Calcaneal apophysitis, also known as Sever disease, is the painful inflammation of the apophysis of the calcaneus.
On this page:
Epidemiology
It typically presents in active young children and adolescents, especially those who enjoy jumping and running sports.
Associations
High plantar foot pressures are associated with Sever disease, although it is unclear whether they are a predisposing factor or a result of the condition. Gastrocnemius equinus may be a predisposing factor for Sever disease 7.
Clinical presentation
Patients present with posterior heel pain that is aggravated by physical activity such as walking, running, or jumping.
Pathology
The condition is thought to result from repetitive microtrauma to the growth plates of the calcaneus. Obesity and high activity levels have been demonstrated as risk factors for Sever disease, but the literature is conflicting as no association with BMI, and association with low activity levels, have been demonstrated in other studies 6,15-17.
Radiographic features
Sever disease is most often diagnosed clinically, and radiographic evaluation is believed to be unnecessary by many physicians, but if a diagnosis of calcaneal apophysitis is made without obtaining radiographs, a lesion requiring more aggressive treatment could be missed 4.
Plain radiograph
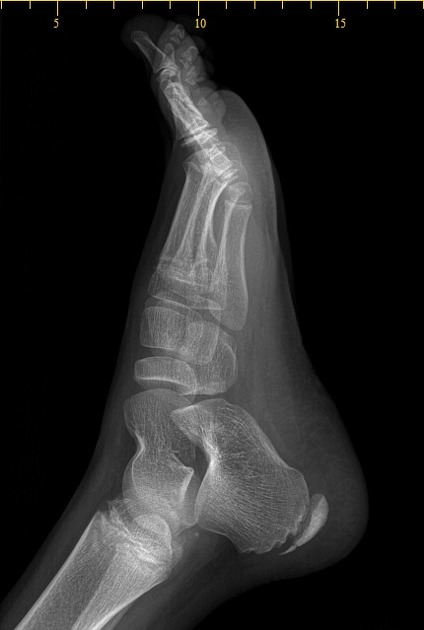
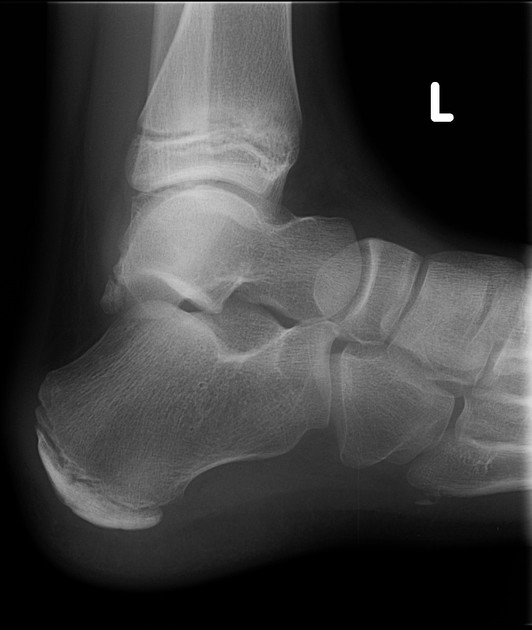
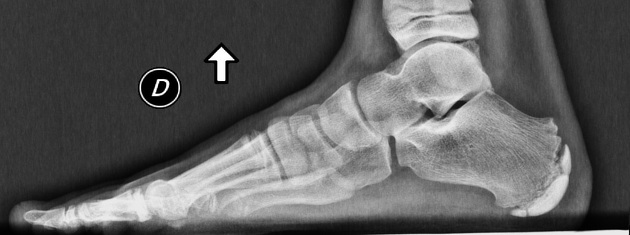
Foot radiographs are usually normal and the radiological identification without clinical information is not reliable 9. When present, the radiological signs, albeit nonspecific, are:
increase in the density of the calcaneal apophysis
fragmentation of the apophysis
Ultrasound
If unilateral may show asymmetrical thickening and in some cases may be associated with a retrocalcaneal bursitis 12. Fragmentation of the apophysis (with a saw teeth appearance) may be visible on ultrasound at times.
MRI
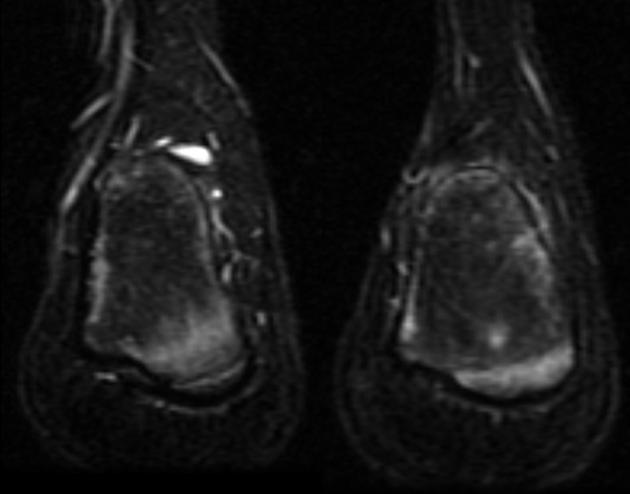
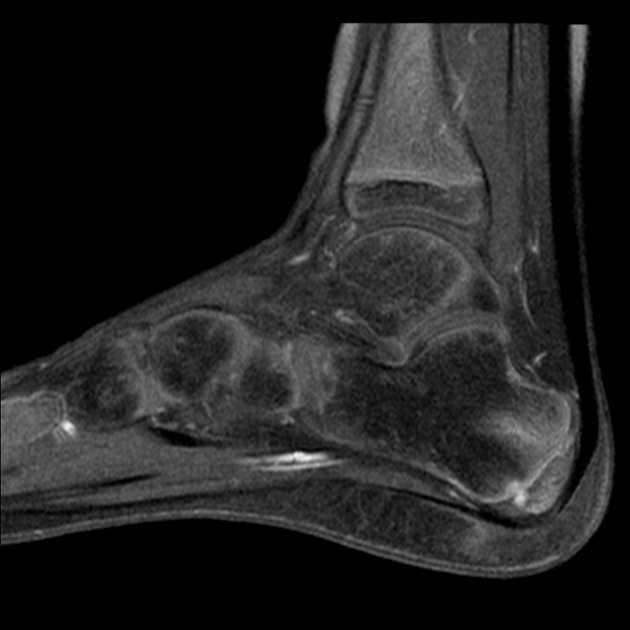
MRI is considered most accurate imaging examination method in assessing damage of the apophysis 13. This may show edematous changes within the calcaneal apophysis, possibly extending into the adjacent calcaneal tuberosity 10. MRI may also show a retrocalcaneal bursal effusion 13.
Treatment and prognosis
The condition is self-limiting with a brief limitation of activity sometimes being advocated. Standard advice is to reduce physical activity 8.
History and etymology
It is named after James Warren Sever (1878-1964), an American orthopedic surgeon, who first described it in 1912 1,11.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.