Intravascular lymphoma (IVL), also known as intravascular lymphomatosis or intravascular large cell lymphoma or intravascular large B-cell lymphoma, corresponds to a rare type of extranodal diffuse large B cell lymphoma that affects small and medium-sized vessels and has no specific clinical or laboratory findings. CNS and skin manifestations are the most common forms, however, any organ may be involved 1,2,6.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Intravascular lymphoma usually affects elderly patients in their sixth to seventh decades of life, with a male-to-female ratio of 1:2 3.
Clinical presentation
It has non-specific clinical features which 3,4,8:
B symptoms, including fever of unknown origin
-
other clinical features which tend to have ethnic predilections:
Western variant: more common CNS and cutaneous involvement
Asian variant: more common bone marrow involvement, splenic involvement, hepatic involvement, and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
CSF analysis
If CNS involvement, a mild to moderate elevation of CSF protein is usually present 4.
Pathology
The reason why lymphoma cells tend to stay in the intravascular space in intravascular lymphoma is a consequence of the absence of CD29 (β1 integrin) and CD54 (ICAM-1) surface ligands, which probably disable them from diapedesis across the endothelium 2.
The diagnosis of intravascular lymphoma is made postmortem in over 50% of cases 2.
Radiographic features
If there is CNS involvement, angiography (DSA), CT and MRI often show evidence of multiple vascular occlusions and stroke as non-specific multifocal abnormalities 4-6.
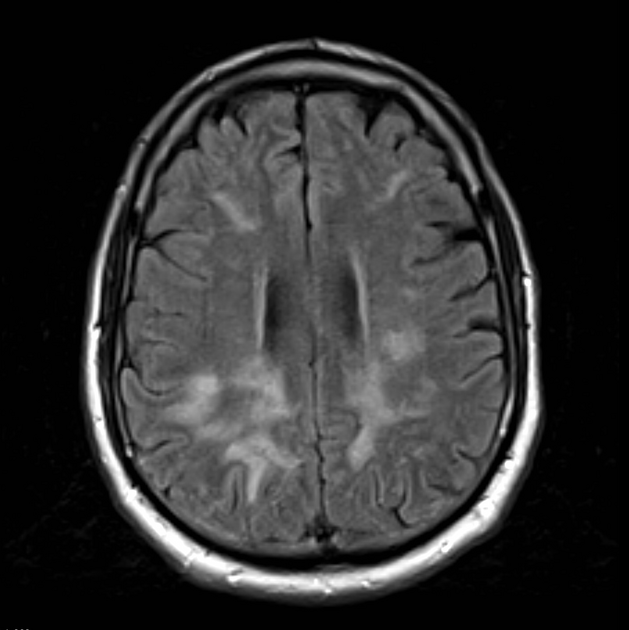
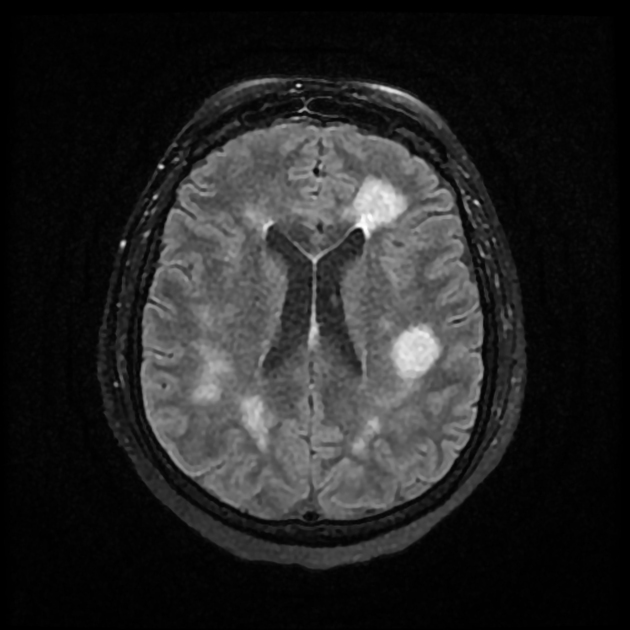
MRI
T2/FLAIR: hypersignal abnormalities in a dynamic pattern (resolution of some and the new appearance of others) 5
DWI/ADC: restriction areas in a dynamic pattern 5
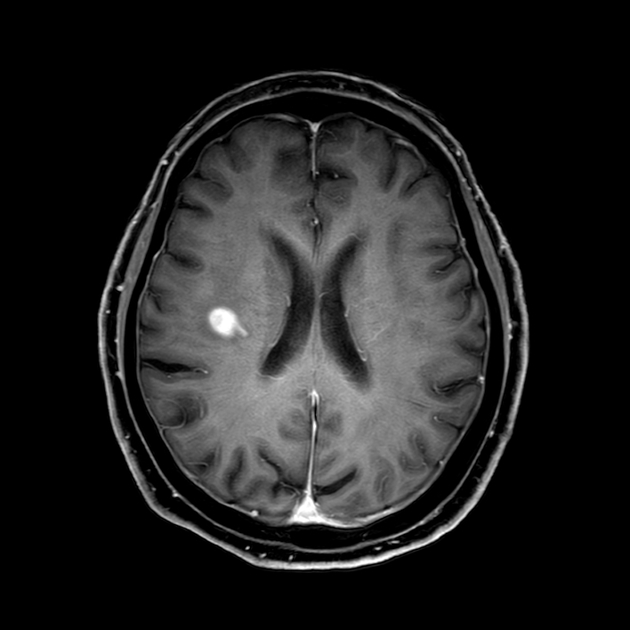
SWI: cerebral microhemorrhages may be present 7
T1 C+ (Gd): a persistent mass-like enhancement may be noted in proximity to the T2 or DWI changes, but different patterns of parenchymal and meningeal enhancement may be seen 5,6
Treatment and prognosis
Intravascular lymphoma usually has a rapidly fatal outcome, with patient overall survival lasting only a few months. Intravascular lymphoma is sensitive to systemic chemotherapy, however, the treatment still remains suboptimal due to the rarity of this disorder and the difficulty to establish a diagnosis in time 2.
History and etymology
This condition was first described in Germany by L Pfleger and J Tappeiner in 1959 and designated as angioendotheliomatosis proliferans systemisata 4.
Differential diagnosis
Entities which result in scattered multifocal brain lesions, particularly small infarcts and hemorrhages, and clinically associated with a rapidly progressive dementia should be considered 4,5,9.
-
hypercoagulable states or multiple emboli
-
other less likely diagnoses to consider





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.