Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Radswiki T, Campos A, Jones J, et al. Fetal ascites. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 25 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-13408
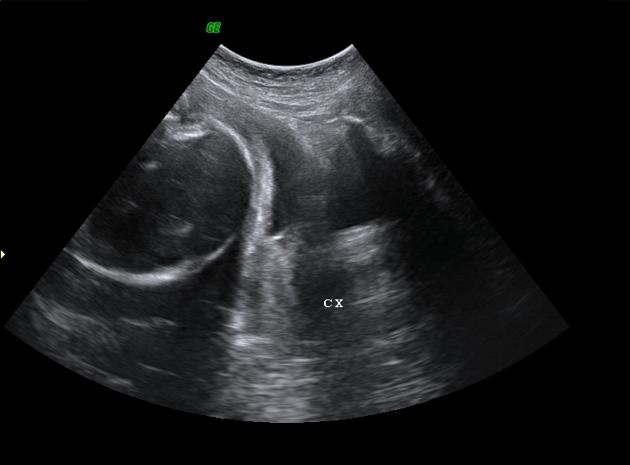
Fetal ascites refers to the accumulation of free fluid in the fetal abdomen. It is often considered under the same spectrum of hydrops fetalis.
Aetiology
Ultrasound
In the case of simple ascites, free anechoic fluid is seen within the fetal abdominal cavity.
General considerations include:
-
1. Hadlock F, Deter R, Garcia-Pratt J et al. Fetal Ascites Not Associated with Rh Incompatibility: Recognition and Management with Sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980;134(6):1225-30. doi:10.2214/ajr.134.6.1225 - Pubmed
-
2. Camanni D, Zaccara A, Capitanucci M et al. Isolated Fetal Ascites Secondary to Persistent Urogenital Sinus. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2009;2009:219010. doi:10.1155/2009/219010 - Pubmed
-
3. Eberhard Merz. Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. (2005) ISBN: 9781588901477 - Google Books
-
4. Michael Entezami. Ultrasound Diagnosis of Fetal Anomalies. (2004) ISBN: 9781588902122 - Google Books
-
5. Maurice M. Reeder. Reeder and Felson’s Gamuts in Radiology. (2006) ISBN: 9780387216867 - Google Books
-
6. Zelop C & Benacerraf B. The Causes and Natural History of Fetal Ascites. Prenat Diagn. 1994;14(10):941-6. doi:10.1002/pd.1970141008 - Pubmed
-
7. Nigam A, Kumar M, Gulati S. Fetal Ascites and Hydrometrocolpos Due to Persistent Urogenital Sinus and Cloaca: A Rare Congenital Anomaly and Review of Literature. BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014:bcr2013202231. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-202231 - Pubmed
Promoted articles (advertising)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.