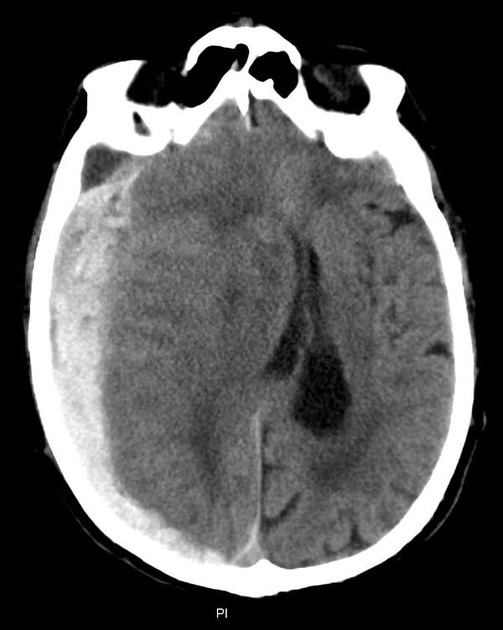
Brain herniation, also referred to as acquired intracranial herniation, refers to the shift of brain tissue from its normal location, into an adjacent space as a result of mass effect. It is a life-threatening condition that requires prompt diagnosis.
Pathology
Several different patterns of brain herniation describe the type of herniation occurring:
transalar herniation: ascending and descending
-
downward: uncal herniation and central herniation
herniation into dural venous sinuses, brain herniation into arachnoid granulation (BHAG)
Aetiology
Any intracranial mass can have this effect:
-
cerebral swelling
peritumoural or periabscess oedema
-
tumours











 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.