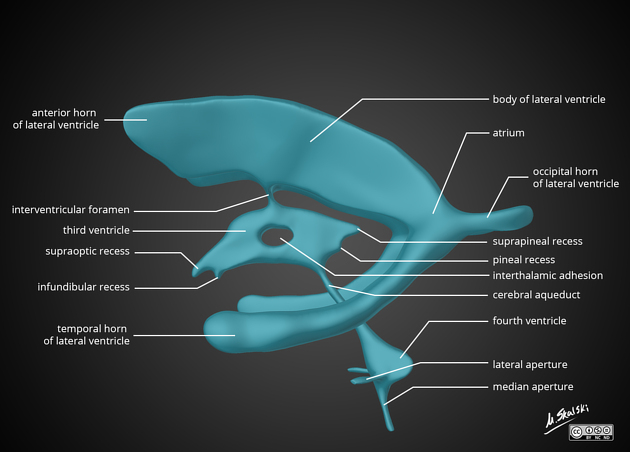
Cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures- Central aqueduct (of Sylvius)
- Aqueduct of Sylvius
- Cerebral aqueduct
The cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius) is the structure within the brainstem that connects the third ventricle to the fourth.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The cerebral aqueduct is located within the midbrain, connecting the third and fourth ventricles and surrounded by periaqueductal grey matter (PAG), with the tectum of the midbrain located posteriorly and the tegmentum anteriorly. It is roughly 1-2 mm in diameter, with common descriptions separating it into pars anterior, an antrum and pars posterior.
It is filled with CSF, and its obstruction leads to obstructive hydrocephalus with dilatation of the lateral and third ventricles.
History and etymology
Franciscus Sylvius (1614-1672) was a Dutch physician and anatomist, after which the duct of Sylvius and the Sylvian fissure are eponymously named.
Related pathology
See also
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Susan Standring. Gray's Anatomy. (2020) ISBN: 9780702077050 - Google Books
- 2. Michael Schünke, Erik Schulte, Udo Schumacher et al. Thieme Atlas of Anatomy. (2010) ISBN: 9781604062908 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Third ventricle
- Third ventriculostomy
- Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
- Chiari II malformation
- Rhomboid fossa (brainstem)
- Ascending transtentorial herniation
- Ciliary muscle
- Central nervous system embryology
- Periaqueductal grey matter
- Sagittal midline of the brain (an approach)
- Kinked brainstem
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (A)
- Posterior commissure
- Central herniation
- Rosette-forming glioneuronal tumour
- Fourth ventricle
- Tegmentum
- Velocity encoding
- Papillary tumour of the pineal region
- Pineal cyst
- Ruptured basilar tip aneurysm
- Pineal region glioblastoma IDH-wildtype
- Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS)
- Obstructive hydrocephalus
- Lissencephaly type II
- Dandy-Walker malformation with callosal dysgenesis
- Meningioma - pineal region
- Supratentorial ependymoma
- Aqueduct stenosis with spontaneous 3rd ventriculostomy
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus
- Bilateral temporal arachnoid cysts type III
- Dandy-Walker malformation
- Aqueductal web
- Triventricular hydrocephalus due to aqueductal web
- Vein of Galen malformation (adult presentation)
- Aqueductal stenosis due to membranous occlusion
- Arachnoid cyst with secondary obstructive hydrocephalus
- Brain ventricle anatomy (illustration)
- Ependymoma - MRS
- Superior medullary velum
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.