Extrapontine myelinolysis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Venkatesh M, Campos A, Gaillard F, et al. Extrapontine myelinolysis. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 21 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-29460
rID:
29460
Article created:
26 May 2014,
Manchikanti Venkatesh
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Manchikanti Venkatesh had no recorded disclosures.
View Manchikanti Venkatesh's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures
Revisions:
12 times, by
9 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Synonyms:
- Extrapontine myelinolysis (EPM)
- Extrapontine demyelination syndrome
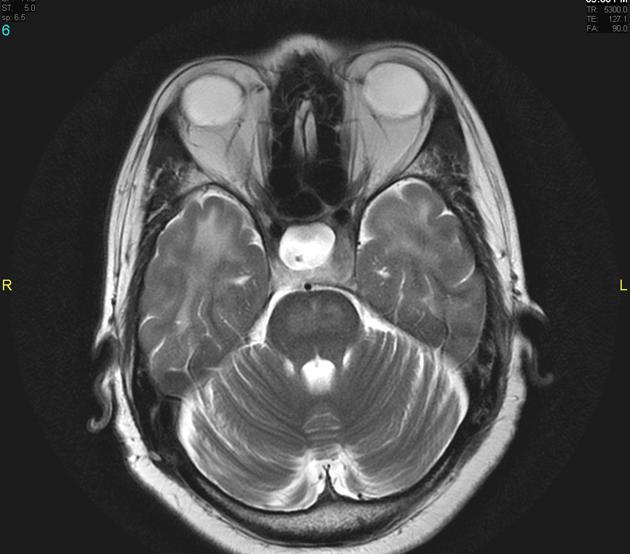
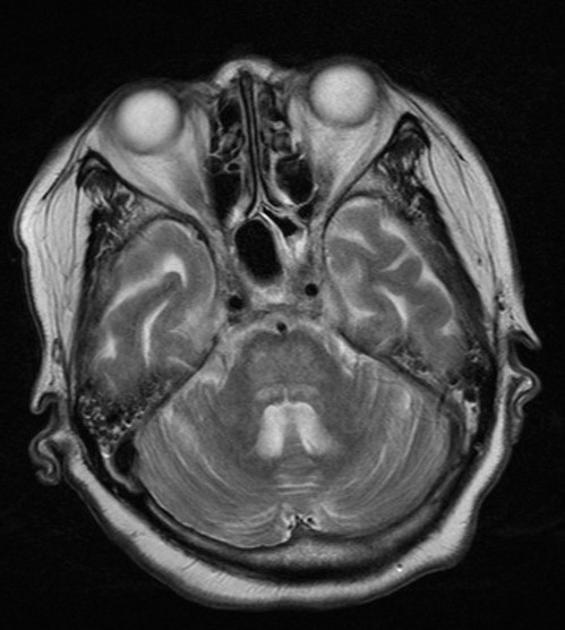
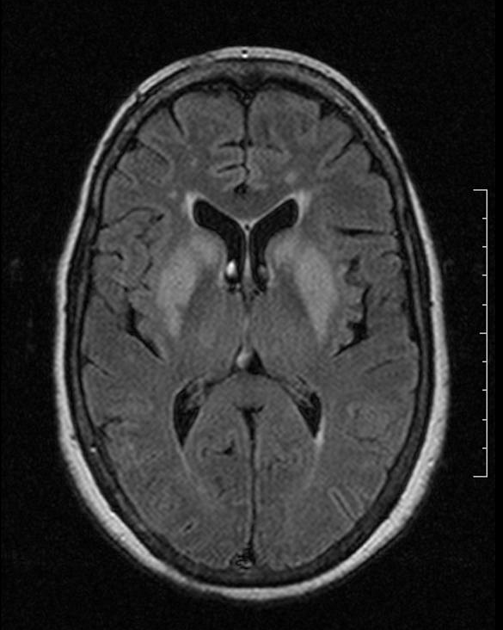
Extrapontine myelinolysis (EPM) is one of the complications occurring secondary to rapid correction of hyponatraemia, and is, along with central pontine myelinolysis encompassed by the term osmotic demyelination syndrome.
In the vast majority of cases, it is associated with central pontine myelinolysis but it can also (rarely) occur as an isolated entity.
Pathology
Location
In extrapontine myelinolysis, sites of involvement include:
ventrolateral thalami
grey-white matter junction
References
- 1. Martin R. Central Pontine and Extrapontine Myelinolysis: The Osmotic Demyelination Syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):iii22-8. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.045906 - Pubmed
- 2. Huin E, Tan KP. CT and MR findings in central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis-a study of two patients. Singapore Med J. 1997;37 (6): 622-6. Pubmed citation
- 3. Brown WD, Caruso JM. Extrapontine myelinolysis with involvement of the hippocampus in three children with severe hypernatremia. J. Child Neurol. 1999;14 (7): 428-33. Pubmed citation
- 4. Aralikatte O Saroja, Karkal R Naik, Rajendra V Mali, Sanjeeva R Kunam. 'Wine Glass' sign in recurrent postpartum hypernatremic osmotic cerebral demyelination. (2013) Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology. 16 (1): 106. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.107719 - Pubmed
- 5. Hornik A, Rodriguez Porcel F, Agha C et al. Central and Extrapontine Myelinolysis Affecting the Brain and Spinal Cord. An Unusual Presentation of Pancreatic Encephalopathy. Front Neurol. 2012;3:135. doi:10.3389/fneur.2012.00135 - Pubmed
- 6. Uchino A, Sawada A, Takase Y, Kudo S. Symmetrical Lesions of the Middle Cerebellar Peduncle: MR Imaging and Differential Diagnosis. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2004;3(3):133-40. doi:10.2463/mrms.3.133 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Articles:
- Basal ganglia and thalamus signal abnormalities
- Hyponatremia
- Central pontine myelinolysis
- Symmetrical cerebral restricted diffusion
- Bilateral middle cerebellar peduncle lesions
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Symmetrical cerebral T2 hyperintensities
- Basal ganglia T2 hyperintensity
- Osmotic demyelination syndrome
- Cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum (CLOCCs)
- Face of the giant panda sign (midbrain)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.