Glenoid labrum
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
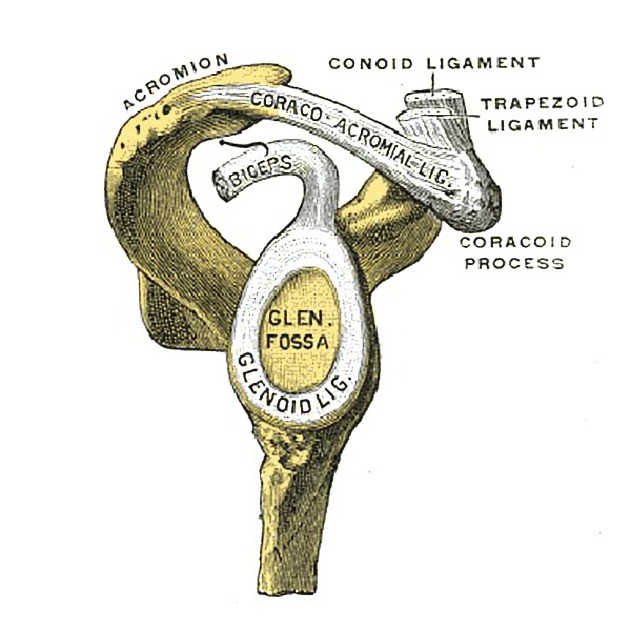
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresThe glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure that attaches as a rim to the articular cartilage of the glenoid fossa and serves to deepen and increase the surface area of the glenoid. In this capacity, it acts as a static stabiliser of the glenohumeral joint, resisting anterior and posterior movement, and preventing dislocation and subluxation at the extremes of the range of motion 4.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The glenoid labrum is made of fibrocartilage, 3 mm thick and 4 mm wide although this is highly variable 4. On cross-section, the labrum can be triangular (more commonly) or round 4. Below the equatorial pole of the glenoid, the labrum becomes more rounded and smaller compared to superiorly where is more triangular in shape and larger.
Attachments
The glenoid labrum forms part of the periarticular fibre system that is continuous with the rotator interval as well as 4:
superiorly: tendon of the long head of biceps brachii
anteriorly: superior and (variably) middle glenohumeral ligaments
inferiorly: inferior glenohumeral ligament consisting of an anterior band, axillary pouch, and a posterior band
Blood supply
Arterial supply is from the ascending glenoid artery, branches of the suprascapular and circumflex scapular arteries, muscular branches of rotator cuff muscles, and anterior and posterior circumflex humeral arteries 5. Blood supply is also received from the underlying bony glenoid 5. The outer glenoid is vascular and the inner glenoid is avascular 4.
Radiographic features
The glenoid labrum can be described in two ways 4:
-
clock face
12 o'clock: superior
3 o'clock: anterior
6 o'clock: inferior
9 o'clock: posterior
-
segments
superior
anterosuperior
anteroinferior
inferior
posteroinferior
posterosuperior
Variant anatomy
variable cross-sectional shape: blunted, cleaved, notched or flat 4
medialised posterior labrum 4
variation in anterior capsulolabral insertion
Related pathology
References
- 1. De Maeseneer M, Van Roy F, Lenchik L et al. CT and MR Arthrography of the Normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior Labrum and Labral-Bicipital Complex. Radiographics. 2000;20 Spec No(suppl_1):S67-81. doi:10.1148/radiographics.20.suppl_1.g00oc03s67 - Pubmed
- 2. Jacob Mandell. Core Radiology. (2013) ISBN: 9781107679689 - Google Books
- 3. Philip Robinson. Essential Radiology for Sports Medicine. (2010) ISBN: 9781441959720 - Google Books
- 4. De Coninck T, Ngai S, Tafur M, Chung C. Imaging the Glenoid Labrum and Labral Tears. Radiographics. 2016;36(6):1628-47. doi:10.1148/rg.2016160020 - Pubmed
- 5. Alashkham A, Alraddadi A, Felts P, Soames R. Blood Supply and Vascularity of the Glenoid Labrum: Its Clinical Implications. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery. 2017;25(3):230949901773163. doi:10.1177/2309499017731632 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Superior labral anterior posterior tear
- Perthes lesion
- Glenohumeral ligaments
- Sublabral foramen
- Capsulolabral insertion classification
- Pseudo-SLAP lesion
- Bankart lesion
- Glenoid
- Cartilage
- Inferior shoulder dislocation
- Glenohumeral joint injection (technique)
- Imaging the shoulder
- Shoulder
- Glenoid labrum ovoid mass sign
- Ball and socket joint
- Double Oreo cookie sign (glenoid labrum)
- Glenohumeral joint
- Kim lesion (shoulder)
- Superior sublabral sulcus
- Posterosuperior impingement of the shoulder
- Humeral avulsion of the glenohumeral ligament (HAGL lesion)
- SLAP tear with paralabral cyst
- Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder
- Parsonage-Turner syndrome
- Perthes lesion
- SLAP lesion - type III
- Buford complex
- SLAP tear and supraspinatus full-thickness tear
- Glenoid rim fracture
- Normal shoulder arthrogram
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centres
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centres
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centres
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.