Cingulate gyrus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Julian Maingard had no recorded disclosures.
View Julian Maingard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Cingulate gyri
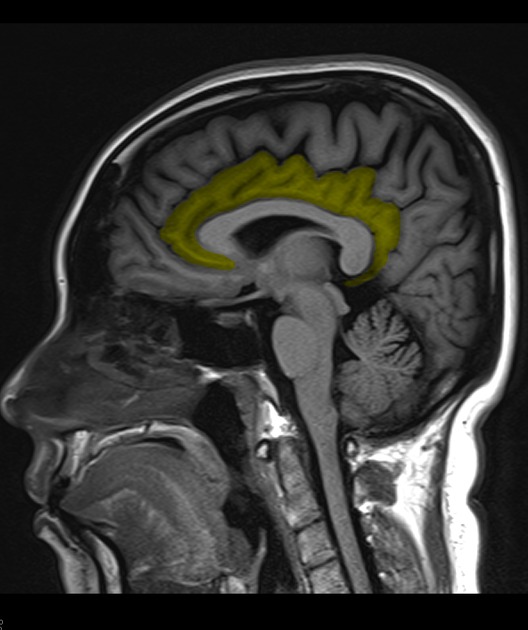
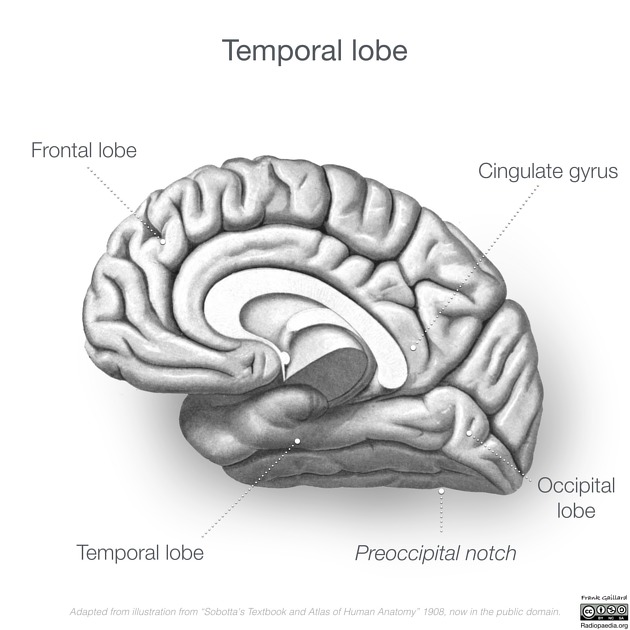
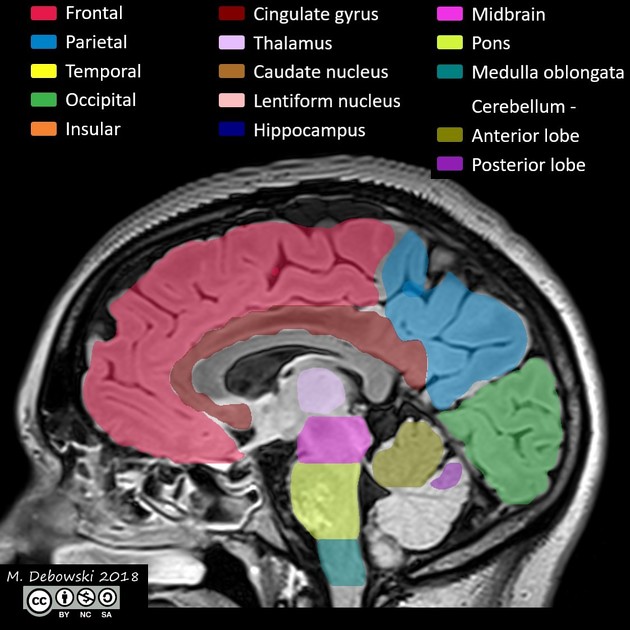
The cingulate gyrus lies on the medial aspect of the cerebral hemisphere. It forms a major part of the limbic system which has functions in emotion and behaviour. The frontal portion is termed the anterior cingulate gyrus (or cortex) 1,2.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Location
The cingulate gyrus extends from the subcallosal gyrus in the frontal lobe anteriorly to the isthmus posteriorly. It follows the superior convexity of the corpus callosum separated from it by the callosal sulcus 1,3.
The anterior portion lies inferior to the medial frontal gyrus separated from it by the cingulate sulcus. The most anterior portion ends below the rostrum of the corpus callosum 1,3.
The middle and most horizontal portion lies inferior to the paracentral lobule separated from it by the cingulate sulcus 1,2.
Its posterior portion (posterior cingulate gyrus) lies inferior to the precuneus separated from it by the subparietal sulcus. Connections between the precuneus and cingulate gyrus are anterior and posterior to this sulcus. The posterior cingulate gyrus and isthmus lie anterior to the occipital lobe separated from it by the parieto-occipital sulcus 1,3.
Arterial supply
It receives vascular supply from the pericallosal arteries, which are branches of the anterior cerebral artery 4.
Related pathology
The cingulate cortex is part of the limbic system and there is evidence that it has a role in emotion, attention and social behaviour 5,6. Cingulate volumetric size and activity may predict response to electroconvulsive therapy for mood disorders 7,8, and abnormalities have been described in schizophrenia 9.
Cingulate gyrus epilepsy can occur but is rare condition. Given the location of the cingulate gyrus, seizures can spread to temporal, frontal, or motor areas, resulting in a diverse range of symptoms 10-12.
anterior cingulate seizures typically present with emotional manifestations (e.g. fright, screaming, aggressive behaviour, laughter), gestural automatisms, hypermotor activity, autonomic changes (e.g. bradycardia), and ictal pouting (a downturned mouth) 10-12
posterior cingulate seizures often mimic temporal lobe seizures and may present with abdominal/gustatory auras, déjà vu, and impaired awareness, as well as bilateral tonic and hypermotor seizures 10-12
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Tamraz J, Comair Y. Atlas of Regional Anatomy of the Brain Using MRI. Springer. ISBN:3540640991. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Schuenke M, Schulte E, Schumacher U et-al. Head and Neuroanatomy. Thieme. ISBN:1604062908. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Singh. Textbook of Anatomy with Colour Atlas. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. ISBN:8180618331. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Henry Gray, Roger Warwick, Peter Llewellyn Williams. Gray's Anatomy. (1980) ISBN: 9780721691282
- 5. Hadland K, Rushworth M, Gaffan D, Passingham R. The Effect of Cingulate Lesions on Social Behaviour and Emotion. Neuropsychologia. 2003;41(8):919-31. doi:10.1016/s0028-3932(02)00325-1
- 6. Drevets W, Savitz J, Trimble M. The Subgenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Mood Disorders. CNS Spectr. 2008;13(8):663-81. doi:10.1017/s1092852900013754 - Pubmed
- 7. Redlich R, Opel N, Grotegerd D et al. Prediction of Individual Response to Electroconvulsive Therapy via Machine Learning on Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73(6):557. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0316 - Pubmed
- 8. Argyelan M, Lencz T, Kaliora S et al. Subgenual Cingulate Cortical Activity Predicts the Efficacy of Electroconvulsive Therapy. Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):e789. doi:10.1038/tp.2016.54 - Pubmed
- 9. Bersani F, Minichino A, Fojanesi M et al. Cingulate Cortex in Schizophrenia: Its Relation with Negative Symptoms and Psychotic Onset. A Review Study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(22):3354-67. - Pubmed
- 10. Yoshimoto A, Morikawa S, Kato E, Takeuchi H, Ikegaya Y. Top-Down Brain Circuits for Operant Bradycardia. Science. 2024;384(6702):1361-8. doi:10.1126/science.adl3353 - Pubmed
- 11. Powell R, Elwes R, Hamandi K, Mullatti N. Cingulate Gyrus Epilepsy. Pract Neurol. 2018;18(6):447-54. doi:10.1136/practneurol-2017-001812 - Pubmed
- 12. Mascia A, Quarato P, Sparano A et al. Cardiac Asystole During Right Frontal Lobe Seizures: A Case Report. Neurol Sci. 2005;26(5):340-3. doi:10.1007/s10072-005-0496-4 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Corpus callosum
- Callosal sulcus
- Telencephalon
- Limbic system
- Isthmus (disambiguation)
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Frontal lobe
- Precentral gyrus
- Brodmann areas
- Medial frontal gyrus
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Papez circuit
- Rostral gyrus
- Precuneus
- Polymicrogyria
- Paracentral lobule
- Limbic lobe
- Viking helmet appearance
- Subfalcine herniation
- Anterior cerebral artery
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.