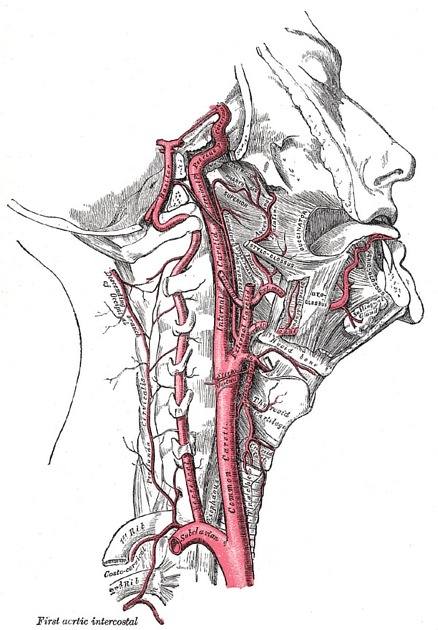
Common carotid artery
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Amir Mahmud had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Amir Mahmud's current disclosures- Common carotid arteries
- Common carotid artery (CCA)
- CCA (common carotid artery)
The common carotid arteries (CCA) are paired branchless arteries of the neck that supply blood to the head, face and neck. Each common carotid bifurcates into internal and external carotid arteries.
On this page:
Summary
-
origin:
left: branch of the aortic arch
right: branch of the brachiocephalic trunk
course: posterior to sternoclavicular joint, lateral to thyroid and trachea
main branches: none (usually)
termination: at the carotid bifurcation approximately at the C4 level to form the external and internal carotid arteries
key relationships: internal jugular vein and vagus nerve
Gross anatomy
Origin and course
Although the left and right common carotid arteries follow the same course through the neck, their origin differs.
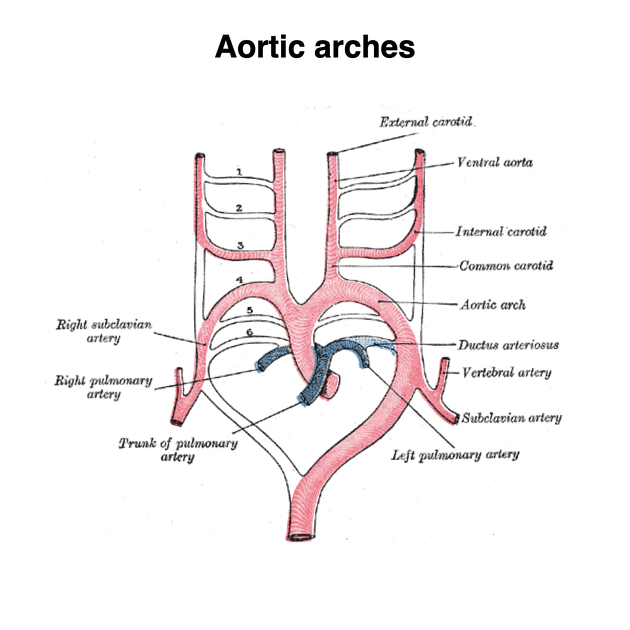
On the left, the CCA arises directly from the aortic arch whereas, on the right, the origin is from the brachiocephalic trunk 10. The left CCA can be thought of as having two distinct parts: thoracic and cervical. Since the right CCA arises cranially, it only really has a cervical portion.
In the thoracic portion, the left CCA ascends through the superior mediastinum to the level of the left sternoclavicular joint where it is continuous with the cervical portion.
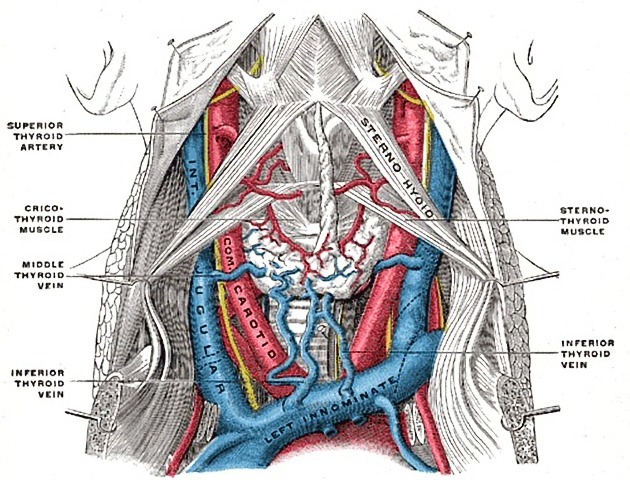
The cervical portion of both CCAs follows a similar course. Each vessel passes obliquely upwards from behind the sternoclavicular joint to the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, at approximately the C4 level 11. In the lower neck, the two CCAs are separated from each other by the trachea. However, as the carotids ascend in the neck, they diverge becoming separated by the thyroid gland, the larynx and pharynx.
The CCA is contained within the carotid sheath which is derived from all three layers of the deep cervical fascia. The carotid sheath also contains the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve: the vein lies lateral to the artery, with the nerve in between the two.
See article on Intima-media thickness (IMT) for normal dimensions of the CCA during sonographic assessment of the degree of atheromatous vascular disease.
Variant anatomy
vertebral artery arising from the CCA 7
left CCA arising from brachiocephalic artery, as in a bovine arch
-
single terminal branch
other branch arising directly from aorta
other branch absent
right CCA gives rise to thyroidea ima artery
History and etymology
The word carotid in the sense of a major neck artery was first recorded in English in 1667, and ultimately derives from the Greek word κάρος (karos) meaning stupor, as compression of the vessel induced "sleep" 8,9.
References
- 1. Gray's Anatomy. (2004) ISBN: 9780443071683 - Google Books
- 2. Michael Schünke. Thieme Atlas of Anatomy. (2007) ISBN: 9783131421210 - Google Books
- 3. Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. (1999) ISBN: 9780683061413 - Google Books
- 4. Mcminn. Last's Anatomy. (2003) ISBN: 9780729537520 - Google Books
- 5. Robert H. Whitaker, Neil R. Borley. Instant Anatomy. (2000) ISBN: 9780632054039 - Google Books
- 6. Paul Butler, Adam Mitchell, Jeremiah C. Healy. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9780521766661 - Google Books
- 7. R. Shane Tubbs, Mohammadali M. Shoja, Marios Loukas. Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. (2016) ISBN: 9781118430354 - Google Books
- 8. Barnhart, Robert K., Steinmetz, Sol.. Chambers Dictionary of Etymology. (1999) ISBN: 9780550142306 - Google Books
- 9. James Diggle. The Cambridge Greek Lexicon. (2021) ISBN: 9781108836982 - Google Books
- 10. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011) Page 43. ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
- 11. Michalinos A, Chatzimarkos M, Arkadopoulos N, Safioleas M, Troupis T. Anatomical Considerations on Surgical Anatomy of the Carotid Bifurcation. Anat Res Int. 2016;2016:6907472. doi:10.1155/2016/6907472 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Subclavian artery
- Third branchial cleft fistula
- Neck dissection classification
- Ansa cervicalis
- Interscalene brachial plexus block
- Longus colli muscle
- Blunt cerebrovascular injury
- Ultrasound assessment of carotid arterial atherosclerotic disease
- Carotid tubercle
- Macaroni sign (arteries)
- Middle thyroid vein
- Superior cervical ganglion
- Thoracic lymph node stations
- Lymph node levels of the neck
- Aortic arch
- Laryngeal carcinoma (staging)
- Bovine arch
- Carotid body
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (C)
- Vagus nerve
- Complete occlusion of left common carotid artery
- Acute submandibular abscess and unpaired anterior jugular vein
- Anomalous separate origins of the right internal and external carotid arteries from the innominate artery
- Situs ambiguus - left isomerism
- Bovine arch and kissing carotid arteries
- Aortic dissection with pulmonary artery intramural haematoma
- Anomalous origin of right vertebral artery from right common carotid artery
- Carotid artery development (Gray's illustration)
- Isolated primary intraventricular haemorrhage
- Double outlet right ventricle
- Stanford type A aortic dissection
- Aortic dissection - Stanford type B
- Incomplete double aortic arch with Kommerell diverticulum
- Thymoma - stage 1 of Masaoka staging system
- Aortic dissection - Stanford type A
- Ascending pharyngeal artery arising from internal carotid artery
- MRA neck (quiz)
- Great vessels (Gray's illustration)
- Normal carotid Doppler ultrasound
- Interrupted aortic arch (type A1)
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.