Fetal death in utero
Updates to Article Attributes
Fetal death in utero (FDIU), also known as intrauterine death (IUD), is the term used when the death of a fetus occurs after the 20th week of pregnancy. Prior to this, it is considered a miscarriage.
Terminology
IUD is often also used as an abbreviation for an intrauterine contraceptive device. However, this shortening is disliked by some specialists in view of its use as an abbreviation for intrauterine death. Therefore for many the preferred abbreviation for an intrauterine contraceptive device is IUCD.
The spelling fetus and fetal are the preferred spellings in the medical world, regardless of location. They are used by virtually all biomedical journals. Therefore they are also the preferred spelling on Radiopaedia and we never use the spelling foetus or foetal (see fetus vs foetus for more detail) 3.
Epidemiology
1% of normal, uncomplicated pregnancies end in fetal death. In ~15% of fetal death in utero, no cause is identified.
Pathology
Aetiology
Maternal
gestational hypertension
blood group incompatibility
metabolic disorders
Fetal
major anomalies
umbilical cord complications (looping, knotting, twisting, straight cord)
Placental
Placental pathologies are thought represent the largest category of cause of intrauterine death 4.
Radiographic features
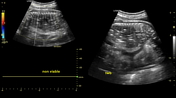
Ultrasound
absent fetal heartbeat
absent fetal movements
-
occasional findings
overlapping of skull bones (Spalding sign)
gross distortion of fetal anatomy (maceration)
soft tissue oedema: skin >5 mm
echogenic amniotic fluid (fetal demise fragments)
-
uncommon findings
thrombus in fetal heart
gas shadow in fetal heart (Robert sign)
See also
-<p><strong>Fetal death in utero (FDIU)</strong>, also known as <strong>intrauterine death</strong> (<strong>IUD</strong>), is the term used when the death of a fetus occurs after the 20<sup>th </sup>week of pregnancy. Prior to this, it is considered a <a href="/articles/miscarriage">miscarriage</a>.</p><h4>Terminology</h4><p>IUD is often also used as an abbreviation for an <a href="/articles/intrauterine-contraceptive-device-1">intrauterine contraceptive device</a>. However, this shortening is disliked by some specialists in view of its use as an abbreviation for intrauterine death. Therefore for many the preferred abbreviation for an intrauterine contraceptive device is IUCD. </p><p>The spelling fetus and fetal are the preferred spellings in the medical world, regardless of location. They are used by virtually all biomedical journals. Therefore they are also the preferred spelling on Radiopaedia and we never use the spelling foetus or foetal (see <a href="/articles/fetus-vs-foetus">fetus vs foetus</a> for more detail) <sup>3</sup>.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>1% of normal, uncomplicated pregnancies end in fetal death. In ~15% of fetal death in utero, no cause is identified.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><h5>Aetiology</h5><h6>Maternal </h6><ul>-<li><p>gestational hypertension</p></li>-<li><p>blood group incompatibility</p></li>-<li><p>metabolic disorders</p></li>-<li><p><a href="/articles/in-utero-infection">intrauterine infections</a></p></li>-</ul><h6>Fetal</h6><ul>-<li><p>major anomalies</p></li>-<li><p>umbilical cord complications (looping, <a href="/articles/umbilical-cord-knot">knotting</a>, <a href="/articles/umbilical-cord-entanglement">twisting</a>, <a href="/articles/straight-umbilical-cord-1">straight cord</a>)</p></li>-</ul><h6>Placental</h6><p>Placental pathologies are thought represent the largest category of cause of intrauterine death <sup>4</sup>.</p><ul>-<li><p><a href="/articles/placental-insufficiency">chronic placental insufficiency</a></p></li>-<li><p><a href="/articles/placental-abruption">placental abruption</a></p></li>-<li><p><a href="/articles/chorioamnionitis">chorioamnionitis</a></p></li>-</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>Ultrasound</h5><ul>-<li><p>absent <a href="/articles/fetal-heart-beat">fetal heartbeat</a></p></li>-<li><p>absent fetal movements</p></li>-<li>-<p>occasional findings</p>-<ul>-<li><p>overlapping of skull bones (<a href="/articles/spalding-sign-fetal-demise">Spalding sign</a>)</p></li>-<li><p>gross distortion of fetal anatomy (<a href="/articles/fetal-maceration">maceration</a>)</p></li>-<li><p>soft tissue oedema: skin >5 mm</p></li>-<li><p><a href="/articles/echogenic-amniotic-fluid">echogenic amniotic fluid</a> (fetal demise fragments)</p></li>-</ul>-</li>-<li>-<p>uncommon findings</p>-<ul>-<li><p>thrombus in fetal heart</p></li>-<li><p>gas shadow in fetal heart (<a href="/articles/roberts-sign-fetal-demise">Robert sign</a>)</p></li>-</ul>-</li>- +<p><strong>Fetal death in utero (FDIU)</strong>, also known as <strong>intrauterine death</strong> (<strong>IUD</strong>), is the term used when the death of a fetus occurs after the 20<sup>th </sup>week of pregnancy. Prior to this, it is considered a <a href="/articles/miscarriage">miscarriage</a>.</p><h4>Terminology</h4><p>IUD is often also used as an abbreviation for an <a href="/articles/intrauterine-contraceptive-device-1">intrauterine contraceptive device</a>. However, this shortening is disliked by some specialists in view of its use as an abbreviation for intrauterine death. Therefore for many the preferred abbreviation for an intrauterine contraceptive device is IUCD. </p><p>The spelling fetus and fetal are the preferred spellings in the medical world, regardless of location. They are used by virtually all biomedical journals. Therefore they are also the preferred spelling on Radiopaedia and we never use the spelling foetus or foetal (see <a href="/articles/fetus-vs-foetus">fetus vs foetus</a> for more detail) <sup>3</sup>.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>1% of normal, uncomplicated pregnancies end in fetal death. In ~15% of fetal death in utero, no cause is identified.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><h5>Aetiology</h5><h6>Maternal </h6><ul>
- +<li><p>gestational hypertension</p></li>
- +<li><p>blood group incompatibility</p></li>
- +<li><p>metabolic disorders</p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/in-utero-infection">intrauterine infections</a></p></li>
- +</ul><h6>Fetal</h6><ul>
- +<li><p>major anomalies</p></li>
- +<li><p>umbilical cord complications (looping, <a href="/articles/umbilical-cord-knot">knotting</a>, <a href="/articles/umbilical-cord-entanglement">twisting</a>, <a href="/articles/straight-umbilical-cord-1">straight cord</a>)</p></li>
- +</ul><h6>Placental</h6><p>Placental pathologies are thought represent the largest category of cause of intrauterine death <sup>4</sup>.</p><ul>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/placental-insufficiency">chronic placental insufficiency</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/placental-abruption">placental abruption</a></p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/chorioamnionitis">chorioamnionitis</a></p></li>
- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>Ultrasound</h5><ul>
- +<li><p>absent <a href="/articles/fetal-heart-beat">fetal heartbeat</a></p></li>
- +<li><p>absent fetal movements</p></li>
- +<li>
- +<p>occasional findings</p>
- +<ul>
- +<li><p>overlapping of skull bones (<a href="/articles/spalding-sign-fetal-demise">Spalding sign</a>)</p></li>
- +<li><p>gross distortion of fetal anatomy (<a href="/articles/fetal-maceration">maceration</a>)</p></li>
- +<li><p>soft tissue oedema: skin >5 mm</p></li>
- +<li><p><a href="/articles/echogenic-amniotic-fluid">echogenic amniotic fluid</a> (fetal demise fragments)</p></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>
- +<p>uncommon findings</p>
- +<ul>
- +<li><p>thrombus in fetal heart</p></li>
- +<li><p>gas shadow in fetal heart (<a href="/articles/roberts-sign-fetal-demise">Robert sign</a>)</p></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
Image 4 Ultrasound ( create )