Gallbladder volvulus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Manchikanti Venkatesh had no recorded disclosures.
View Manchikanti Venkatesh's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Vikas Shah had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Vikas Shah's current disclosures- Gallbladder volvulus
- Volvulus of gallbladder
- Torsion of the gallbladder
- Gallbladder torsion
Gallbladder volvulus is a relatively rare condition in which there is a rotation of the gallbladder around the axis of the cystic duct and artery.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Symptoms are non-specific. There may be a sudden onset of epigastric or right upper quadrant pain, and vomiting, in contradistinction to a more insidious onset of similar symptoms with acute cholecystitis or intermittent symptoms as with biliary colic. Laboratory evaluations are often non-specific, and generally, symptoms are worse than the laboratory tests. If there is fever or leukocytosis, then acute cholecystitis may have developed.
Epidemiology
Gallbladder volvulus predominantly affects older people. One study found a median age of presentation of 77 years, with a female: male ratio of 4:1 5.
Pathology
It has been observed in patients with significant weight loss, in which there is loss of the pericholecystic supporting fat.
Complications are related to torsion with ensuing vascular compromise and resultant gallbladder ischemia. This can lead to gallbladder necrosis, perforation and biliary peritonitis.
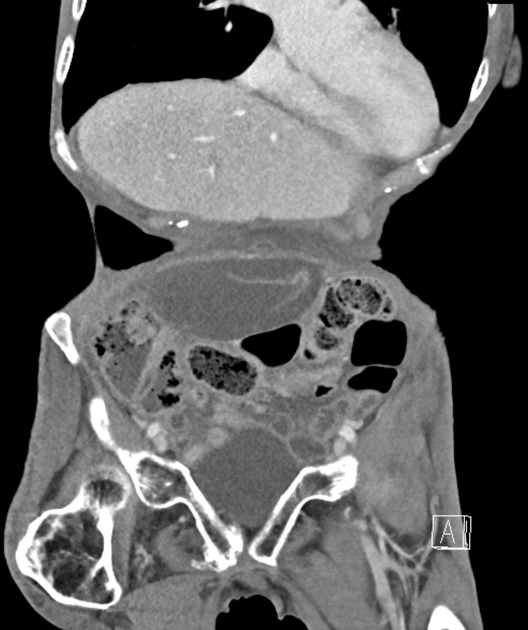
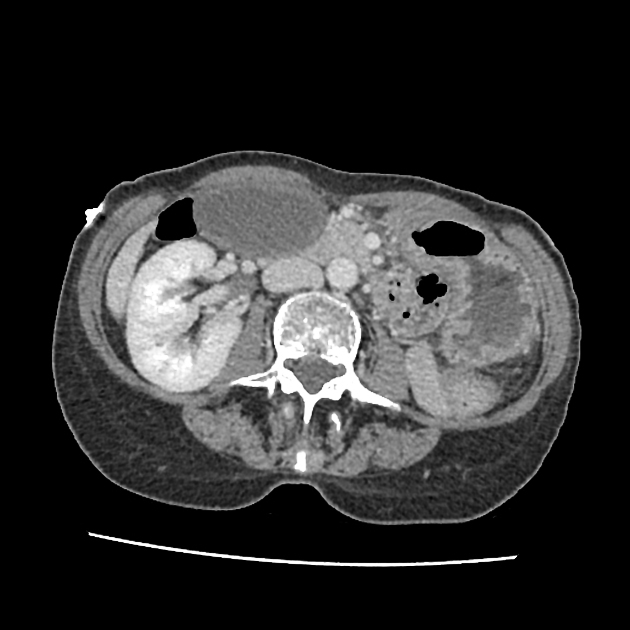
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
large floating gallbladder
wall thickening
gallbladder outside the normal anatomical fossa
CT
massively distended gallbladder
pericholecystic fluid
gallbladder outside the normal anatomical fossa
change in anatomical orientation, from vertical to horizontal 3
medially pointing gallbladder fundus
indrawing of the vascular pedicle and surrounding fat (swirl sign) 4
loss of enhancement
abrupt tapering of cystic duct (beak sign)
Treatment and prognosis
Cholecystectomy is the preferred treatment.
References
- 1. Smith E, Dillman J, Elsayes K, Menias C, Bude R. Cross-Sectional Imaging of Acute and Chronic Gallbladder Inflammatory Disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192(1):188-96. doi:10.2214/ajr.07.3803
- 2. Matsuhashi N, Satake S, Yawata K et al. Volvulus of the Gall Bladder Diagnosed by Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography, Coronal Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Cholangio-Pancreatography. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(28):4599-601. doi:10.3748/wjg.v12.i28.4599
- 3. Kachi A, Nicolas G, Nasser J, Hashem M, Abou Sleiman C. A Rare Presentation of Gall Bladder Volvulus: A Case Report. Am J Case Rep. 2019;20:1466-70. doi:10.12659/ajcr.916234
- 4. Layton B, Rudralingam V, Lamb R. Gallbladder Volvulus: It’s a Small Whirl. BJR|case reports. 2016;2(3):20150360. doi:10.1259/bjrcr.20150360
- 5. Reilly D, Kalogeropoulos G, Thiruchelvam D. Torsion of the Gallbladder: A Systematic Review. HPB (Oxford). 2012;14(10):669-72. doi:10.1111/j.1477-2574.2012.00513.x - Pubmed
- 6. Dawson G, Shah V, Bhardwaj N. Gallbladder Volvulus: Putting a Spin on Acute Cholecystitis. Annsurgcaserepimages. 2024;1(2). doi:10.52768/annsurgcaserepimages/1011
- 7. Escalard C, Calinghen A, Habchi N. Gallbladder Volvulus: A Rare Cause of Acute Gallbladder Distension. J of Gastro and Hepatol. 2019;34(7):1133. doi:10.1111/jgh.14619 - Pubmed
- 8. Bouzas Cardaci M & Bivoleanu C. Gallbladder Volvulus, a Rare Cause of Acute Abdomen, a Case Report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;75:81-4. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.09.001 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- benign epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumors
- primary malignant epithelial tumors
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumors
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumors
- hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumors
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumors
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic hemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumor
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumor
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumor
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumors
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumors
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumors
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.