Infectious bronchiolitis refers to a subtype of bronchiolitis where there is a definite infective precipitant. It falls under the subgroup of inflammatory bronchiolitides and by some authors is considered a type of cellular bronchiolitis 3. It tends to be more clinically severe in children than adults.
Pathology
It is characterised histologically by a pattern of acute bronchiolar injury, with epithelial necrosis, inflammation of the bronchiolar walls and intraluminal exudates. There can also be oedematous change and fibrosis within bronchiolar walls.
Aetiology
-
viruses (viral bronchiolitis)
respiratory syncytial virus (RSV): particularly in children (RSV bronchiolitis)
-
other less common agents include
coronavirus spp coronavirus OC43 5
bacterial species
-
mycobacterial species
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: see pulmonary manifestations of tuberculosis
atypical mycobacterial species
fungal species, e.g. Aspergillus fumigatus, particularly in immunocompromised patients
Radiographic features
CT
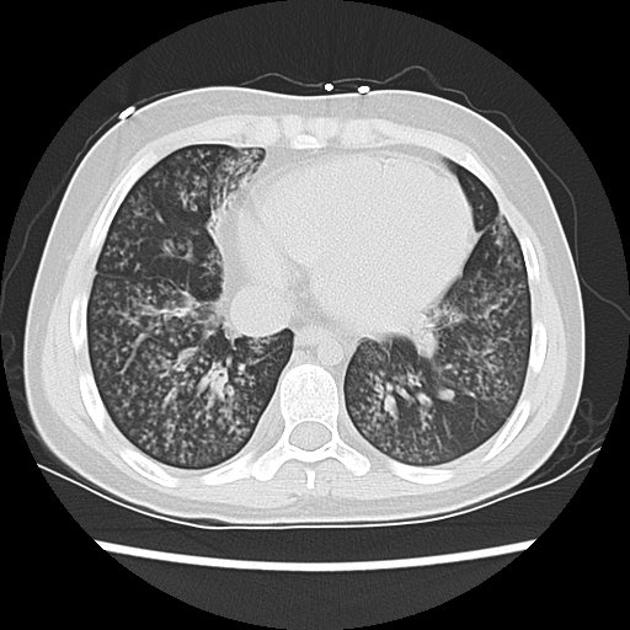
Intense bronchiolar mural inflammation of cellular bronchiolitis results in centrilobular nodules that are usually associated with a tree-in-bud pattern 1. There can also be bronchiolar wall thickening.
In some patients, consolidative changes or ground-glass attenuation may also be present 1.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.