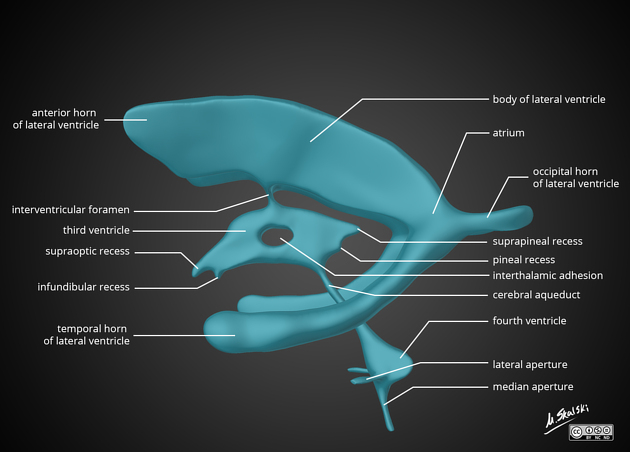
Interthalamic adhesion
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Massa intermedia
- Interthalamic adhesion (ITA)
- thalamic adhesion
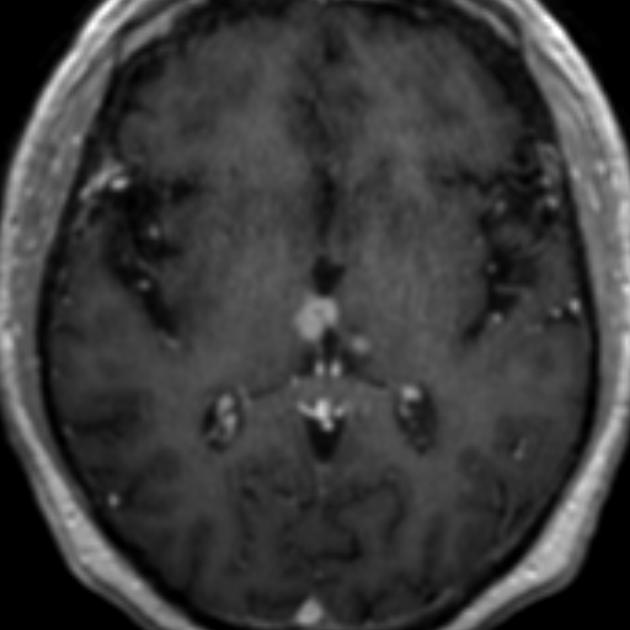
The interthalamic adhesion, or massa intermedia, is a small variably present non-neural connection between the medial apposing surfaces of the two thalami that passes through the third ventricle7. It is not a commissure as once thought, as it does not contain neurones; instead, it is composed of glial tissue. Its functional significance is unknown 5.
If a cast is made of the ventricular system when the adhesion is present, it will create a hole (fenestration or window) in the centre of the third ventricle.
The reported presence of the adhesion varies in the literature, ranging from 75% 4 to 96% 5. It has been reported to be more commonly present in females than males. Interestingly Damle et al. found that when present, the adhesion is larger in females and this correlates with increased attention 5.
Related pathology
It is larger in patients with Chiari II malformations 3.
It is suggested aberrations of the massa intermedia are associated with 6:
References
- 1. Henry Gray, Patricia Collins. Gray's Anatomy. (2005) ISBN: 0443071683 - Google Books
- 2. Mcminn. Last's Anatomy. (2003) ISBN: 9780729537520 - Google Books
- 3. Wolpert S, Anderson M, Scott R, Kwan E, Runge V. Chiari II Malformation: MR Imaging Evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;149(5):1033-42. doi:10.2214/ajr.149.5.1033 - Pubmed
- 4. Lang J. Topographic Anatomy of Preformed Intracranial Spaces. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 1992;54:1-10. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-6687-1_1 - Pubmed
- 5. Damle N, Ikuta T, John M et al. Relationship Among Interthalamic Adhesion Size, Thalamic Anatomy and Neuropsychological Functions in Healthy Volunteers. Brain Struct Funct. 2017;222(5):2183-92. doi:10.1007/s00429-016-1334-6 - Pubmed
- 6. Whitehead M & Najim N. Thalamic Massa Intermedia in Children with and Without Midline Brain Malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020;41(4):729-35. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A6446 - Pubmed
- 7. Parra J, Ripoll Á, García J. Interthalamic Adhesion in Humans: A Gray Commissure? Anat Cell Biol. 2022;55(1):109-12. doi:10.5115/acb.21.164 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.