Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Weerakkody Y, Hacking C, Alsmair A, et al. Cowper duct syringocele. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 27 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-52717
Cowper duct syringocele refers to cystic dilatation of the main duct of the bulbourethral (Cowper) glands.
Affected patients may present with postvoid dribbling, urinary frequency, weak stream, or hematuria.
Four groups of syringoceles have been described 2:
- simple syringocele
- minimally dilated duct
- most frequent
- perforate syringocele
- bulbous duct that drains into the urethra via a patulous ostium
- can appear as a diverticulum
- imperforate syringocele: bulbous duct that resembles a submucosal cyst and appears as a radiolucent mass
- ruptured syringocele: fragile membrane that remains in the urethra after a dilated duct ruptures
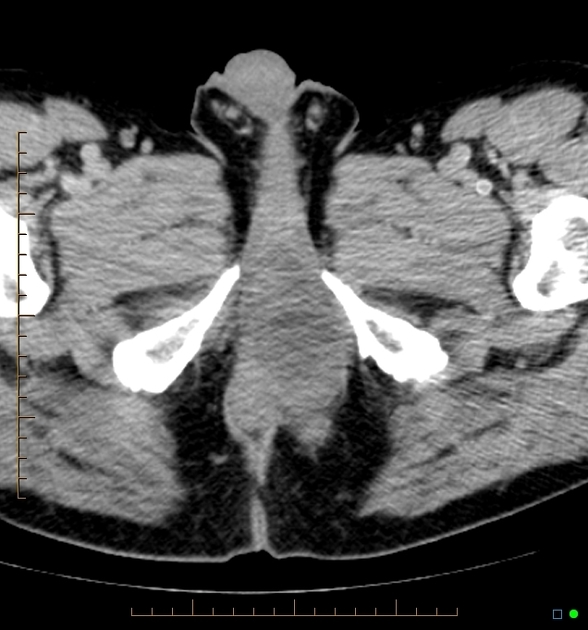
Ultrasound
May be seen a unilocular cystic lesion at the posterior or posterolateral aspect of the posterior urethra 8.
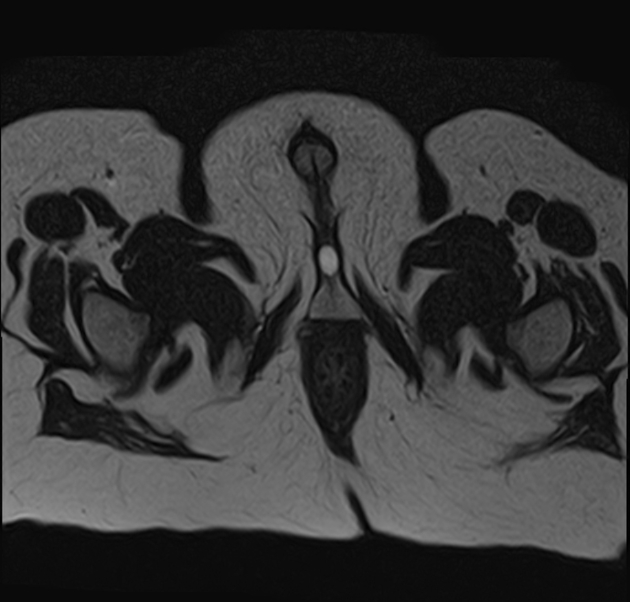
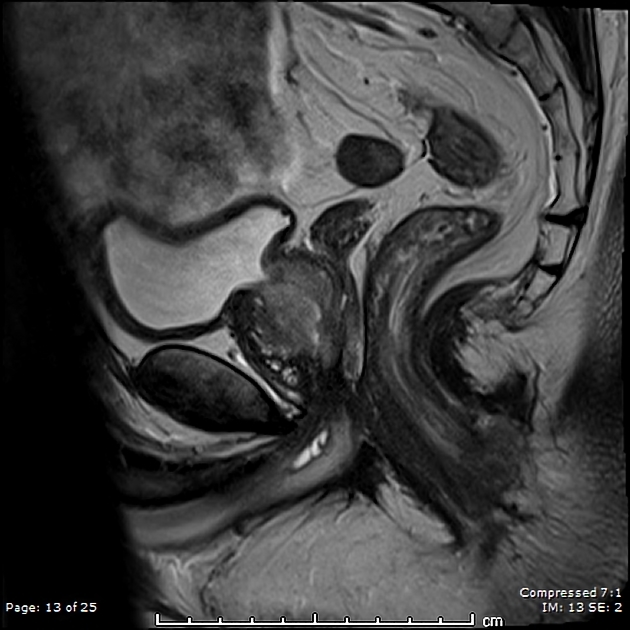
MRI
Usually seen as a midline oval structure at the penile base adjacent to the ventral aspect of the proximal bulbous urethra.
-
T1: low signal intensity
-
T2: high signal intensity
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment options include surgical incision of the obstructed duct (considered generally curative).
History and etymology
The Cowper glands and ducts were named for William Cowper (1666–1709), an English surgeon, who described the detailed anatomy of the bulbourethral glands in 1699. In actuality, the bulbourethral glands were first described by Jean Méry (1645– 1722), a French surgeon in 1684 11. To be fair to Cowper, he never claimed to have discovered his eponymous glands 11!
-
1. Pretorius E, Siegelman E, Ramchandani P, Banner M. MR Imaging of the Penis. Radiographics. 2001;21 Spec No(suppl_1):S283-98; discussion S298-9. doi:10.1148/radiographics.21.suppl_1.g01oc24s283 - Pubmed
-
2. Maizels M, Stephens F, King L, Firlit C. Cowper's Syringocele: A Classification of Dilatations of Cowper's Gland Duct Based Upon Clinical Characteristics of 8 Boys. J Urol. 1983;129(1):111-4. doi:10.1016/s0022-5347(17)51946-1 - Pubmed
-
3. Moskowitz P, Newton N, Lebowitz R. Retention Cysts of Cowper's Duct. Radiology. 1976;120(2):377-80. doi:10.1148/120.2.377 - Pubmed
-
4. Yaffe D & Zissin R. Cowper's Glands Duct: Radiographic Findings. Urol Radiol. 1991;13(2):123-5. doi:10.1007/BF02924604 - Pubmed
-
5. Bevers R, Abbekerk E, Boon T. Cowper's Syringocele: Symptoms, Classification and Treatment of an Unappreciated Problem. J Urol. 2000;163(3):782-4. doi:10.1016/s0022-5347(05)67803-2 - Pubmed
-
6. Melquist J, Sharma V, Sciullo D, McCaffrey H, Khan S. Current Diagnosis and Management of Syringocele: A Review. Int Braz J Urol. 2010;36(1):3-9. doi:10.1590/s1677-55382010000100002 - Pubmed
-
7. Türker Köksal I, Erdoğru T, Usta M, Ateş M, Baykara M. Unexpected Presentation of Syringocele. Acontractile Bladder. Urol Int. 2003;71(2):222-3. doi:10.1159/000071853 - Pubmed
-
8. Shebel H, Farg H, Kolokythas O, El-Diasty T. Cysts of the Lower Male Genitourinary Tract: Embryologic and Anatomic Considerations and Differential Diagnosis. Radiographics. 2013;33(4):1125-43. doi:10.1148/rg.334125129 - Pubmed
-
9. Selli C, Nesi G, Pellegrini G, Bartoletti R, Travaglini F, Rizzo M. Cowper's Gland Duct Cyst in an Adult Male. Radiological and Clinical Aspects. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1997;31(3):313-5. doi:10.3109/00365599709070358 - Pubmed
-
11. Ellis H. Two Eponymous Surgeons: William Cowper and François Poupart. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2009;70(4):225. doi:10.12968/hmed.2009.70.4.41627 - Pubmed
-
Kickuth R, Laufer U, Pannek J, Kirchner T, Herbe E, Kirchner J. Cowper's Syringocele: Diagnosis Based on MRI Findings. Pediatr Radiol. 2002;32(1):56-8. doi:10.1007/s00247-001-0580-8 - Pubmed
Promoted articles (advertising)





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.