Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Weerakkody Y, Silverstone L, Haghighi S, et al. Fetal toxoplasmosis. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 23 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-13967
Fetal toxoplasmosis is an in utero infection that results from transplacental transmission and subsequent infection with the organism Toxoplasma gondii. It falls in the TORCH group of infections.
Please refer to congenital cerebral toxoplasmosis for a specific discussion on this condition.
The incidence is highly variable dependent on individual countries.
The majority of infants (~75%) are asymptomatic. For those symptomatic, the severity of symptoms is related to the trimester of pregnancy when transmission occurred 11:
- first trimester: fetal death
- second trimester: retinochoroiditis, microcephaly, and intellectual disability
- third trimester: lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, eye injuries, and brain calcifications
Fetal transmission occurs in ~40% of cases where the primary maternal infection is acquired during pregnancy 3. Transmission of infection acquired prior to conception is uncommon and in most cases, infection is transmitted in the 3rd trimester. In ~10% cases the infection tends to be severe.
It classically gives a triad of (affected in ~80% 3):
Serological tests
- PCR test on amniotic fluid: more specific 7
-
cordocentesis for the detection of T. gondii-specific IgM antibodies: usually detectable after 20 weeks of gestation
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Ultrasound
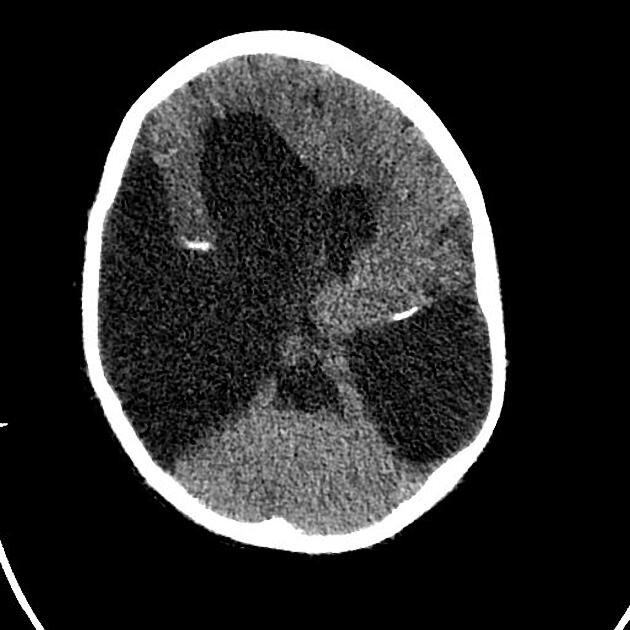
Intracranial findings that may be present sonographically include:
There may also be the presence of microcephaly.
See: congenital cerebral toxoplasmosis
Other findings include:
- development of fetal hydrops
- after birth late sequelae: mainly ocular and neurological
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment involves maternal therapy with medications such as spiramycin +/- sulfadiazine +/- pyrimethamine depending on gestational age and the infective status of the fetus. Prognosis is variable dependant on fetal CNS manifestations. Long term disability can occur with intellectual disability and blindness. Overall mortality can be as high as 12% 10.
-
1. Hohlfeld P, Daffos F, Thulliez P et-al. Fetal toxoplasmosis: outcome of pregnancy and infant follow-up after in utero treatment. J. Pediatr. 1989;115 (5 Pt 1): 765-9. - Pubmed citation
-
2. Bessières MH, Berrebi A, Rolland M et-al. Neonatal screening for congenital toxoplasmosis in a cohort of 165 women infected during pregnancy and influence of in utero treatment on the results of neonatal tests. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2001;94 (1): 37-45. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. (link) - Pubmed citation
-
3. Entezami M, Albig M, Knoll U et-al. Ultrasound Diagnosis of Fetal Anomalies. Thieme. (2003) ISBN:1588902129. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
-
4. Winn HN, Hobbins JC. Clinical maternal-fetal medicine. Taylor & Francis. (2000) ISBN:1850707987. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
-
5. Levene MI, Chervenak FA. Fetal and Neonatal Neurology and Neurosurgery. Churchill Livingstone. (2009) ISBN:0443104077. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
-
6. Gay-andrieu F, Marty P, Pialat J et-al. Fetal toxoplasmosis and negative amniocentesis: necessity of an ultrasound follow-up. Prenat. Diagn. 2003;23 (7): 558-60. doi:10.1002/pd.632 - Pubmed citation
-
7. Foulon W, Pinon JM, Stray-pedersen B et-al. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis: a multicenter evaluation of different diagnostic parameters. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999;181 (4): 843-7. - Pubmed citation
-
8. Antsaklis A, Daskalakis G, Papantoniou N et-al. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis. Prenat. Diagn. 2002;22 (12): 1107-11. doi:10.1002/pd.476 - Pubmed citation
-
9. Foulon W, Naessens A, Ho-yen D. Prevention of congenital toxoplasmosis. J Perinat Med. 2000;28 (5): 337-45. doi:10.1515/JPM.2000.043 - Pubmed citation
-
10. Entezami M, Albig M, Knoll U et-al. Ultrasound Diagnosis of Fetal Anomalies. Thieme. (2003) ISBN:1588902129. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
-
11. Capobiango JD, Breganó RM, Navarro IT et-al. Congenital toxoplasmosis in a reference center of Paraná, Southern Brazil. Braz J Infect Dis. 2014;18 (4): 364-71. doi:10.1016/j.bjid.2013.11.009 - Pubmed citation
Promoted articles (advertising)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.