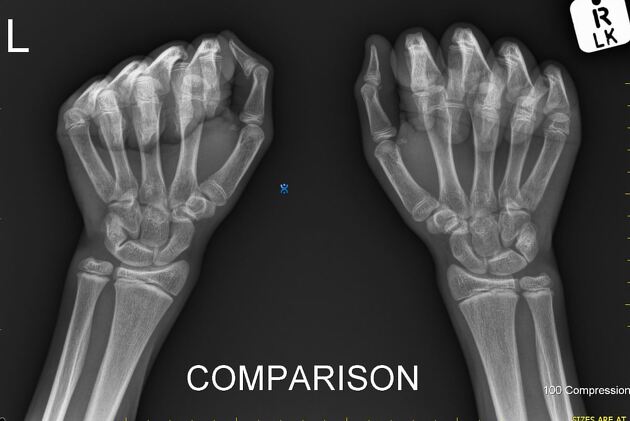
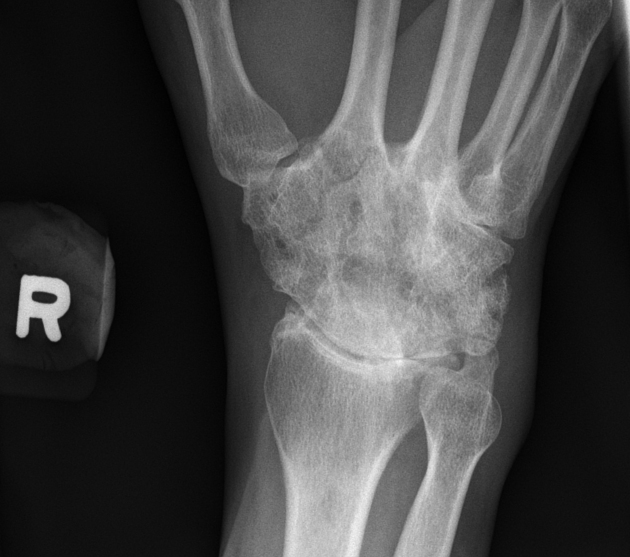
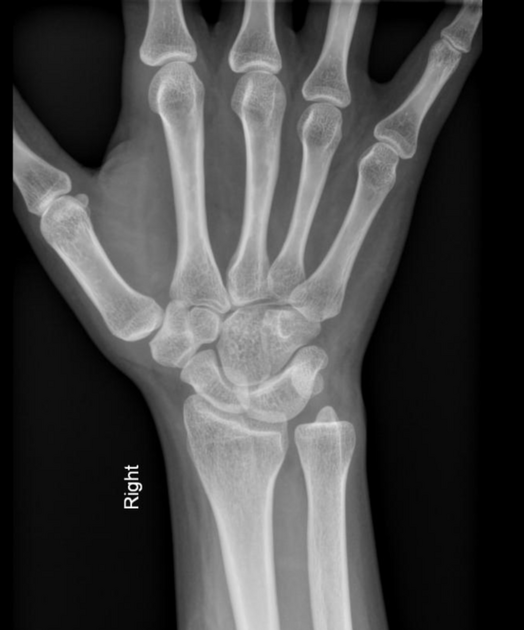
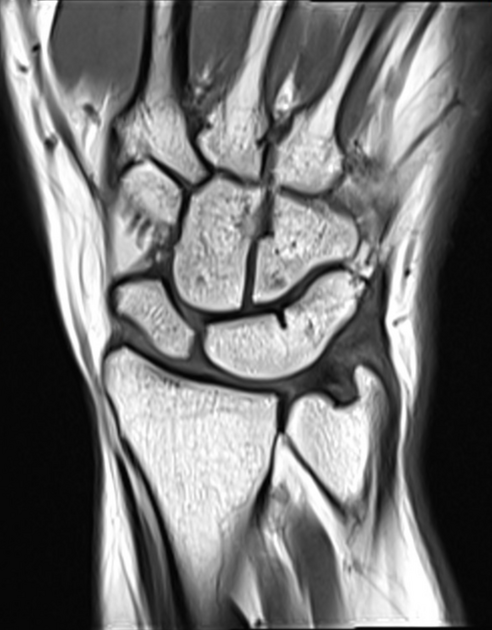
Carpal coalition
Updates to Article Attributes
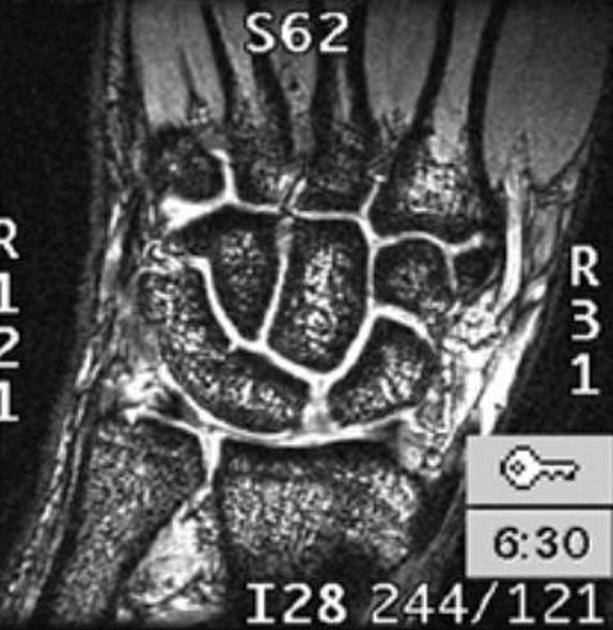
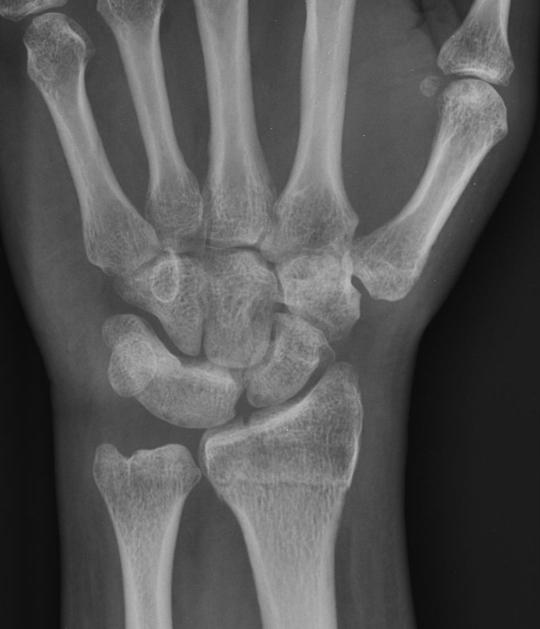
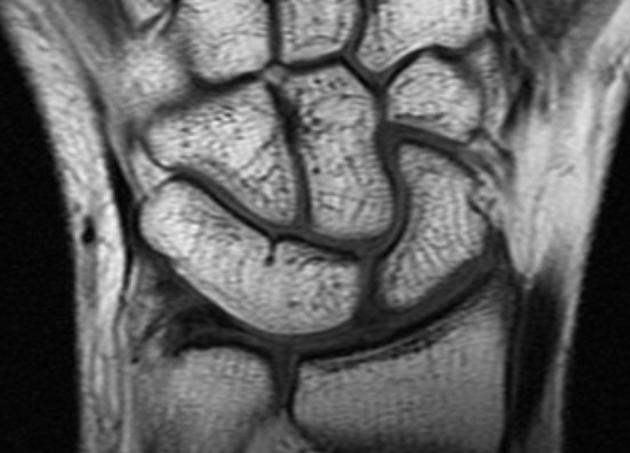
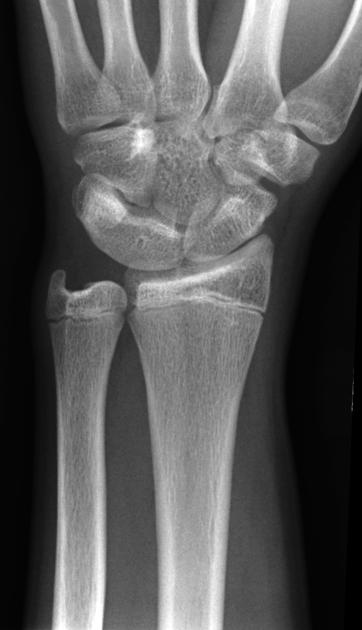
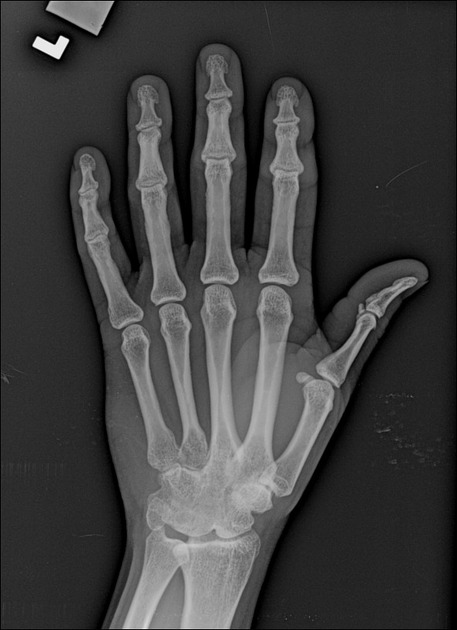
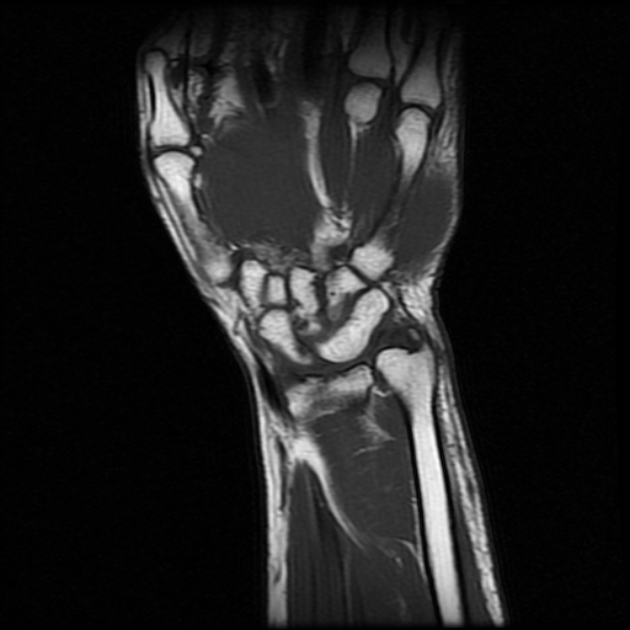
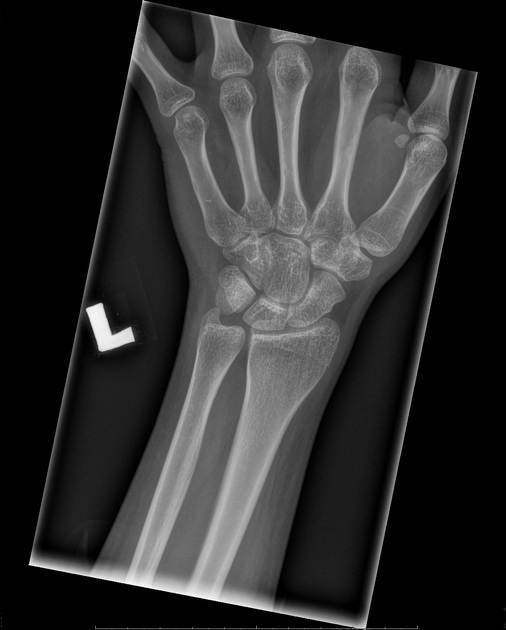
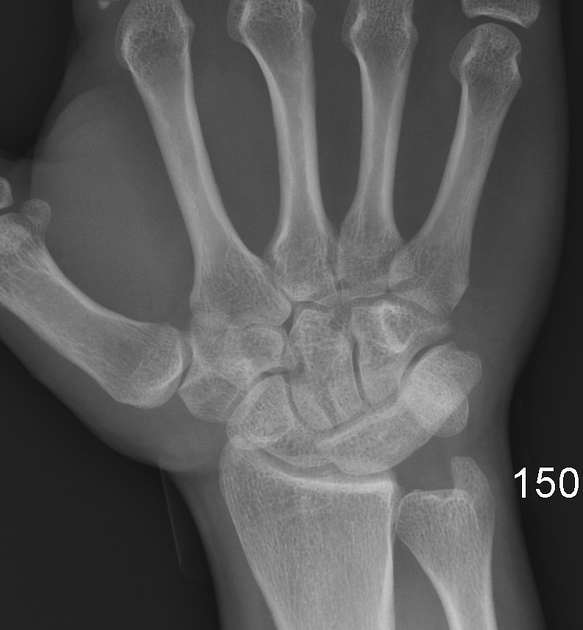
Carpal coalition refers to fusion of two or more carpal bones, and although the most commonly involved bones are the lunate and triquetrum, most combinations of adjacent bones can be found to be coalesced.
Epidemiology
The estimated prevalence is ~0.1% in Caucasian Americans and ~1.5% in African Americans, and it tends to affect women more commonly 1-2.
EtiologyPathology
Aetiology
Non-syndromatic congenital carpal coalition is transmitted via a mendelian inheritance pattern. Acquired intercarpal fusion can either be a consequence of an inflammatory arthropathy (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis) or injury, or due to surgical arthrodesis.
Pathology
Types
- luno-triquetral coalition (most common)
- capito-hamate coalition
Associations
There are several associated conditions, especially with multiple coalitions:





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.