Leukaemia CNS manifestations can be divided into those related to the disease itself and those associated with its treatment. Leukaemias are haematologic malignancies in which there is a proliferation of haematopoietic cells at an undifferentiated or partially differentiated stage of maturation.
CNS manifestations directly attributed to leukaemia
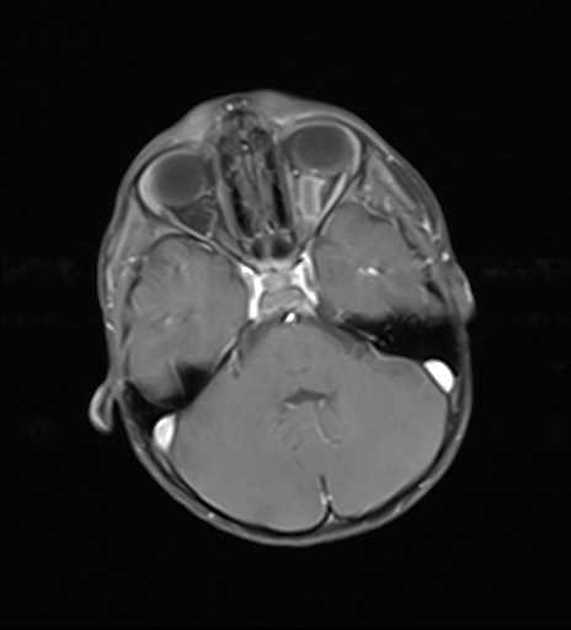
granulocytic sarcoma (chloroma)
-
haematological and cerebrovascular complications
-
most common in acute leukaemia 2
disseminated intravascular coagulation: multiple microhaemorrhages in the subcortical white matter 1
also due alterations in coagulation factors, thrombocytopenia and leucocytosis 2
-
CNS infections due to immunosuppression (e.g. CNS aspergillosis and neurocandidiasis)
bone marrow infiltration: fat is replaced by leukaemic elements 3
-
ocular manifestations
retinal haemorrhage
leukaemic infiltration of the optic nerve 4
Leukaemia treatment-related CNS complications
-
chemotherapy
drug-induced PRES 1
-
methotrexate neurotoxicity
aseptic meningitis
transverse myelopathy
stroke-like syndrome
demyelination and leukoencephalopathy
CNS infections due to immunosuppression (e.g. CNS aspergillosis and neurocandidiasis)
-
radiation-induced neoplasms (e.g. meningioma, glioma and sarcoma)
See also
-
systemic involvement of leukaemia




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.