Intrahepatic arterioportal shunt
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Ahmed Abdrabou had no recorded disclosures.
View Ahmed Abdrabou's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Khalid Alhusseiny had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Khalid Alhusseiny's current disclosures- Intrahepatic arterio-portal shunts
- Intrahepatic arterio-portal shunting
- Intrahepatic arterio-portal fistula
- Intrahepatic arterio-portal fistutation
- Intrahepatic arterio-portal fistulas
- Intrahepatic arterio-portal shunt
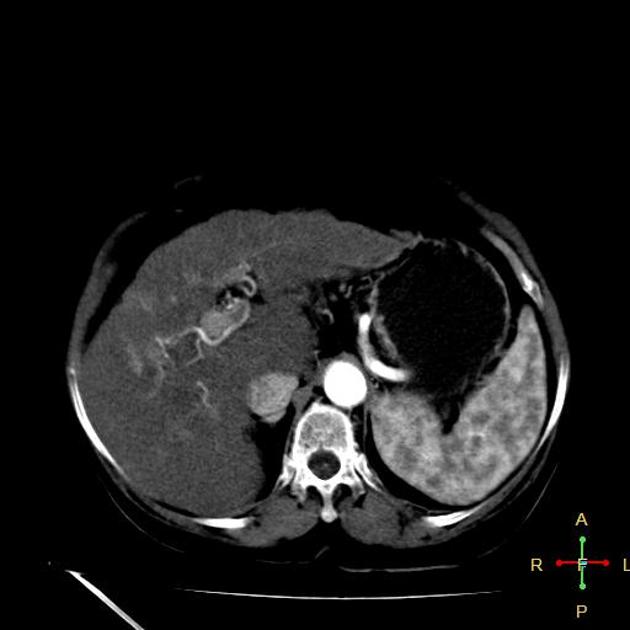
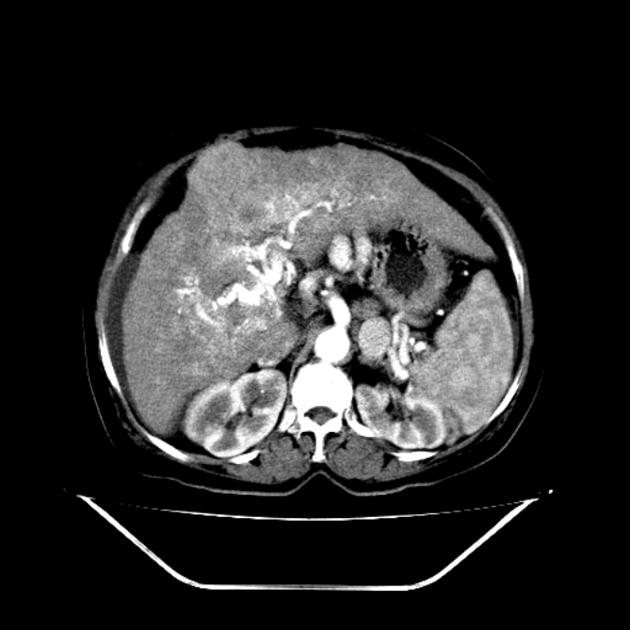
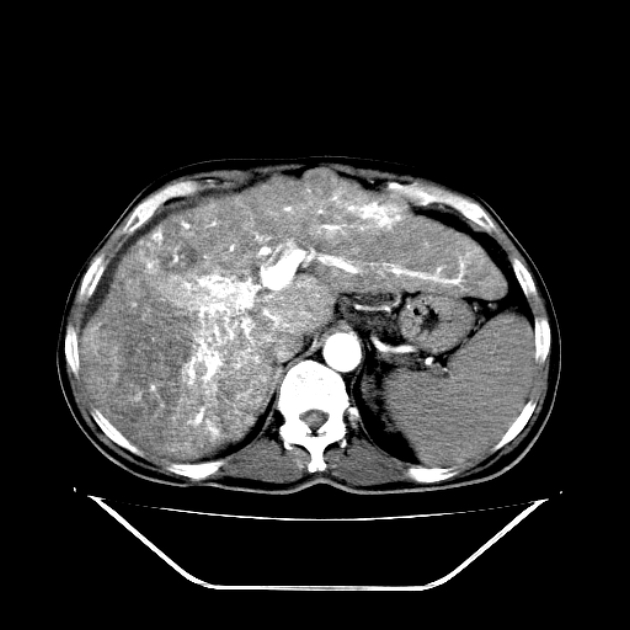
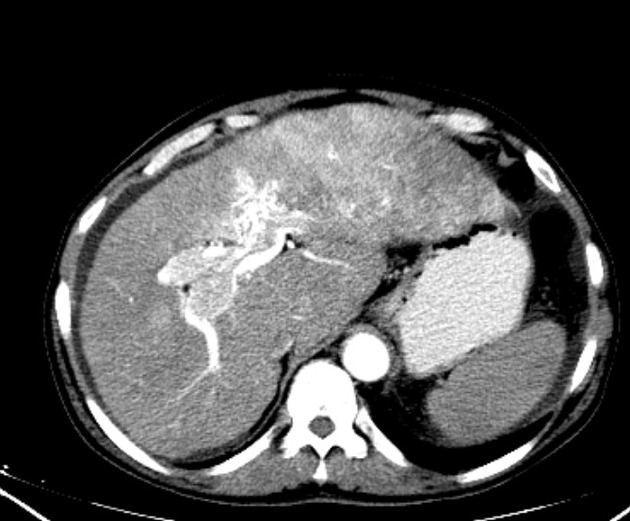
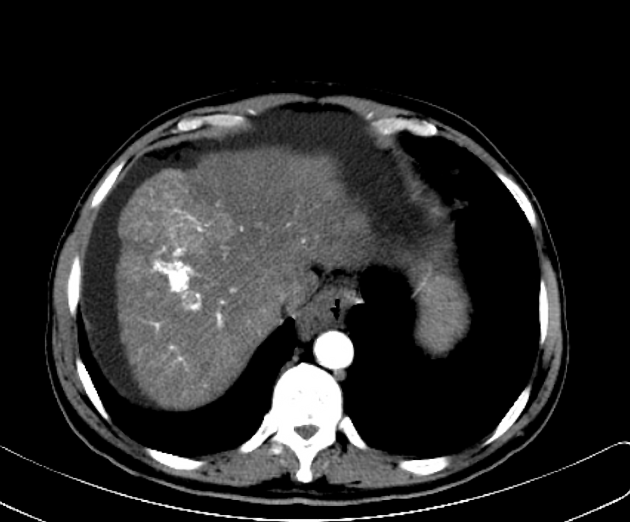
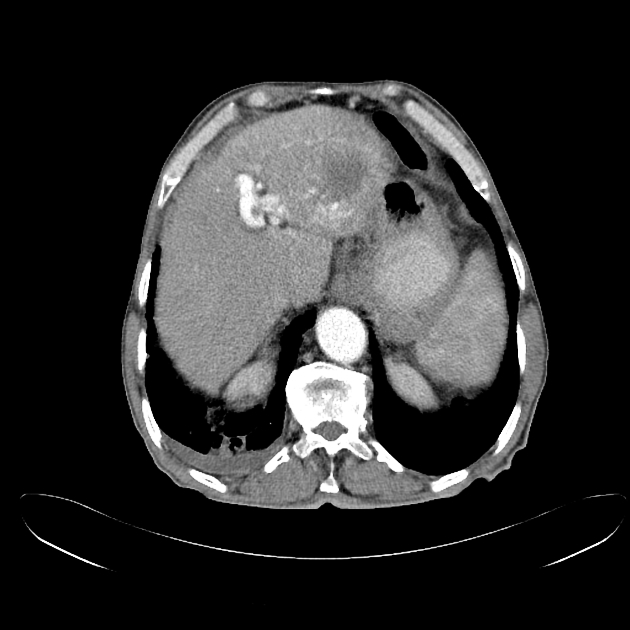
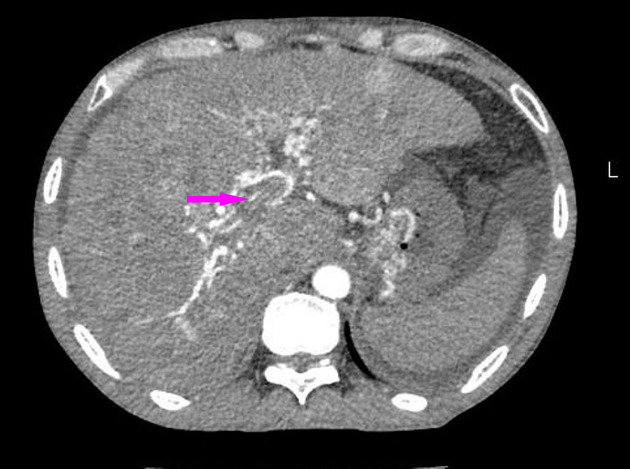
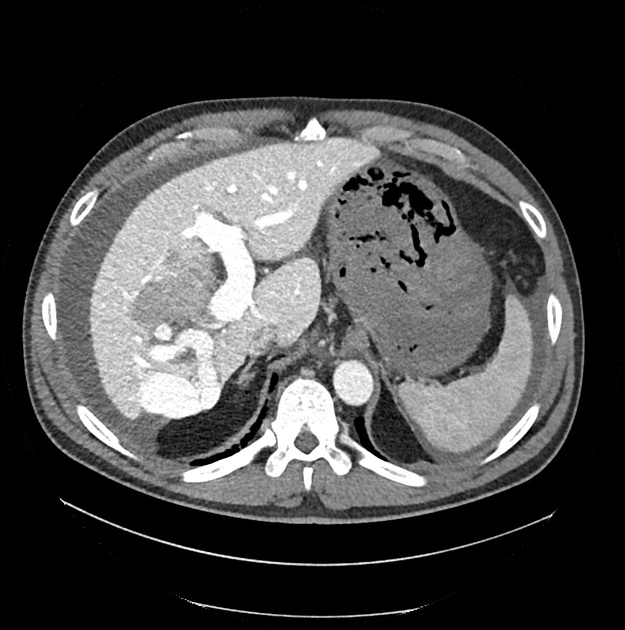
Intrahepatic arterioportal shunts, also known as arterioportal fistulas, represent abnormal flow between the portal venous system and a hepatic arterial system within the liver. They can be a reversible cause of portal hypertension.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Clinical features will depend on the size and other underlying pathology. Small shunts can be asymptomatic.
Pathology
Intrahepatic vascular shunts can be divided according to the cause into:
-
tumorous shunt
occurs with hepatocellular carcinoma and to a lesser extent hepatic haemangioma
transtumoural shunt is due to abnormal communication between the feeding artery and draining vein of the tumour which results in increased vascularity around the tumour manifested as peritumoral transient hepatic attenuation differences (THAD)
portal vein may show early enhancement in the dynamic arterial scan without enhancement of its main tributaries, the splenic and superior mesenteric veins
-
non-tumorous shunt
mainly due to liver biopsy and other hepatic intervention
may be due to liver cirrhosis itself owing to deformation of hepatic sinusoids which increases arterial pressure or portal vein extrinsic compression that also leads to increased arterial pressure
Differential diagnosis
Sometimes arterioportal shunts appear in dynamic CT as enhancing nodules, which can mimic hepatocellular carcinoma. The best way to differentiate is by using MRI with SPIO (superparamagnetic iron oxide) which is deposited in hepatocellular carcinoma and washed out in vascular shunt.
References
- 1. Focal Liver Lesions: Detection, Characterization, Ablation. Springer. ISBN:3540644644. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Guzman EA, McCahill LE, Rogers FB. Arterioportal fistulas: introduction of a novel classification with therapeutic implications. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2006;10 (4): 543-50. doi:10.1016/j.gassur.2005.06.022 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Norton SP, Jacobson K, Moroz SP et-al. The congenital intrahepatic arterioportal fistula syndrome: elucidation and proposed classification. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006;43 (2): 248-55. doi:10.1097/01.mpg.0000221890.13630.ad - Pubmed citation
- 4. Bolognesi M, Sacerdoti D, Bombonato G et-al. Arterioportal fistulas in patients with liver cirrhosis: usefulness of color Doppler US for screening. Radiology. 2000;216 (3): 738-43. Radiology (full text) - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Intrahepatic arteriovenous shunt
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Hepatic vascular and perfusion disorders
- Threads and streaks sign
- Hypervascular liver lesions
- Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (liver manifestations)
- Transient hepatic attenuation differences
- Pseudolesions of the liver
- Hepatic haemangioma
- Intrahepatic arterioportal fistula with portal hypertension
- Diffuse hepatocellular carcinoma with malignant portal vein thrombosis and arterioportal shunt
- Hepatic arteriovenous malformation
- Multicentric Hepatocellular carcinoma with arterio-portal shunt
- Periampullary diverticulum
- Hepatocellular carcinoma with arterioportal shunt
- Hepatocellular carcinoma and arterio-portal fistula
- Diffuse hepatocellular carcinoma with malignant portal vein thrombosis and arterioportal shunt
- Multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma with arterioportal fistula and portal vein thrombosis
- Diffuse hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis and arterioportal shunt
- Diffuse hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis and arterioportal shunt
- Traumatic AV fistula following RF ablation
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- benign epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumours
- primary malignant epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumours
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumours
- haematopoietic and lymphoid tumours
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumours
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumours
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic haemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumour
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumour
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumour
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour (inflammatory pseudotumour)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumours
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumours
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridaemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.