Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Knipe H, Flat-top talus. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 27 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-152631
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Radiopaedia Events Pty Ltd, Speaker fees (past)
- Integral Diagnostics, Shareholder (ongoing)
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to
not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Radiopaedia Events Pty Ltd, Speaker fees (past)
- Integral Diagnostics, Shareholder (ongoing)
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to
not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures
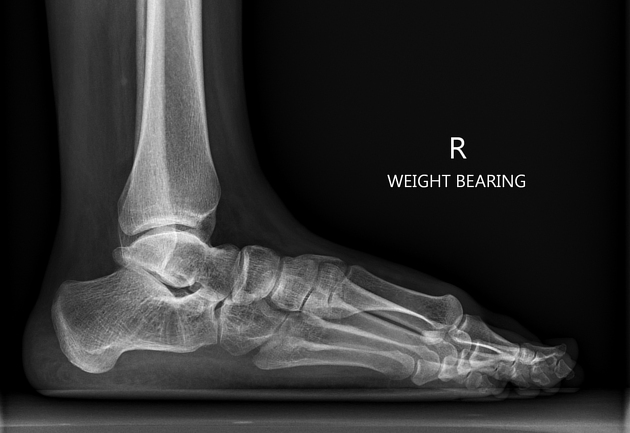
Flat-top talus is considered a complication of non-operative treatment of congenital talipes equinovarus (clubfoot) but can also be seen in surgically treated and non-treated patients and the aetiology is not clear 1,2. It results in reduced ankle dorsiflexion due to anterior ankle impingement from the talus and/or navicular 1.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
Talar dome flattening can be described as 3-5:
- none
- mild: talar trochlear curve is incongruous with the distal tibial articular surface
- moderate: moderate incongruity of the articular surfaces or shortened AP curve extent with no incongruity
- severe: trochlea is completely flat with marked incongruity of the articular surfaces
Other features of flat-top talus include 4,5:
- increased R/L-ratio (radius-length ratio)
- on a lateral ankle radiograph, measuring the radius (R) of the talar dome trochlear curvature vs length (L) from posterior extreme to the distal talar head
- higher R/L-ratios are seen with flatter talar domes
- normal R/L-ratio reported to be 0.365 mm +/- 0.045 mm
-
1. Scott Ellis. Complications of Foot and Ankle Surgery, An Issue of Foot and Ankle Clinics of North America, E-Book. (2022) ISBN: 9780323835299 - Google Books
-
2. Sullivan R & Davidson R. When Does the Flat-Top Talus Lesion Occur in Idiopathic Clubfoot: Evaluation with Magnetic Resonance Imaging At Three Months of Age. Foot Ankle Int. 2001;22(5):422-5. doi:10.1177/107110070102200511 - Pubmed
-
3. Dunn H & Samuelson K. Flat-Top Talus. A Long-Term Report of Twenty Club Feet. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(1):57-62. - Pubmed
-
4. Kolb A, Willegger M, Schuh R, Kaider A, Chiari C, Windhager R. The Impact of Different Types of Talus Deformation After Treatment of Clubfeet. International Orthopaedics (SICOT). 2016;41(1):93-9. doi:10.1007/s00264-016-3301-5 - Pubmed
-
5. Bach C, Goebel G, Mayr E, Biedermann R, Rachbauer F. Assessment of Talar Flattening in Adult Idiopathic Clubfoot. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(9):754-60. doi:10.1177/107110070502600914 - Pubmed
Promoted articles (advertising)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.