Isomerism is a term which in general means 'mirror-image' and refers to finding normally-asymmetric bilateral structures to be similar. It is used in the context of heterotaxy and is of two types:
- left isomerism
- right isomerism
On this page:
Left isomerism
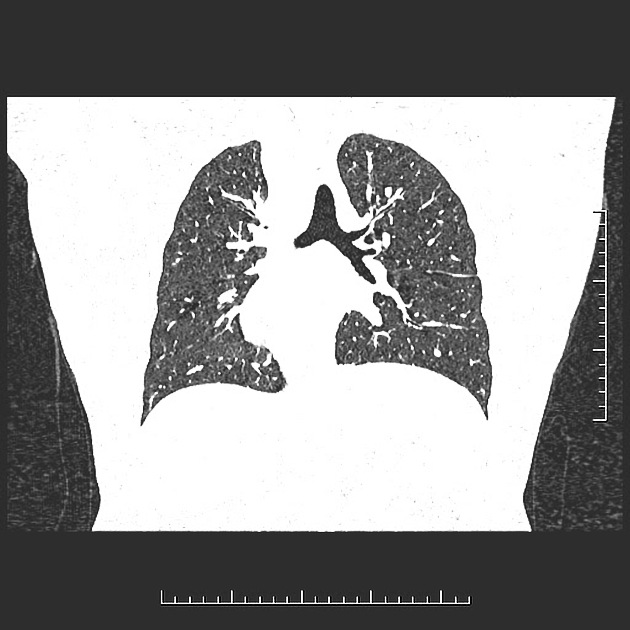
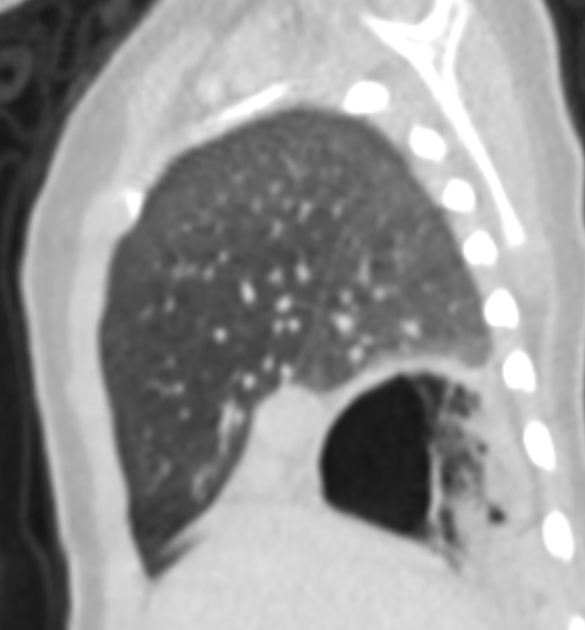
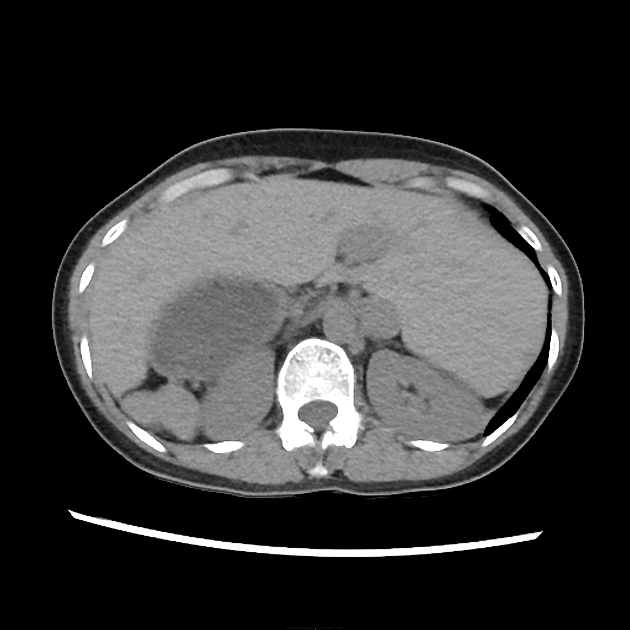
Mirror image of the structures on the left side of the chest along the left-right axis of the body, i.e. patients with isomeric left atrial appendages frequently have bilobed lungs bilaterally and each with a long bronchus 1. Additionally, they have polysplenia and pulmonary veins connecting to both atrial chambers.
Right isomerism
Mirror image of the structures on the right side of the chest along the left-right axis of the body, i.e. patients with isomeric right atrial appendages frequently have trilobed lungs bilaterally and each with a short bronchus 1. Additionally characterised by asplenia.
100% symmetry does not occur.
History and etymology
The term isomerism is derived from Greek: "iso" meaning equal and "meros" meaning part.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.