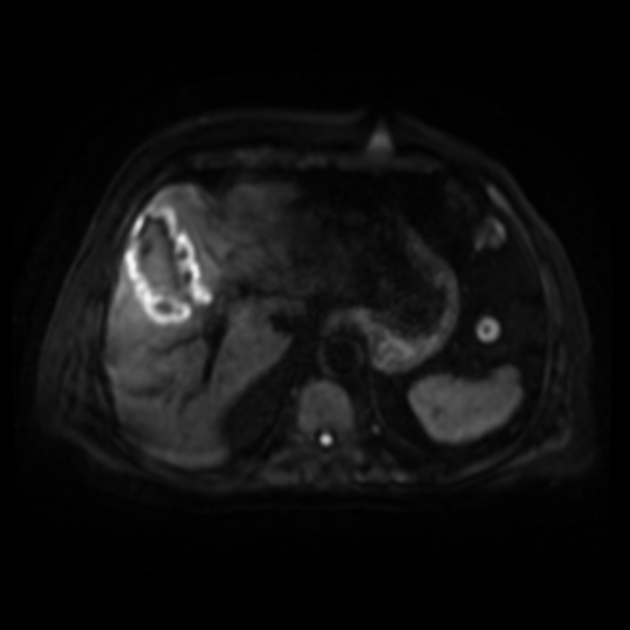
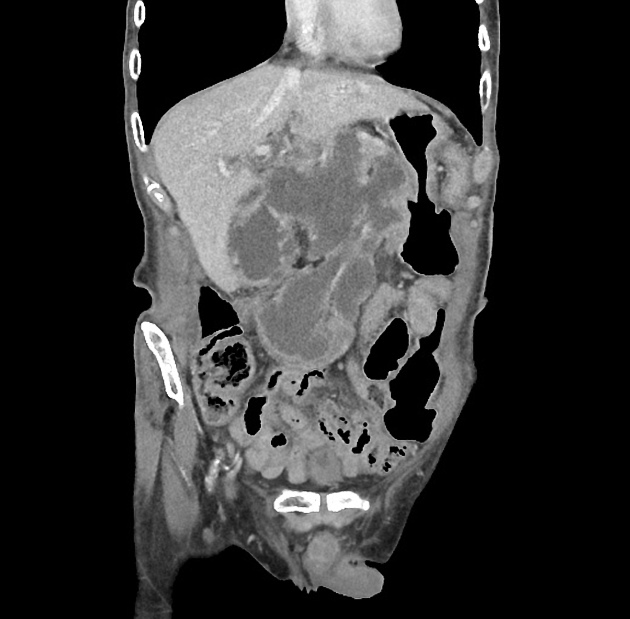
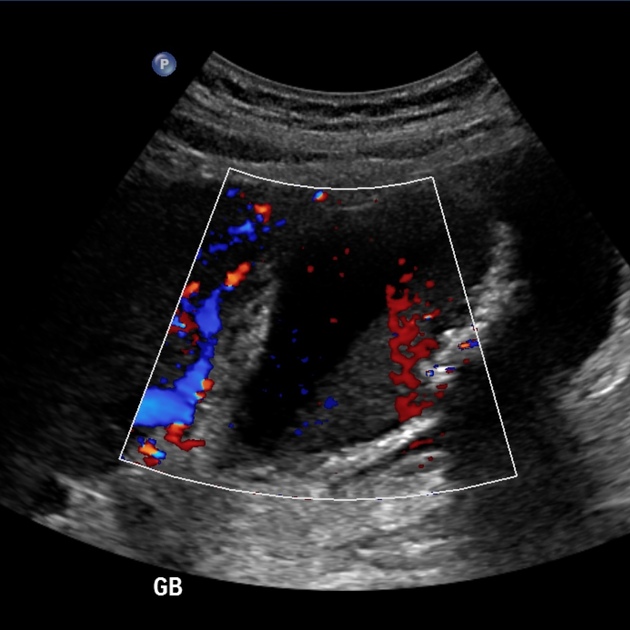
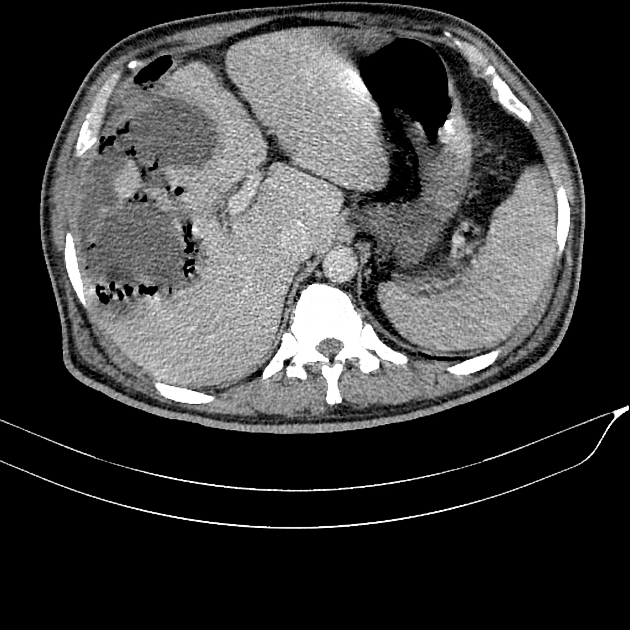
Gangrenous cholecystitis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Manchikanti Venkatesh had no recorded disclosures.
View Manchikanti Venkatesh's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Liz Silverstone had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Liz Silverstone's current disclosures- Membranous cholecystitis
Gangrenous cholecystitis is the most common complication of acute cholecystitis, affecting ~15% (range 2-30%) of patients.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Risk factors
- male
- increasing age
- delayed surgery
- cardiovascular disease
- diabetes mellitus
- systemic inflammatory response syndrome 5
Pathology
Gangrenous cholecystitis occurs as a result of ischaemia with necrosis of the gallbladder wall 4.
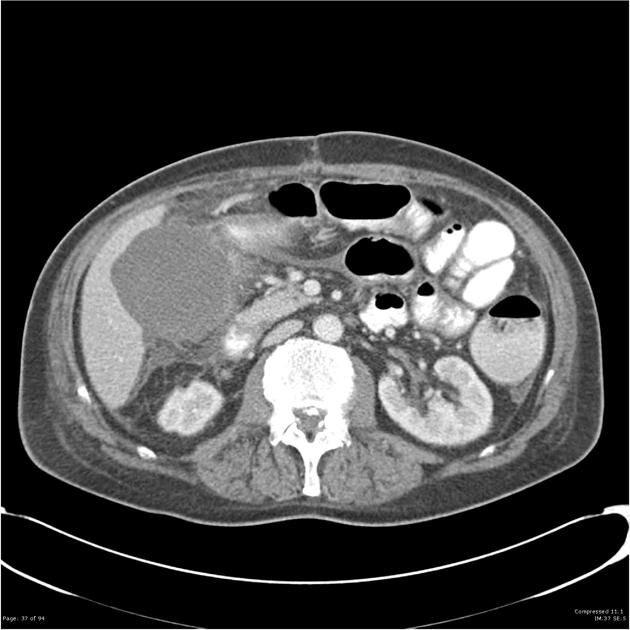
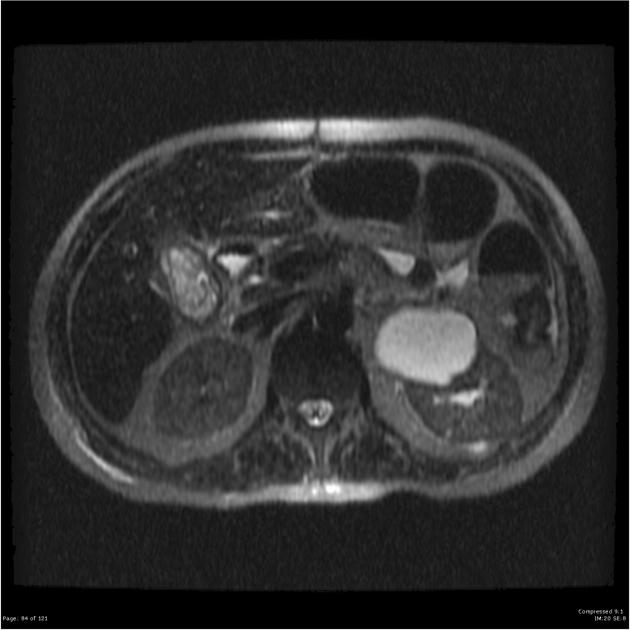
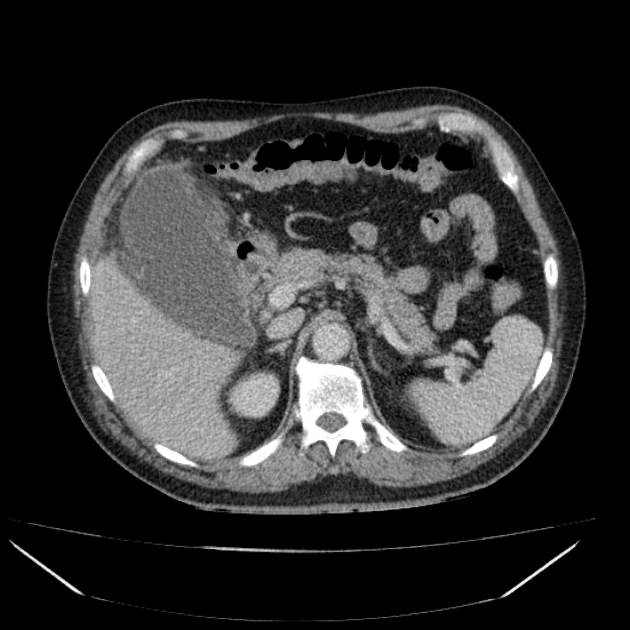
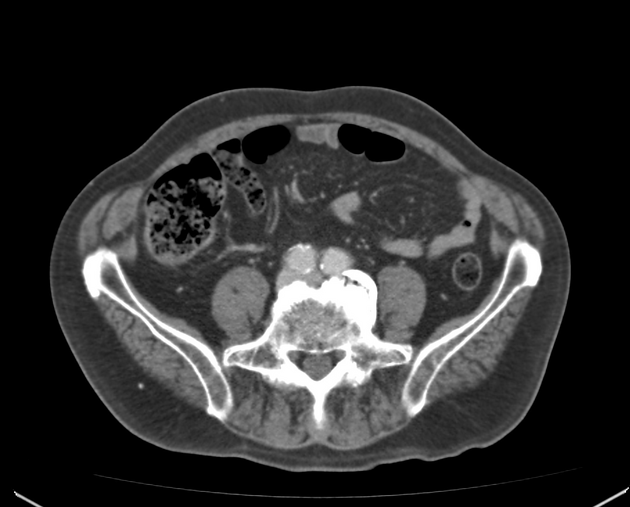
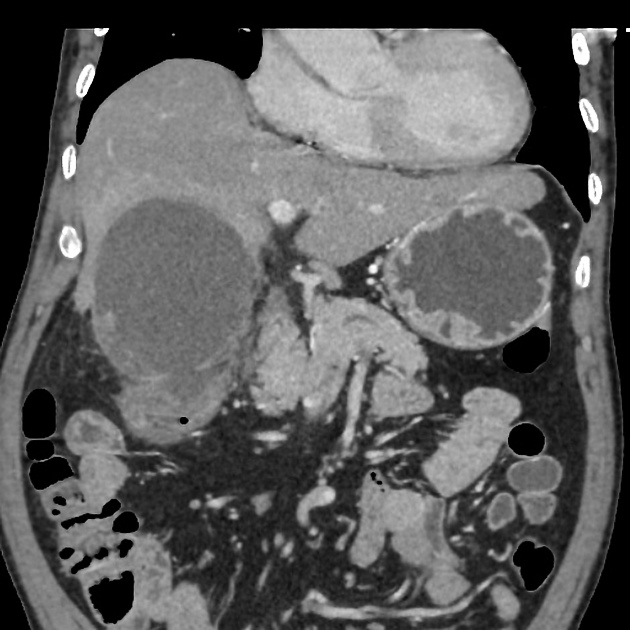
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
In addition to features of acute cholecystitis, the following may help diagnose gangrenous cholecystitis 3:
- intraluminal membranes
- asymmetrical wall thickness
- with possible wall disruption and/or ulceration
- focal perfusion defects on Doppler (representing areas of necrosis)
- variable absence of the sonographic Murphy sign 7
- attributed to ischaemic denervation of the gallbladder 6
CT
In addition to features of acute cholecystitis, the following may help diagnose gangrenous cholecystitis 1:
- gallbladder wall or lumen gas (emphysematous cholecystitis)
- focal irregularity or defect in the gallbladder wall
- intraluminal membranes
- absence of mural enhancement
- pericholecystic abscess
Treatment and prognosis
Mortality is increased compared to uncomplicated acute cholecystitis, estimated at between 15-50% 4.
References
- 1. Bennett GL, Rusinek H, Lisi V et-al. CT findings in acute gangrenous cholecystitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178 (2): 275-81. doi:10.2214/ajr.178.2.1780275 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Jeffrey RB, Laing FC, Wong W et-al. Gangrenous cholecystitis: diagnosis by ultrasound. Radiology. 1983;148 (1): 219-21. Radiology (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Corr P. Sonography of gangrenous cholecystitis. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2012;5 (1): 82-3. doi:10.4103/0974-2700.93112 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 4. Önder A, Kapan M, Ülger BV, Oğuz A, Türkoğlu A, Uslukaya Ö. Gangrenous cholecystitis: mortality and risk factors. International surgery. 100 (2): 254-60. doi:10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00222.1 - Pubmed
- 5. Bourikian S, Anand RJ, Aboutanos M, Wolfe LG, Ferrada P. Risk factors for acute gangrenous cholecystitis in emergency general surgery patients. (2015) American journal of surgery. 210 (4): 730-3. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2015.05.003 - Pubmed
- 6. Oppenheimer DC, Rubens DJ. Sonography of Acute Cholecystitis and Its Mimics. (2019) Radiologic clinics of North America. 57 (3): 535-548. doi:10.1016/j.rcl.2019.01.002 - Pubmed
- 7. Simeone JF, Brink JA, Mueller PR, Compton C, Hahn PF, Saini S, Silverman SG, Tung G, Ferrucci JT. The sonographic diagnosis of acute gangrenous cholecystitis: importance of the Murphy sign. (1989) AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 152 (2): 289-90. doi:10.2214/ajr.152.2.289 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Complicated emphysematous cholecystitis
- Acute cholecystitis
- Perforated cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Subacute pericholecystic abscess
- Bouveret syndrome
- Severe gangrenous cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
- Cholecystitis with focal perforation and hepatic abscess
- Emphysematous cholecystitis
- Gangrenous cholecystitis
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- benign epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumours
- primary malignant epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumours
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumours
- haematopoietic and lymphoid tumours
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumours
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumours
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic haemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumour
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumour
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumour
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour (inflammatory pseudotumour)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumours
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumours
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridaemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.