Mastectomy is a surgical treatment for breast cancer in which the entire breast tissue is removed through a surgical procedure as opposed to a wide local excision. Sometimes, adjacent structures, such as lymph nodes, are removed to prevent recurrence or metastasis. In some cases, mastectomy is done for the prevention of breast cancer development.
The following subtypes are distinguished 1,2:
simple or total mastectomy
radical mastectomy
modified radical mastectomy (MRM): resection of the breast including the skin, nipple-areolar complex, and an axillary dissection with sparing of the ipsilateral pectoralis major muscle 3,5
skin-sparing mastectomy
nipple-sparing mastectomy
double mastectomy
On this page:
Indications
Mastectomy has the following indications 2,3:
-
cancers that are not suitable for breast-conserving surgery, including
large tumour-versus-breast ratio
widespread or multicentric disease, located in more than one quadrant, and cannot be removed through a single incision with achievement of negative margins
poor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and endocrine therapy
contraindication to radiation therapy (e.g. early pregnancy)
diffuse and extensive suspicious or malignant-appearing microcalcifications
persistent positive margins after excision
local recurrence after breast-conserving therapy and/or radiation therapy
active connective tissue disease involving skin (e.g. scleroderma, SLE)
-
breast cancer prophylaxis in high-risk patients in the following settings
proven genetic susceptibility
history of prior mantle radiation
patient preference
Contraindications
Contraindications include the following:
distant metastatic disease at presentation
patients in whom the primary mode of treatment remains systemic therapy
intolerance to general anaesthesia
Radiographic appearance
The following appearances are described here for normal post-operative state.
Plain radiograph
In uncomplicated post-op status, normal breast tissue shadow will be absent on the corresponding side.
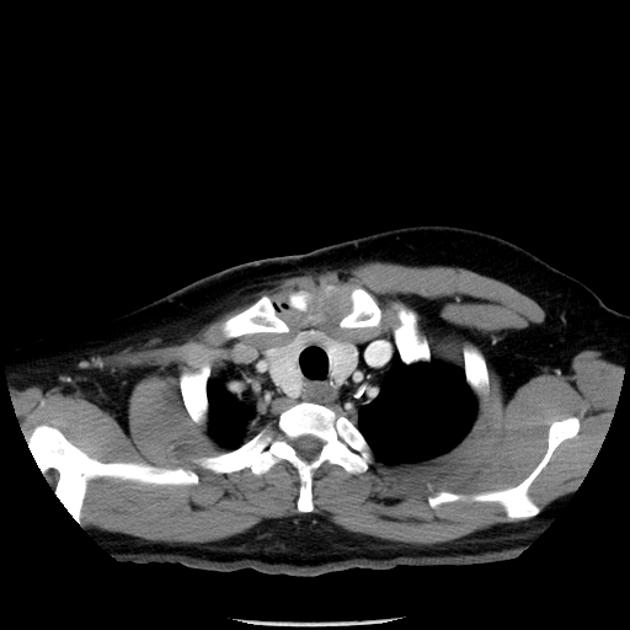
CT/MRI
The absence of breast tissues will be seen in the form of an asymmetric anterior chest wall.
Complications
Common complications include the following:
infection
skin necrosis
Differential diagnosis
For absent tissue on one side on mammography and radiography, consider:








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.