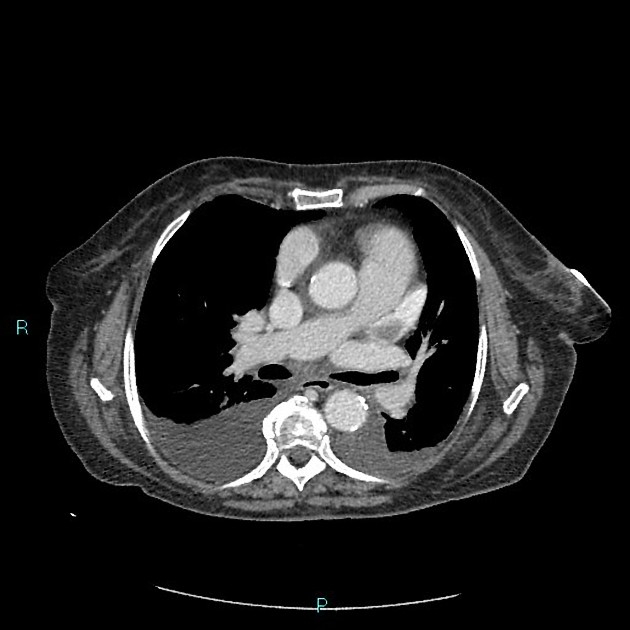
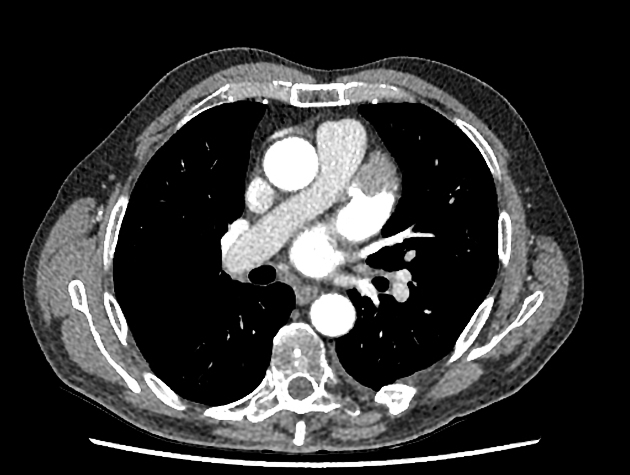
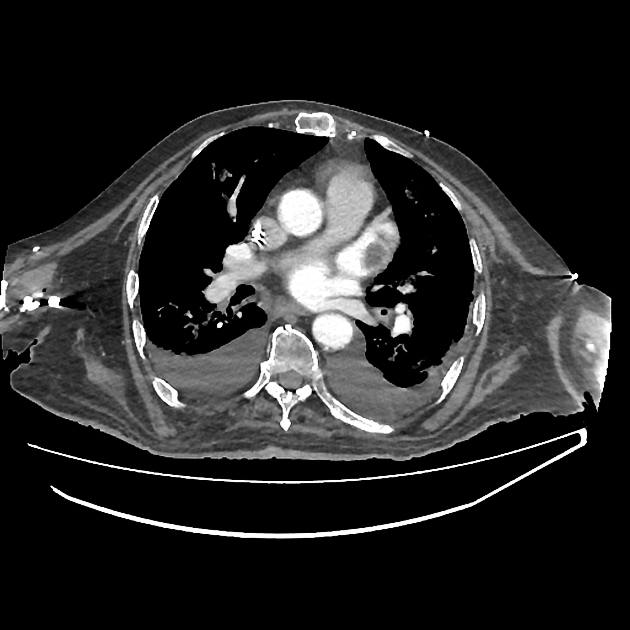
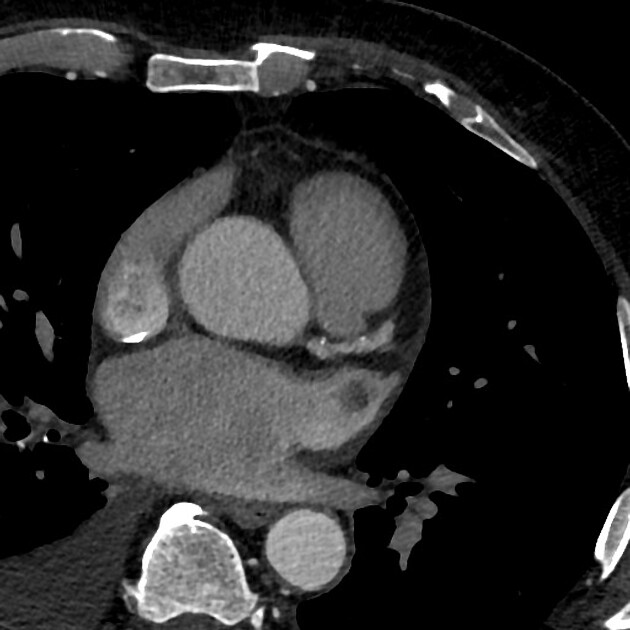
Left atrial appendage thrombus is a site of intra-cardiac thrombus and refers to the presence of thrombus within the left atrial appendage.
The left atrial appendage is considered the main location of thrombus formation, predominantly in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
Radiographic features
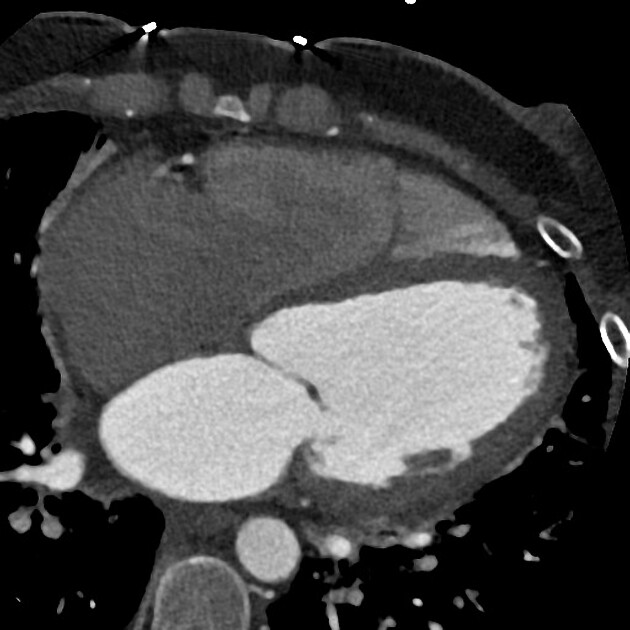
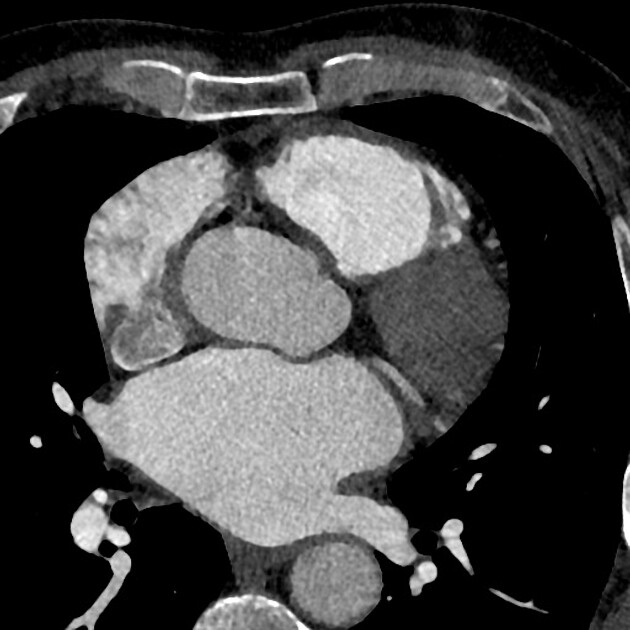
Cardiac CT
Maybe reasonably specific but not as much sensitive 7.
Thrombus detection by cardiac CT relies on filling defects within the left atrial appendage. However, low blood flow velocity may also present as filling defects, and differentiation between thrombi from low blood flow/stasis during early imaging method may be difficult due to the interval between contrast arrival and left atrial appendage image capture being too short. Some authors have suggested a delayed imaging (around 6 minutes) phase to help to differentiate thrombi and low/slow flow 2,5.
Ultrasound
Echocardiography
Trans-esophageal echocardiography (TEE/TOE)
considered the gold standard for detecting LAA thrombus but may be difficult in certain patients.
Differential diagnosis
On CT in certain situations consider
left atrial appendage flow stasis causing a apparent filling defect (pseudothrombus) due to irregular mixing of blood and contrast which can be assessed with the use of a delayed phase





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.