Carpal tunnel
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Matthew Jarvis had no recorded disclosures.
View Matthew Jarvis's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
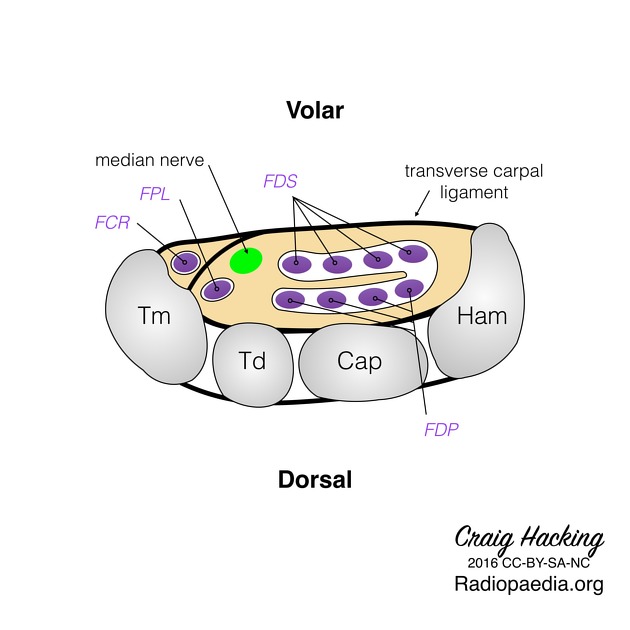
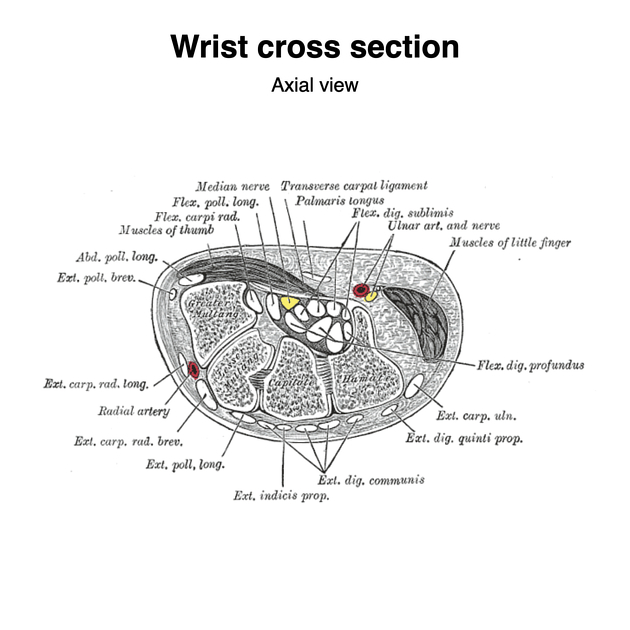
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresThe carpal tunnel is a fibro-osseous canal in the anterior (volar) wrist that acts as a passageway for structures between the anterior forearm and the hand.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Boundaries
- superficial border (roof): flexor retinaculum
- deep border (floor): carpal groove (formed by palmar aspect of carpal bones)
- medial/ulnar border: lateral surface of hamate
- lateral/radial border: medial surface of trapezium
Attachments
- medial/ulnar: pisiform bone and hook of hamate
- lateral/radial: scaphoid tubercle and ridge of trapezium
Contents
The carpal tunnel contains the following structures, from superficial to deep:
- flexor digitorum superficialis tendons (four) (with middle and ring finger more superficial to the index and little finger)
- median nerve (laterally)
- flexor pollicis longus tendon (laterally)
- flexor digitorum profundus tendons (four)
Note, the flexor carpi radialis is often wrongly stated to be within the carpal tunnel. Its course is in fact between the superficial and deep layers of the flexor retinaculum itself within its own compartment.
The tendons within the carpal tunnel are surrounded by synovial sheaths: one which envelops the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus together, and a separate sheath for the flexor pollicis longus.
Onto the surface of the medial aspect is formed the Guyon's canal through which runs the ulnar nerve and artery (ulnar nerve more medial), superficial to the tunnel. More laterally, the palmaris longus is attached to the superficial surface. The palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve runs superficial.
Variant anatomy
Variant anatomical structures within the carpal tunnel 2:
- persistent median artery of the forearm
- bifid median nerve
- presence of the motor branch of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel
- presence of palmaris longus tendon within the carpal tunnel
Related pathology
References
- 1. Buchberger W. Radiologic imaging of the carpal tunnel. Eur J Radiol. 1997;25 (2): 112-7. Pubmed citation
- 2. Presazzi A, Bortolotto C, Zacchino M et-al. Carpal tunnel: Normal anatomy, anatomical variants and ultrasound technique. J Ultrasound. 2011;14 (1): 40-6. doi:10.1016/j.jus.2011.01.006 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis muscle
- Ultrasound of the wrist
- Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
- Carpal tunnel syndrome causes (mnemonic)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Scaphoid
- Flexor retinaculum (wrist)
- Supracondylar spur
- Recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome
- Bifid median nerve
- Persistent median artery of the forearm
- Flexor carpi radialis tendon tunnel
- Flexor carpi radialis muscle
- Flexor pollicis longus muscle
- Smith fracture
- Median nerve
- Zone classification of flexor tendon injury
- Flexor digitorum profundus muscle
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery
- Trifid median nerve
- Normal carpal tunnel US
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Acute carpal tunnel syndrome due to foreign body
- Carpal tunnel (diagram)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Reversed palmaris longus muscle
- Median nerve traumatic neuroma - wrist
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Wrist cross section diagrams (Gray's illustrations)
- Wrist laceration (ultrasound)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome - postoperative ultrasound
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery
- Giant cell tumour of the tendon sheath
- Carpal tunnel syndrome and De Quervain tenosynovitis
- Self-inflicted wrist injury (ultrasound)
- Thrombosis of persistent median artery
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Carpal tunnel syndrome - with inverted notch sign
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centres
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centres
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centres
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.