinaceous substance composed of cross-ß-pleated sheets which display apple-green birefringence when viewed under polarised light after being treated with Congo red stain 1.
History and etymology
The word “amylon” was first used in 1834 by the German botanist Matthias Schleiden to describe the waxy starch in plants ref. Rudolph Virchow then coined the word “amyloid” in 1854 to describe tissue deposits that stained like cellulose when exposed to iodine ref.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.