Meckel-Gruber syndrome (MGS) is a rare, lethal multi-system disorder with a variable phenotype but characterized by multicystic dysplastic kidneys and CNS and hepatic abnormalities.
On this page:
Epidemiology
The incidence is estimated to be 1:135,000, although much more prevalent (1:9000) in Finland, Belgium and certain populations in India and the Middle East 10.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Meckel-Gruber syndrome is generally made when renal cystic dysplasia and at least one other typical feature (e.g. occipital encephalocele (or other CNS malformation), hepatic fibrosis, and/or polydactyly) are present 10,11. On imaging, cystic kidneys and dilated intrahepatic ducts have been proposed to the pathognomic 10. The definitive diagnosis is made by genetic testing 10.
Pathology
Meckel-Gruber syndrome shares some features with trisomy 13 and is also called pseudotrisomy 13 1. Karyotyping is recommended if the above triad is seen on antenatal scanning.
Markers
elevated maternal alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) 10
Genetics
Meckel-Gruber syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion; the risk of the condition affecting a subsequent child is therefore 25% 1. There is genetic heterogeneity with at least three genes (MKS1, MKS2 and MKS3) having been identified 4,7:
MKS1: on chromosome 17q
MKS2: on chromosome 11q
MKS3: on chromosome 8q or 13q
Associations
-
central nervous system / craniofacial
-
cardiovascular
-
musculoskeletal
-
hepatobiliary
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
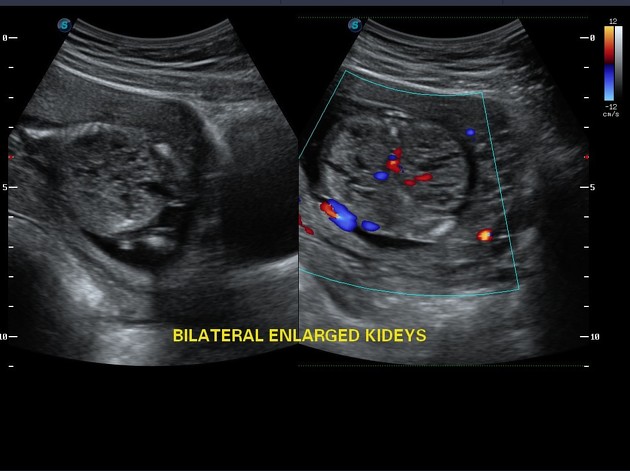
In addition to the demonstration of the classical features such as an occipital encephalocele, multiple renal cysts and polydactyly, there may be evidence of oligohydramnios (or anhydramnios in severe cases) and microcephaly.
In utero (and early neonatal life) multicystic renal disease is usually evident as enlarged echogenic kidneys: demonstration of physical cysts within the kidneys only occurs in the minority of cases.
Treatment and prognosis
The condition is almost always fatal at birth either because of pulmonary hypoplasia or neonatal renal failure 3,5. Parents can be counseled appropriately that the subsequent risk is 25%.
History and etymology
Meckel-Gruber syndrome is named after 10
Johann Friedrich Meckel (the younger) (1781-1833), a German anatomist (also known for Meckel diverticulum) 9
Georg Gruber (1884-1977), a German physician 9 who first described the constellation of findings in 1934, terming it dysencephalia splanchnocystica
It was only in 1969 that the moniker "Meckel-Gruber syndrome" was coined by Opitz and Howe 9.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.