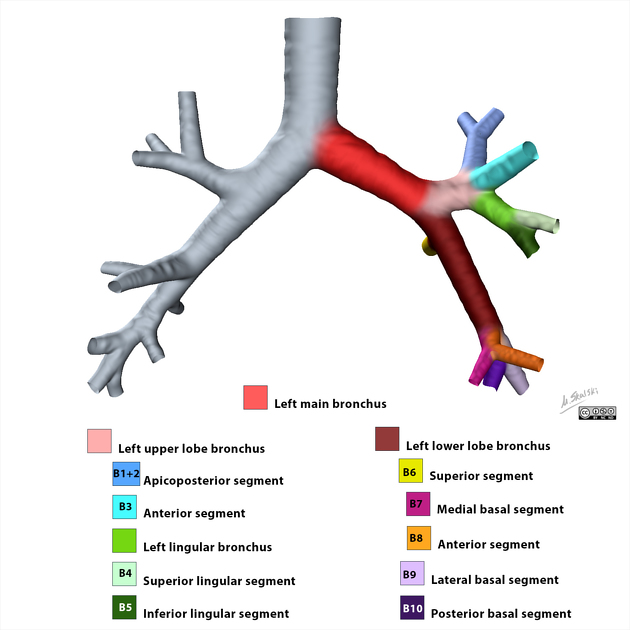
Left main bronchus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Masaki Bannai had no recorded disclosures.
View Masaki Bannai's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Left main bronchus (LMB)
The trachea bifurcates into the right and left main bronchi at the level of the carina, supplying air to the right and left lungs respectively. Each main or primary bronchus enters the hilum of its lung and gives rise to secondary lobar bronchi, which further divide into tertiary segmental bronchi supplying the individual bronchopulmonary segments.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The left main bronchus is longer, runs more horizontally (40 degrees to the median plane) 3 and is about twice as long as the right main bronchus 1,2. It reaches the hilum of the left lung at the level of T6, lying inferior to the aortic arch and anterior to the oesophagus and thoracic aorta.1,2 It is about 5 cm long and 1.2 cm in diameter.3
It gives rise to two lobar bronchi, the left upper and lower lobar bronchi 1.
Relations
At left pulmonary hilum:
superiorly: left pulmonary artery (aortic arch superior to pulmonary artery)
inferiorly: left pulmonary veins
anteriorly: left pulmonary veins
posteriorly: descending thoracic aorta
Arterial supply
The left main bronchus is supplied by two arteries, the superior and inferior left bronchial arteries arising directly from the descending aorta 2.
Venous drainage
The left main bronchus drains into the left bronchial vein which drains into the accessory hemiazygos vein 5.
Variant anatomy
tracheal bronchus (pig bronchus)
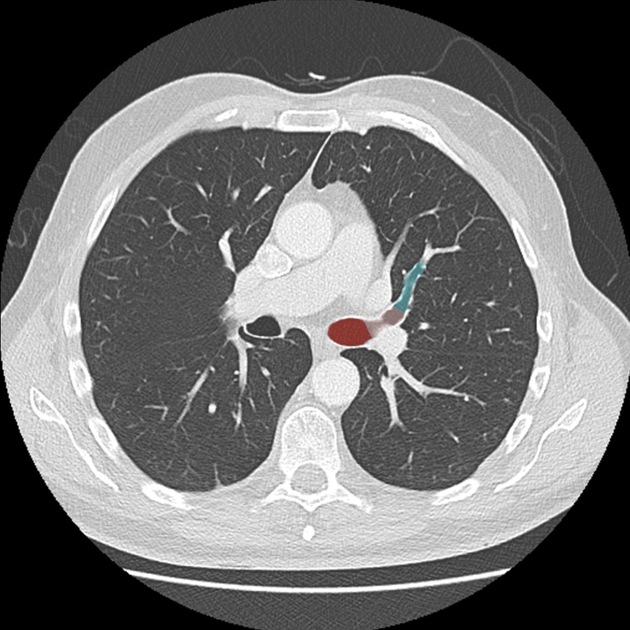
Radiological features
CT
The left main bronchus is most often elliptic in shape on its cross section.4
References
- 1. Paul Butler, Adam Mitchell, Jeremiah C. Healy et al. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9780521766661 - Google Books
- 2. Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, Anne M. R. Agur. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. (2009) ISBN: 9781605476520 - Google Books
- 3. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011) ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
- 4. Olivier P, Hayon-Sonsino D, Convard J, Laloë P, Fischler M. Measurement of Left Mainstem Bronchus Using Multiplane CT Reconstructions and Relationship Between Patient Characteristics or Tracheal Diameters and Left Bronchial Diameters. Chest. 2006;130(1):101-7. doi:10.1378/chest.130.1.101 - Pubmed
- 5. Chummy S. Sinnatamby. Last's Anatomy. (2011) ISBN: 9780702033940 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Left upper lobe
- Trachea
- Pulmonary trunk
- Tracheobronchial tree
- Bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy
- Left pulmonary artery
- Lung hilum
- Bronchial artery
- Left upper lobe bronchus
- Mitral valve regurgitation
- Third mogul sign
- Button battery ingestion
- Left lower lobe
- Right main bronchus
- Left lower lobe bronchus
- Descending aorta
- Right lung
- Bridging bronchus
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Left upper lobe collapse
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax
- thoracic viscera
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- oesophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax
- innervation of the thorax






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.