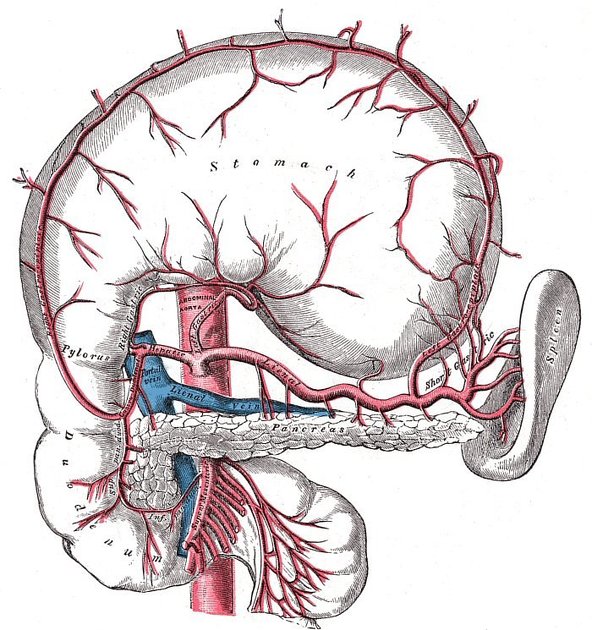
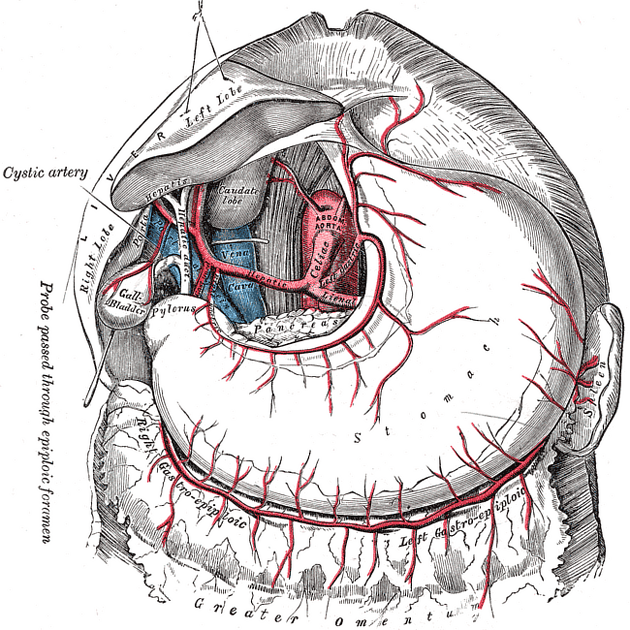
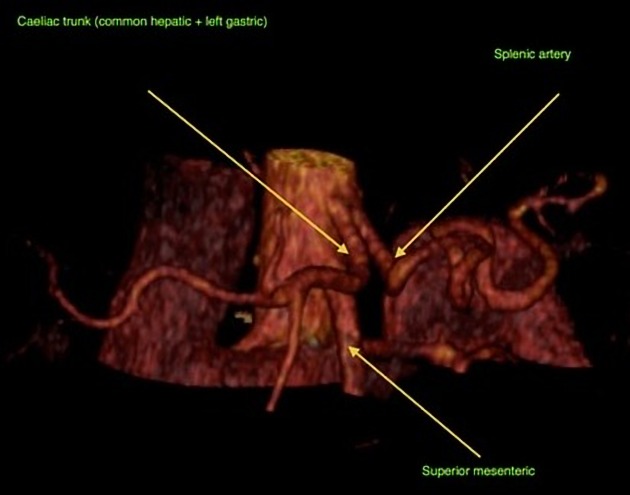
The coeliac artery, also known as the coeliac axis or coeliac trunk, is a major splanchnic artery in the abdominal cavity supplying the foregut. It arises from the abdominal aorta and commonly gives rise to three branches: left gastric artery, splenic artery, and common hepatic artery.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Origin
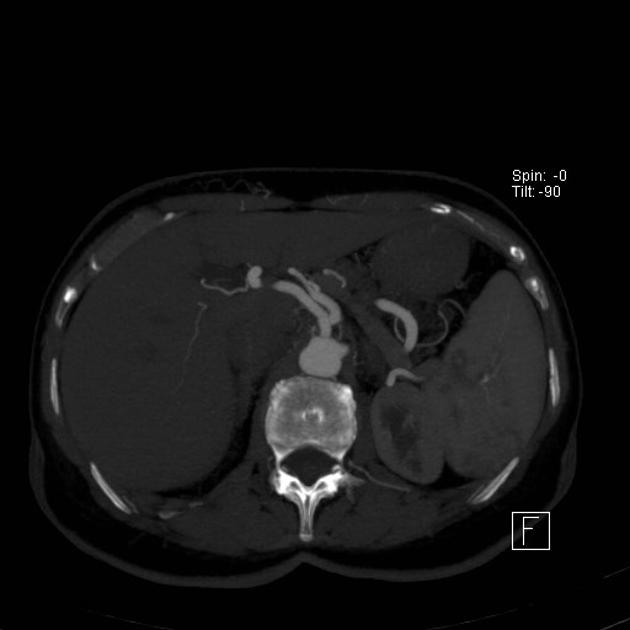
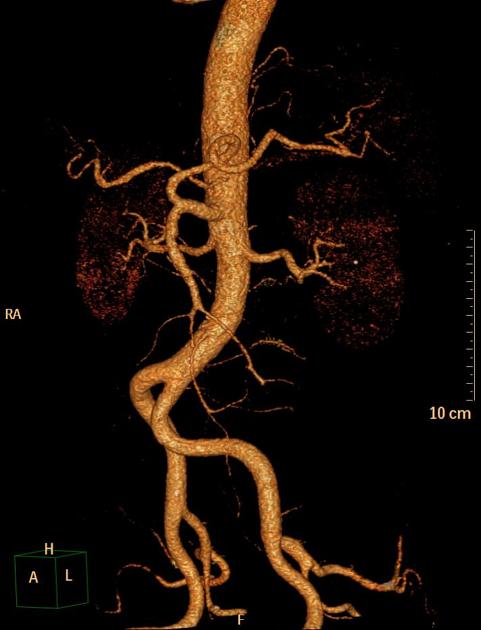
The coeliac artery arises anteriorly from the abdominal aorta just below the diaphragm at the T12 level, behind the median arcuate ligament, just as the aorta enters the abdomen in between the right and left crura. The coeliac ganglia and plexus surround the vessel at its origin.
Course
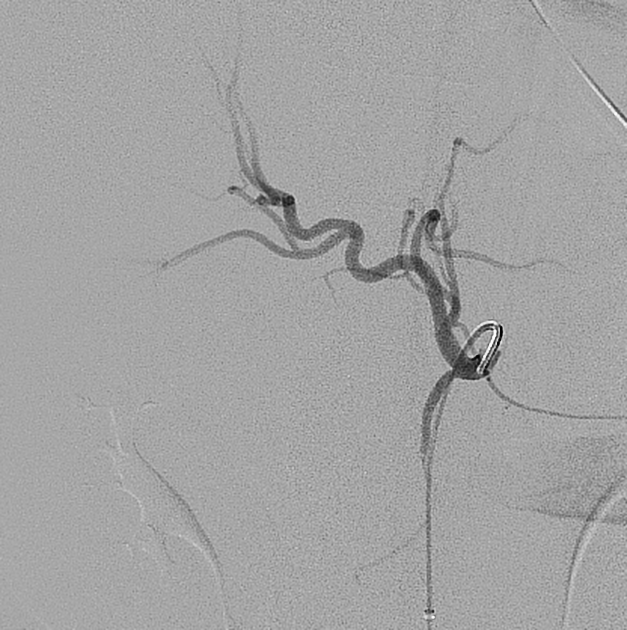
The coeliac artery is typically a short vessel that passes underneath the median arcuate ligament, often indented on its superior surface by this ligament, and then courses anteriorly or slightly anterolaterally in the lesser sac. It is surrounded by coeliac lymph nodes and the coeliac plexus. At the upper border of the pancreas, it divides into three branches: left gastric, splenic, and common hepatic arteries. The left gastric artery is usually the first branch, after which the coeliac artery bifurcates into the splenic artery (coursing to the left) and the common hepatic artery (coursing to the right).
Branches
Branching patterns
common trunk with bifurcation into the hepatosplenic trunk and left gastric artery: 50-76%
common trunk with trifurcation into the common hepatic artery, splenic artery and left gastric artery: 10-19%
quadrifurcating or pentafurcating trunk with the gastroduodenal artery, right and left hepatic arteries and dorsal pancreatic artery potentially originating from the trunk: 10% 4
Supply
The coeliac artery supplies the foregut, which is defined by the following structures 6:
gut from the distal oesophagus to the ampulla of Vater of 2nd part of the duodenum
gallbladder and biliary tree
greater omentum
lesser omentum
Variant anatomy
Classic branching of the coeliac artery into the left gastric artery, splenic artery, and the common hepatic artery is seen in approximately 70%. Variations are present in approximately 30%. In general, any of the three coeliac branches may arise independently from the aorta or SMA (superior mesenteric artery), or the coeliac artery may give rise to other branches. A coeliacomesenteric trunk occurs when both the SMA and the coeliac trunk originate as a single trunk from the aorta.
Extra-coeliac origin of its three branches
From aorta
left gastric artery: 2-3%
splenic artery: <1%
common hepatic artery: 2%
From SMA
left gastric artery: extremely rare
splenic artery: <1%
common hepatic artery: 2%
Other branches that may arise directly from the coeliac artery
Variant origin
common origin of the coeliac artery and SMA (coeliacomesenteric trunk): <1%
Many branching variations of the second and third-order branches of the coeliac artery exist, particularly of the hepatic artery. These variations are discussed with the common hepatic artery.
History and etymology
The term "coeliac" is derrived from the Greek word "koilia", meaning "belly", in reference to the abdominal cavity 7.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.