Lipiodol (also known as ethiodized oil) is an oil-based iodinated contrast medium that was historically used for myelography and hysterosalpingography 1. Newer, less hazardous agents later superseded it and are now used primarily as therapeutic agents. Guerbet was previously the sole manufacturer of this agent. Vivere Imaging has also formulated a similar agent named Vividol, which has obtained FDA approval.
On this page:
Structure
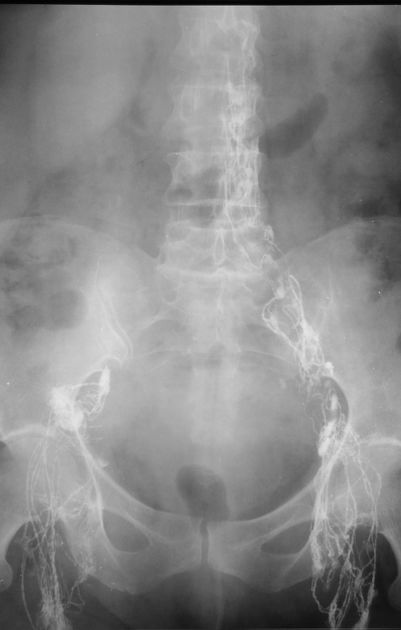
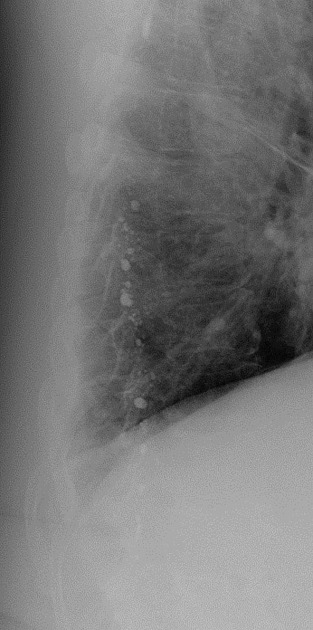
Lipiodol combines iodine and ethyl esters of poppy seed oil 2. The iodine is intercalated into the constituent fatty acids to produce a mixture of iodostearic and stearic-acid-derived esters. The precise structure of Lipiodol has never been characterised 2.
Uses
Diagnostic
Therapeutic
-
radiolabeled Lipiodo
Lipiodol has been tagged with radioisotopes for locoregional therapy of primary and secondary liver tumours
-
I131-Lipiodol 12
first intra-arterial radioisotope therapy to be developed
Lipiodol was labelled with I-131 using an isotopic ion exchange process
limitations in its utility as a locoregional therapy agent was a long isolation time of 7-14 days post administration
-
Re188-Lipiodol
radiopharmaceutical that can be used to treat patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
188Re-HDD (4-hexadecyl-4,7-diaza-1,10-decanedithiol)] lipiodol is widely used but unfortunately, the labelling yield with 188Re-HDD lipiodol is poor; chelating agent N-DEDC (nitrido-diethyl-dithicarbamato) is cheaper, easier to tag and more stable 13, and the final lipophilic complex, bis-(diethyldithiocarbamato) nitrido rhenium-188, to be administered through the hepatic artery, is labelled Re-188 N (DEDC) 2-Lipiodol 3-6.
conventional transcatheter hepatic arterial chemoembolisation (cTACE): transcatheter radioembolisation was initially developed using Lipiodol, but now non-Lipiodol drug-eluted glass or resin microspheres are preferred 7-9
-
glue embolisation
varying concentration ratios of Lipiodol to N- Butyl cyanoacrylate can be used to vary the polymerisation rates within a target vessel or angiosomal bed ref
concentrated ratios ~50% are used for proximal embolisation and ~16/ 33% are used for distal/mid embolisation ref
a combination of different ratios may be useful when treating complex arterio-venous malformations, e.g. dilute ratio of Lipiodol-NBCA might be utilised for bleeding vessel / pseudoaneurysm embolisation from a proximal catheter position when a distal deeper position might not be possible for coil embolisation ref
History and etymology
Lipiodol was discovered by the co-founders of the healthcare company Guerbet, Marcel Guerbet and Laurent Lafay in 1901 10. Indeed originally it was marketed as Lipiodol Lafay. Initially it was developed as a therapeutic agent - a way to deliver iodine to tissues.
It was first employed in radiology in 1921 by Jean-Athanase Sicard and Jacques Forestier, French radiologists, who developed positive contrast myelography. This supplanted air myelography which had been used until then. Due to complications (e.g. chemical arachnoiditis) Lipiodol was itself superseded by iophendylate.
It was previously marketed as Ethiodol in the US but is now globally sold as Lipiodol. Vividol - developed in India and being made available globally is emerging as a bio- similar alternative.
An article was published in 2021 to celebrate one hundred years of continuous use of Lipiodol in radiology 11.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.